Shrinkage-compensating concrete reduces cracking by expanding slightly during curing, counteracting typical shrinkage and improving durability compared to standard concrete. Standard concrete often experiences shrinkage as it dries, leading to potential cracks and weakened structural integrity over time. Using shrinkage-compensating concrete enhances long-term performance and minimizes maintenance needs in various construction applications.
Table of Comparison
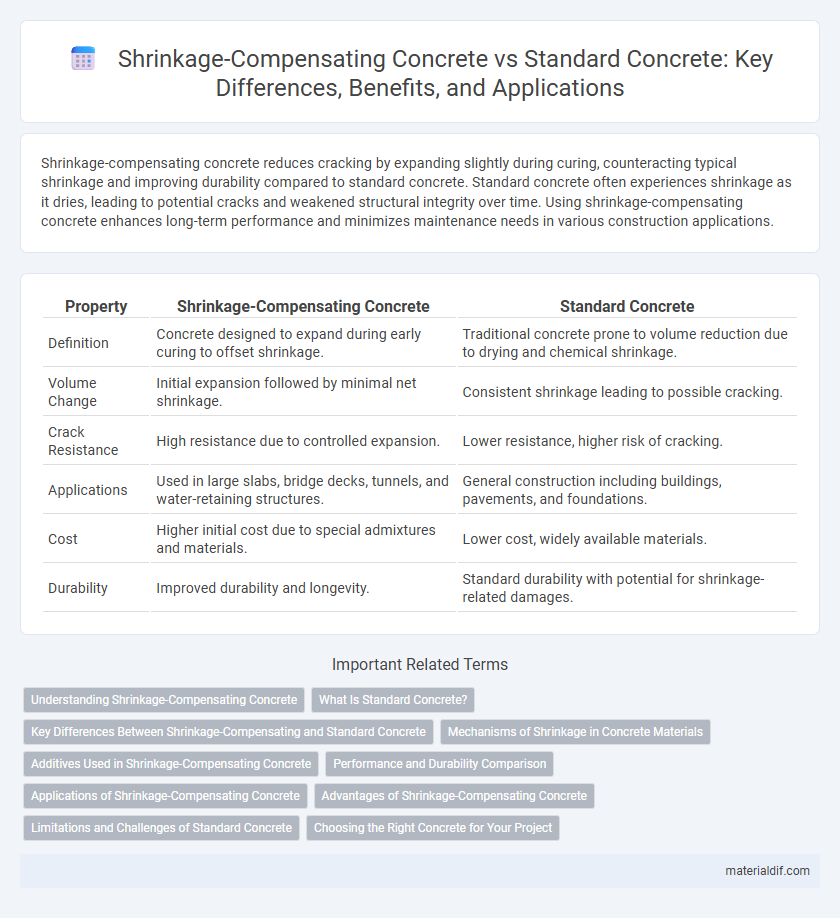
| Property | Shrinkage-Compensating Concrete | Standard Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete designed to expand during early curing to offset shrinkage. | Traditional concrete prone to volume reduction due to drying and chemical shrinkage. |
| Volume Change | Initial expansion followed by minimal net shrinkage. | Consistent shrinkage leading to possible cracking. |
| Crack Resistance | High resistance due to controlled expansion. | Lower resistance, higher risk of cracking. |
| Applications | Used in large slabs, bridge decks, tunnels, and water-retaining structures. | General construction including buildings, pavements, and foundations. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to special admixtures and materials. | Lower cost, widely available materials. |
| Durability | Improved durability and longevity. | Standard durability with potential for shrinkage-related damages. |
Understanding Shrinkage-Compensating Concrete
Shrinkage-compensating concrete incorporates expansive agents that counteract drying shrinkage, reducing the risk of cracks and structural damage. This concrete type typically contains calcium sulfoaluminate cement, which produces controlled expansion during the early curing process to balance shrinkage strains. Compared to standard concrete, it enhances durability and long-term dimensional stability in construction applications.
What Is Standard Concrete?
