Enamel offers a durable, highly glossy finish that is resistant to scratches and chemicals, making it ideal for metal and ceramic surfaces. Glass coating provides a transparent, protective layer that enhances shine while offering superior UV resistance and hydrophobic properties. Choosing between enamel and glass coating depends on whether durability and color vibrancy or advanced protection and maintenance ease are your primary needs.
Table of Comparison
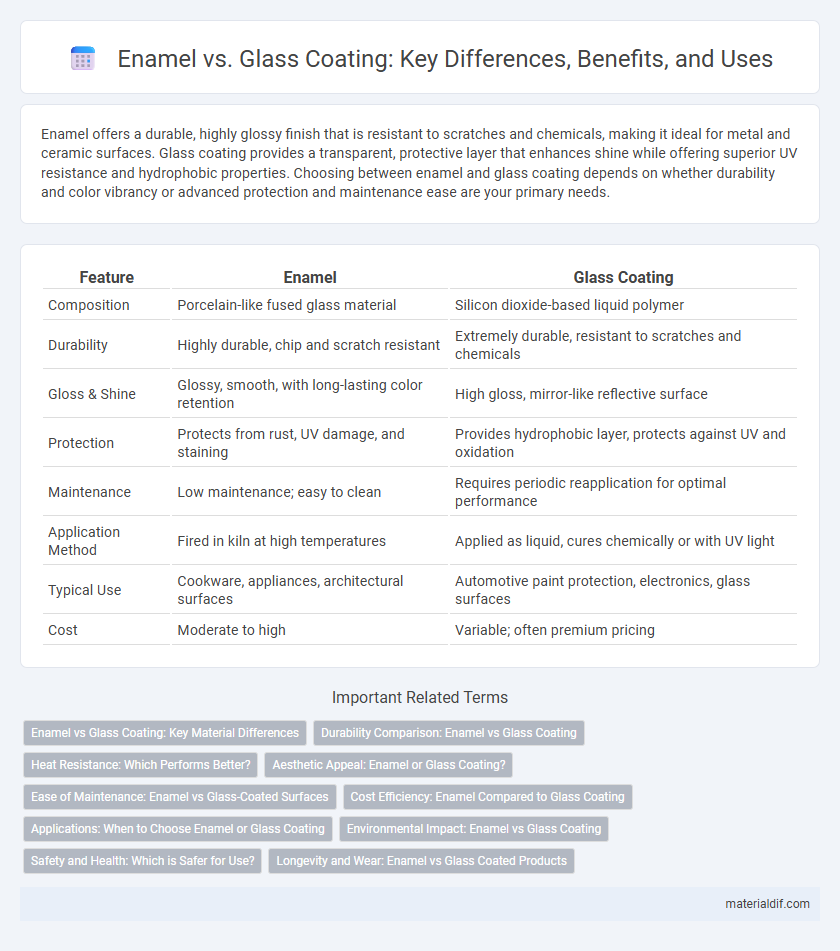
| Feature | Enamel | Glass Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Porcelain-like fused glass material | Silicon dioxide-based liquid polymer |
| Durability | Highly durable, chip and scratch resistant | Extremely durable, resistant to scratches and chemicals |
| Gloss & Shine | Glossy, smooth, with long-lasting color retention | High gloss, mirror-like reflective surface |
| Protection | Protects from rust, UV damage, and staining | Provides hydrophobic layer, protects against UV and oxidation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Requires periodic reapplication for optimal performance |
| Application Method | Fired in kiln at high temperatures | Applied as liquid, cures chemically or with UV light |
| Typical Use | Cookware, appliances, architectural surfaces | Automotive paint protection, electronics, glass surfaces |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Variable; often premium pricing |
Enamel vs Glass Coating: Key Material Differences
Enamel consists of a fused glass-like ceramic coating applied through high-temperature firing, creating a durable, chip-resistant surface with excellent heat and chemical resistance. Glass coating, often a liquid polymer, forms a thin, transparent protective layer that enhances gloss and hydrophobicity but lacks the thickness and hardness of enamel. Key material differences include enamel's vitrified, robust structure compared to glass coating's flexible, easily reapplyable film.
