Single firing in ceramics involves firing the glazed and unglazed pottery in one kiln cycle, resulting in energy savings and a faster production process. Double firing separates the process into bisque firing first, then a second glaze firing, which enhances durability and allows for better glaze adhesion and color vibrancy. Choosing between single and double firing depends on the desired finish quality, production speed, and kiln efficiency.
Table of Comparison
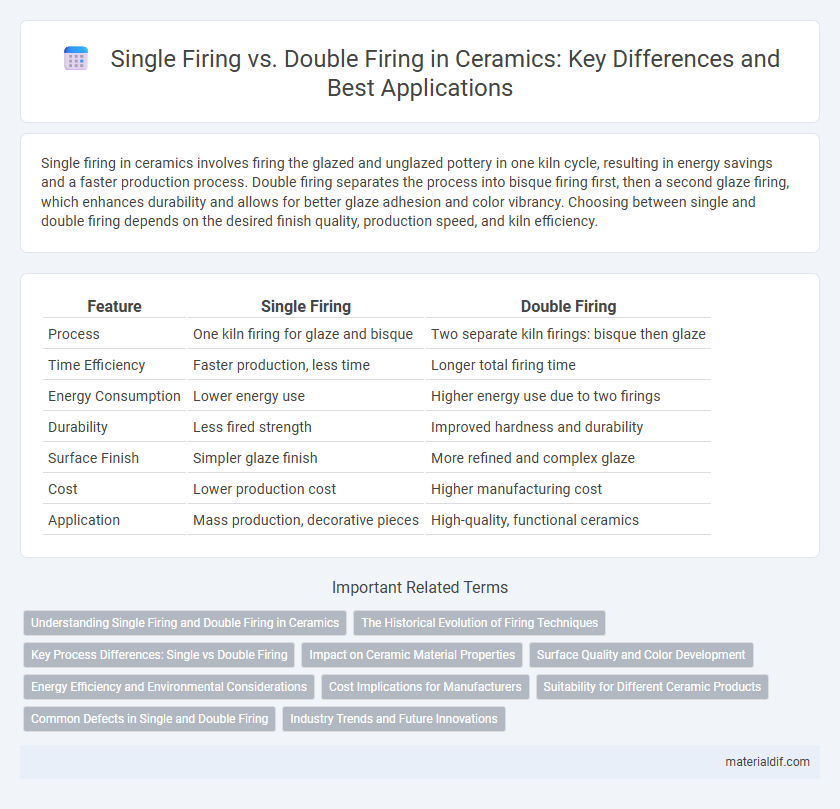
| Feature | Single Firing | Double Firing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | One kiln firing for glaze and bisque | Two separate kiln firings: bisque then glaze |
| Time Efficiency | Faster production, less time | Longer total firing time |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy use | Higher energy use due to two firings |
| Durability | Less fired strength | Improved hardness and durability |
| Surface Finish | Simpler glaze finish | More refined and complex glaze |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Application | Mass production, decorative pieces | High-quality, functional ceramics |
Understanding Single Firing and Double Firing in Ceramics
Single firing in ceramics involves shaping and glazing the clay body before firing it once at a high temperature, which fuses the glaze and clay simultaneously, making the process more time-efficient and energy-saving. Double firing involves an initial bisque firing to harden the clay, followed by glazing and a second firing that matures the glaze, resulting in enhanced durability and finer surface detail. Understanding these methods helps ceramists choose between workflow efficiency and the quality of finish based on project requirements.
The Historical Evolution of Firing Techniques
Single firing emerged as a pivotal innovation in ceramic production during the early 20th century, streamlining the process by combining biscuit and glaze firing into one step. Double firing, a traditional technique dating back to ancient civilizations, involved two separate firings: first for bisque hardness and second after applying glaze to achieve finishing durability and aesthetic depth. This evolution from double to single firing reflects advances in kiln technology and ceramic chemistry, enhancing efficiency while maintaining material integrity and surface quality.
Key Process Differences: Single vs Double Firing
Single firing in ceramics involves applying glaze and firing the piece once, combining both bisque and glaze firing stages, resulting in reduced energy consumption and faster production times. Double firing requires an initial bisque firing to harden the clay body, followed by a separate glaze firing, allowing for better glaze adhesion and reduced risk of defects like blistering. The key process difference lies in the number of firings and the sequential application of glaze, impacting durability and finish quality in ceramic products.
Impact on Ceramic Material Properties
Single firing ceramics enhances color vibrancy and reduces production time by combining glaze melting and clay body firing into one bake, resulting in increased energy efficiency. Double firing allows better control over glaze application and surface texture, minimizing defects like pinholes and crazing but may cause slight shrinkage or warping due to repeated thermal cycles. Understanding these firing impacts on ceramic microstructure and durability is critical for optimizing strength, porosity, and aesthetic quality in ceramic production.
Surface Quality and Color Development
Single firing in ceramics results in a smoother surface finish and vibrant, consistent color development due to the glaze and clay body maturing simultaneously at high temperatures. Double firing, involving separate bisque and glaze firings, enhances surface texture control and allows for richer, more nuanced color layering, reducing the risk of glaze defects. Choosing between single and double firing depends on the desired surface quality, color precision, and the ceramic piece's functional requirements.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Considerations
Single firing in ceramics combines bisque and glaze firing into one process, significantly reducing energy consumption and lowering carbon emissions compared to double firing. Double firing requires two separate firings--first for bisque and then for glaze--doubling fuel usage and increasing environmental impact. Choosing single firing enhances energy efficiency and promotes sustainable ceramic production by minimizing resource use and reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost Implications for Manufacturers
Single firing reduces manufacturing costs by eliminating the need for a separate glaze firing, saving energy and labor expenses. Double firing increases production time and operational costs due to two kiln cycles, but offers greater control over glaze quality and durability. Manufacturers must balance initial savings against potential quality improvements when deciding between these firing methods.
Suitability for Different Ceramic Products
Single firing is ideal for functional ceramics like stoneware and porcelain, where durability and efficiency are prioritized, as it combines bisque and glaze firing into one process. Double firing suits decorative ceramics and complex designs requiring precise glaze control, allowing for detailed surface treatments and multiple glaze layers. Artists and manufacturers select the method based on factors like product purpose, desired finish quality, and production time constraints.
Common Defects in Single and Double Firing
Single firing in ceramics often leads to common defects such as warping, cracking, and incomplete glaze maturation due to rapid temperature changes and reduced thermal stability. Double firing improves glaze durability and surface finish but introduces risks like glaze crawling, pinholing, and additional shrinkage from repeated thermal cycles. Understanding the thermal expansion properties and firing schedules is crucial to minimizing defects in both single and double firing processes.
Industry Trends and Future Innovations
Single firing techniques gain traction in the ceramic industry due to energy efficiency and reduced production time, aligning with sustainability goals. Emerging innovations in high-temperature glazes and advanced kiln technology promise enhanced durability and aesthetic quality, supporting broader application scopes. Industry trends emphasize automation and smart kiln integration to optimize firing precision and resource management.
Single Firing vs Double Firing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com