Standard concrete is a mixture of cement, water, aggregates, and often admixtures, designed to achieve specific strength and durability without addressing shrinkage-induced cracking. It undergoes volumetric reduction as it cures, leading to potential shrinkage cracks that can compromise structural integrity. Unlike shrinkage-compensating concrete, standard concrete lacks mechanisms to counteract these dimensional changes during the hardening process.
Key Differences Between Shrinkage-Compensating and Standard Concrete
Shrinkage-compensating concrete incorporates expansive agents that counteract drying shrinkage, minimizing cracking and structural deformation compared to standard concrete. Standard concrete experiences volume reduction upon drying, leading to potential cracks and compromised durability, whereas shrinkage-compensating concrete enhances long-term dimensional stability. The key differences lie in the material composition and resulting mechanical behavior, with shrinkage-compensating concrete offering superior resistance to shrinkage-induced stresses.
Mechanisms of Shrinkage in Concrete Materials
Shrinkage-compensating concrete incorporates expansive agents that counteract tensile stresses caused by hydration and drying shrinkage, reducing cracking risk. Standard concrete typically experiences autogenous and drying shrinkage leading to volume reduction and potential microcracking. The primary mechanism in shrinkage-compensating concrete involves controlled expansion through ettringite formation, balancing shrinkage strains and enhancing dimensional stability.
Additives Used in Shrinkage-Compensating Concrete
Shrinkage-compensating concrete incorporates expansive agents such as calcium sulfoaluminate or magnesium oxide to counteract volume reduction during curing, whereas standard concrete typically lacks these additives. These expansive minerals chemically react with the cement hydration process, producing controlled expansion that balances shrinkage stresses and reduces cracking risk. Incorporating such additives enhances durability and structural integrity in applications prone to shrinkage-induced damage.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Shrinkage-compensating concrete significantly reduces the risk of cracking by expanding slightly during curing, enhancing long-term structural integrity compared to standard concrete. Its controlled expansion counters shrinkage stresses, resulting in superior durability under cyclic loading and environmental exposure. Standard concrete tends to develop microcracks over time, which can lead to reduced performance and increased permeability, whereas shrinkage-compensating formulations maintain tighter crack widths and improved resistance to freeze-thaw cycles and chemical ingress.
Applications of Shrinkage-Compensating Concrete
Shrinkage-compensating concrete is widely used in applications requiring minimized cracking, such as bridge decks, concrete pavements, and large structural slabs, where volume stability is crucial. Its expansion properties counteract drying shrinkage, making it ideal for restrained structures and thin elements exposed to high tensile stresses. This concrete type enhances durability and reduces maintenance costs in infrastructure projects subjected to dynamic loading and environmental fluctuations.
Advantages of Shrinkage-Compensating Concrete
Shrinkage-compensating concrete significantly reduces the risk of cracking by expanding slightly during the curing process, counteracting the natural shrinkage that occurs in standard concrete. This enhanced dimensional stability improves the durability and lifespan of structures, especially in large slabs and bridge decks where shrinkage-induced tension can cause severe damage. The use of expansive agents in shrinkage-compensating concrete also minimizes maintenance costs and improves the overall performance under harsh environmental conditions.
Limitations and Challenges of Standard Concrete
Standard concrete faces significant limitations due to its inherent shrinkage, which often leads to cracking and reduced structural durability. This shrinkage-induced cracking compromises the integrity of concrete elements, increasing maintenance costs and decreasing lifespan. Addressing these challenges requires specialized materials or reinforcement techniques to manage dimensional changes and enhance performance.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Project
Shrinkage-compensating concrete reduces cracking and structural damage by expanding slightly during curing to offset shrinkage, making it ideal for large slabs, industrial floors, and precast elements where durability and dimensional stability are critical. Standard concrete, while cost-effective and widely used, can develop shrinkage cracks over time, potentially compromising structural integrity in projects with high stress or exposure to environmental changes. Understanding project requirements such as load conditions, environmental exposure, and long-term performance helps determine whether shrinkage compensation or standard concrete is the optimal choice.
Shrinkage-compensating concrete vs standard concrete Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com