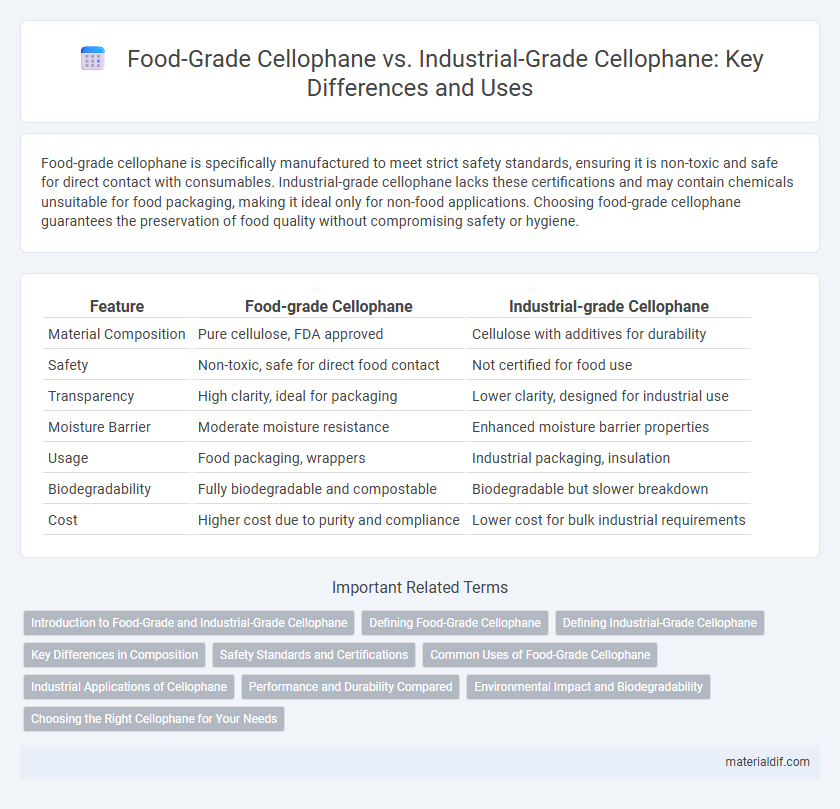
Food-grade cellophane is specifically manufactured to meet strict safety standards, ensuring it is non-toxic and safe for direct contact with consumables. Industrial-grade cellophane lacks these certifications and may contain chemicals unsuitable for food packaging, making it ideal only for non-food applications. Choosing food-grade cellophane guarantees the preservation of food quality without compromising safety or hygiene.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Food-grade Cellophane | Industrial-grade Cellophane |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure cellulose, FDA approved | Cellulose with additives for durability |
| Safety | Non-toxic, safe for direct food contact | Not certified for food use |
| Transparency | High clarity, ideal for packaging | Lower clarity, designed for industrial use |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate moisture resistance | Enhanced moisture barrier properties |
| Usage | Food packaging, wrappers | Industrial packaging, insulation |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable and compostable | Biodegradable but slower breakdown |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity and compliance | Lower cost for bulk industrial requirements |
Introduction to Food-Grade and Industrial-Grade Cellophane
Food-grade cellophane is produced using non-toxic, safe materials that comply with stringent food safety regulations, making it ideal for packaging consumables like bakery products and confectionery. Industrial-grade cellophane, in contrast, is manufactured with materials suited for applications such as insulation, packaging non-food items, or wrapping industrial goods, where food safety standards are not required. The distinction lies primarily in the purity and safety standards adhered to during production, ensuring food-grade variants do not release harmful substances when in contact with edible products.
Defining Food-Grade Cellophane
Food-grade cellophane is a transparent film made from regenerated cellulose that meets strict safety standards for direct contact with food, ensuring non-toxicity and resistance to oils and moisture. Unlike industrial-grade cellophane used for packaging and insulation, food-grade variants are free from harmful chemicals such as plasticizers and chlorine, complying with FDA and EU food safety regulations. Its biodegradable nature and excellent oxygen barrier properties make food-grade cellophane ideal for preserving freshness in bakery, confectionery, and fresh produce packaging.