Durability Comparison: Enamel vs Glass Coating
Enamel offers exceptional hardness and resistance to scratches due to its thick, vitreous surface, making it highly durable for long-term use on metals and ceramics. Glass coating, while providing a sleek, hydrophobic layer that resists minor abrasions and chemical stains, tends to be thinner and may require more frequent reapplication to maintain its protective properties. When comparing durability, enamel typically surpasses glass coating in resistance to physical wear and environmental factors, ensuring prolonged surface integrity in harsh conditions.
Heat Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Enamel demonstrates superior heat resistance compared to glass coating, maintaining its structural integrity and color under temperatures exceeding 800degF (427degC), while most glass coatings typically withstand up to 600degF (315degC) before degradation. This makes enamel ideal for cookware and industrial applications requiring prolonged exposure to high heat. Glass coating, although durable, is better suited for environments with moderate heat due to its lower thermal tolerance.
Aesthetic Appeal: Enamel or Glass Coating?
Enamel provides a rich, glossy finish with vibrant colors that enhance the aesthetic appeal of surfaces, creating a classic and durable look. Glass coating offers a sleek, high-gloss shine with superior scratch resistance and a modern, mirror-like surface that maintains clarity over time. Choosing between enamel and glass coating depends on whether the desired finish prioritizes timeless color depth or advanced protective shine.
Ease of Maintenance: Enamel vs Glass-Coated Surfaces
Enamel surfaces offer high durability and resistance to scratches, making maintenance straightforward with regular wiping and mild cleaning agents. Glass-coated surfaces provide a smoother finish that repels dirt and stains more effectively, reducing cleaning frequency and effort. Both materials enhance ease of maintenance, but glass coatings generally require less intensive upkeep due to their hydrophobic and self-cleaning properties.
Cost Efficiency: Enamel Compared to Glass Coating
Enamel offers significant cost efficiency compared to glass coating due to its lower material and application expenses, making it an economical choice for large-scale projects. The durability of enamel reduces the frequency of reapplications, further minimizing long-term costs. Glass coating, while providing a glossier finish, generally incurs higher upfront and maintenance expenses, impacting overall budget considerations.
Applications: When to Choose Enamel or Glass Coating
Enamel is ideal for high-temperature applications such as cookware, appliances, and industrial equipment due to its durable, heat-resistant, and chemically inert properties. Glass coatings excel in automotive and architectural surfaces where scratch resistance, UV protection, and aesthetic longevity are crucial. Choose enamel for robust, heat-exposed environments and glass coatings for surfaces requiring enhanced visual appeal and environmental protection.
Environmental Impact: Enamel vs Glass Coating
Enamel production typically involves higher energy consumption and releases more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to glass coating, impacting air quality and carbon emissions. Glass coatings often use fewer hazardous chemicals and can be more environmentally friendly due to their longer durability and lower need for reapplication, reducing waste. Choosing glass coating over enamel can contribute to a smaller ecological footprint through reduced resource use and minimized pollution.
Safety and Health: Which is Safer for Use?
Enamel coatings generally contain fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to glass coatings, reducing the risk of toxic fumes during application and curing. Glass coatings often require high-temperature processes that may emit harmful gases, posing greater safety concerns in enclosed or poorly ventilated areas. Enamel's lower chemical reactivity and non-toxic composition make it a safer choice for both users and the environment in everyday applications.
Longevity and Wear: Enamel vs Glass Coated Products
Enamel coatings offer superior hardness and resistance to abrasive wear, often lasting decades with minimal degradation, making them ideal for high-traffic surfaces. Glass coatings provide excellent chemical resistance and hydrophobic properties but may show signs of wear within a few years under continuous exposure to mechanical stress. Longevity of enamel products generally surpasses glass coatings due to their dense, vitrified structure that withstands UV radiation and temperature fluctuations effectively.
Enamel vs Glass Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com