Cellophane coating offers a transparent, glossy finish that enhances product visibility while providing moisture resistance and breathability, making it ideal for fresh produce packaging. Wax coating provides a thicker, more durable barrier that excels in water resistance and extends shelf life but can reduce transparency and breathability. Choosing between cellophane and wax coatings depends on the desired balance between aesthetic appeal, moisture protection, and product preservation.
Table of Comparison
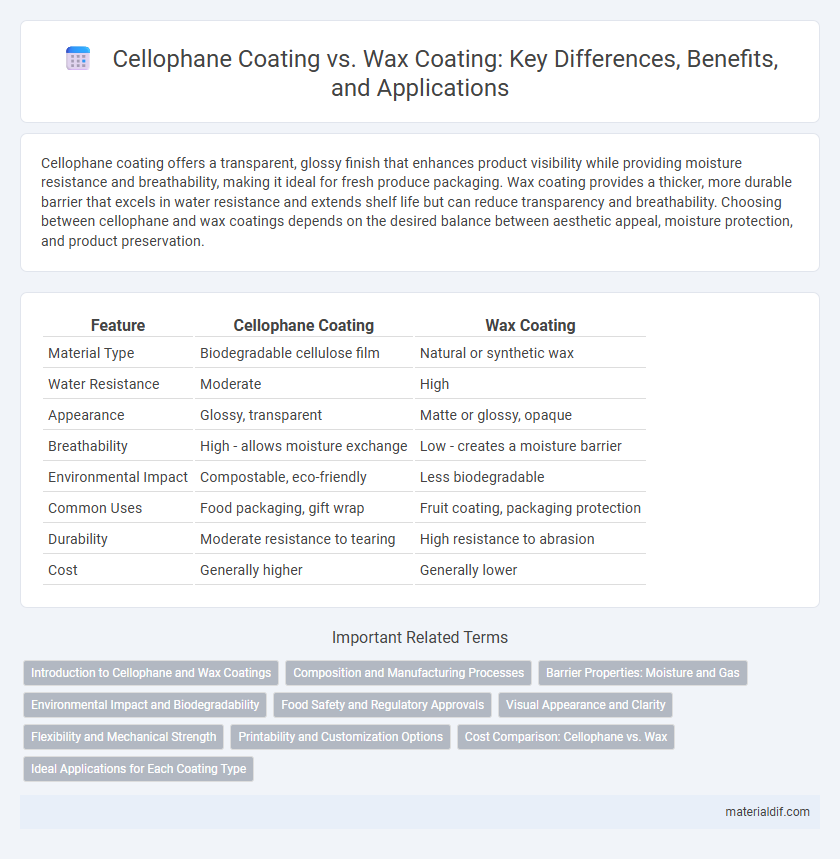
| Feature | Cellophane Coating | Wax Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable cellulose film | Natural or synthetic wax |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Appearance | Glossy, transparent | Matte or glossy, opaque |
| Breathability | High - allows moisture exchange | Low - creates a moisture barrier |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable, eco-friendly | Less biodegradable |
| Common Uses | Food packaging, gift wrap | Fruit coating, packaging protection |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to tearing | High resistance to abrasion |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Introduction to Cellophane and Wax Coatings
Cellophane coating provides a transparent, glossy finish that enhances product visibility while offering moisture resistance and breathability, making it ideal for food packaging. Wax coating, commonly applied to paper or cardboard, creates a water-resistant barrier but lacks the clarity and flexibility of cellophane, often used to protect produce or bakery goods. Both coatings serve protective functions but differ significantly in appearance, permeability, and application suitability.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Cellophane coating is derived from regenerated cellulose, produced by dissolving wood pulp or cotton linters and then extruding the solution to form a thin, transparent film with a biodegradable composition. Wax coating, on the other hand, involves applying natural or synthetic waxes such as paraffin onto paper or cardboard substrates through a process of melting and spreading, creating a moisture-resistant barrier. The manufacturing of cellophane includes viscose or cuprammonium processes that involve chemical treatments for film clarity and strength, whereas wax coating relies on thermal application techniques to achieve surface hydrophobicity.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas
Cellophane coating offers superior moisture vapor transmission resistance compared to wax coating, making it highly effective for maintaining product freshness. In terms of gas barrier properties, cellophane provides moderate oxygen permeability, which can be enhanced through metalized or coated variants, whereas wax coatings generally exhibit poor gas barrier performance. The choice between cellophane and wax coatings depends on the specific requirements for moisture and gas protection in packaging applications.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Cellophane coating is derived from cellulose, making it biodegradable and compostable, which significantly reduces environmental impact compared to wax coating. Wax coatings, often petroleum-based, are less biodegradable and contribute to long-term waste pollution due to their resistance to natural decomposition. Choosing cellophane coatings supports sustainable packaging by enabling easier recycling and minimizing plastic waste accumulation in ecosystems.
Food Safety and Regulatory Approvals
Cellophane coating offers superior food safety by providing a breathable, biodegradable barrier that resists moisture and contamination without harmful chemicals, aligning with stringent FDA and EU regulatory approvals for direct food contact. Wax coating, while also used for moisture resistance, may pose challenges in regulatory compliance due to potential migration of wax components and limited biodegradability. Regulatory bodies prioritize coatings like cellophane that ensure food preservation without compromising safety standards or environmental impact.
Visual Appearance and Clarity
Cellophane coating provides superior visual clarity with a glossy, transparent finish that enhances product presentation and allows vibrant colors to show through distinctly. Wax coating, however, often results in a duller appearance and reduced transparency, which can obscure fine details and affect overall aesthetics. For packaging requiring high visual appeal, cellophane coating is preferred due to its crystal-clear surface and smooth texture.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Cellophane coating offers superior flexibility compared to wax coating, allowing it to better withstand bending and folding without cracking. In terms of mechanical strength, cellophane provides enhanced durability and resistance to tearing, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring robustness. Wax coatings, while water-resistant, typically lack the mechanical resilience and flexibility of cellophane, limiting their use in dynamic environments.
Printability and Customization Options
Cellophane coating offers superior printability due to its smooth, transparent surface that allows high-quality, vibrant graphics and detailed designs. Wax coating, while providing moisture resistance, typically results in a less consistent print surface, limiting color accuracy and sharpness. Customization options are more extensive with cellophane coatings, enabling a variety of finishes such as gloss, matte, or satin, which enhance product appeal and branding flexibility.
Cost Comparison: Cellophane vs. Wax
Cellophane coating generally incurs higher initial costs compared to wax coating due to its complex manufacturing process and material properties. Wax coating offers a more economical option for packaging, especially in bulk applications, but may lack the glossy finish and moisture resistance provided by cellophane. Cost efficiency depends on the balance between volume, desired finish, and barrier qualities required for specific packaging needs.
Ideal Applications for Each Coating Type
Cellophane coating is ideal for products requiring a clear, glossy finish with excellent moisture barriers, such as food packaging, gift wraps, and medical supplies, where transparency and breathability are important. Wax coating excels in applications needing water resistance and grease repellency, like paper cups, bakery boxes, and takeaway containers, providing a protective layer against liquids and oils. Choosing between cellophane and wax coatings depends on the specific packaging requirements related to product preservation, visual appeal, and environmental factors.
Cellophane Coating vs Wax Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com