Defining Industrial-Grade Cellophane
Industrial-grade cellophane is a versatile cellulose-based film primarily designed for packaging non-food products due to its lower purity and different chemical treatments compared to food-grade variants. Unlike food-grade cellophane, which meets strict safety and hygiene standards for direct contact with consumables, industrial-grade cellophane is commonly used for packaging items such as textiles, hardware, and industrial goods where food safety is not a concern. This type is typically less transparent and less odor- and taste-neutral, making it unsuitable for edible product packaging but ideal for protective wrapping and moisture barriers in industrial applications.
Key Differences in Composition
Food-grade cellophane is manufactured using purified cellulose and plasticizers like glycerin to ensure it is safe for direct contact with food products, meeting stringent health and safety regulations. Industrial-grade cellophane contains additives such as colorants and stabilizers tailored for enhanced durability and moisture resistance, but these may not be safe for food packaging. The key compositional difference lies in the purity and types of additives used, with food-grade cellophane prioritizing non-toxic, food-safe ingredients, while industrial-grade emphasizes functional properties for packaging non-food items.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Food-grade cellophane complies with strict safety standards such as FDA approval and EU food contact regulations, ensuring it is free from harmful chemicals and safe for direct contact with consumables. Industrial-grade cellophane lacks these certifications and may contain additives or impurities unsuitable for food packaging, posing potential health risks. Choosing food-grade cellophane guarantees compliance with hygiene protocols and consumer safety requirements in the food industry.
Common Uses of Food-Grade Cellophane
Food-grade cellophane is commonly used for packaging perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, bakery items, and confectionery to maintain freshness and provide a moisture-resistant barrier. Its biodegradable and non-toxic properties make it ideal for direct food contact, ensuring safety and compliance with health regulations. Unlike industrial-grade cellophane, which is used for applications like packaging electronics or gifts, food-grade cellophane prioritizes food preservation and hygiene.
Industrial Applications of Cellophane
Industrial-grade cellophane is extensively used in packaging applications requiring moisture resistance and oxygen barrier properties to preserve product integrity during storage and transport. It finds utility in wrapping non-food items such as pharmaceuticals, textiles, and electrical insulation materials due to its high tensile strength and chemical resistance. Unlike food-grade cellophane, industrial-grade variants are not certified for direct food contact, prioritizing functional characteristics over safety certifications.
Performance and Durability Compared
Food-grade cellophane offers superior clarity and moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging fresh produce and confectionery, while industrial-grade cellophane prioritizes tensile strength and chemical resistance for heavy-duty applications. The food-grade variant ensures compliance with safety standards and maintains product freshness, whereas industrial-grade cellophane demonstrates enhanced durability under mechanical stress and exposure to harsh environments. Performance metrics highlight that food-grade cellophane excels in barrier properties, whereas industrial-grade cellophane withstands wear and tear more effectively.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Food-grade cellophane, made primarily from regenerated cellulose, offers superior environmental benefits due to its complete biodegradability and compostability, breaking down naturally without releasing harmful residues. Industrial-grade cellophane often contains additives or plasticizers that reduce its biodegradability, leading to longer environmental persistence and potential microplastic pollution. Choosing food-grade cellophane reduces ecological footprint and supports sustainable packaging by minimizing waste accumulation and promoting soil health.
Choosing the Right Cellophane for Your Needs
Food-grade cellophane is made from pure cellulose and meets strict safety regulations for direct food contact, ensuring it is non-toxic, odorless, and moisture-resistant, making it ideal for packaging fresh produce, candies, and baked goods. Industrial-grade cellophane, while also transparent and biodegradable, often contains additives that improve strength and durability but may not be safe for consumable items due to potential chemical residues. Selecting the right cellophane depends on the application, prioritizing food-grade for edible products to ensure compliance with health standards and industrial-grade for packaging non-food items requiring enhanced mechanical properties.
Food-grade Cellophane vs Industrial-grade Cellophane Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com