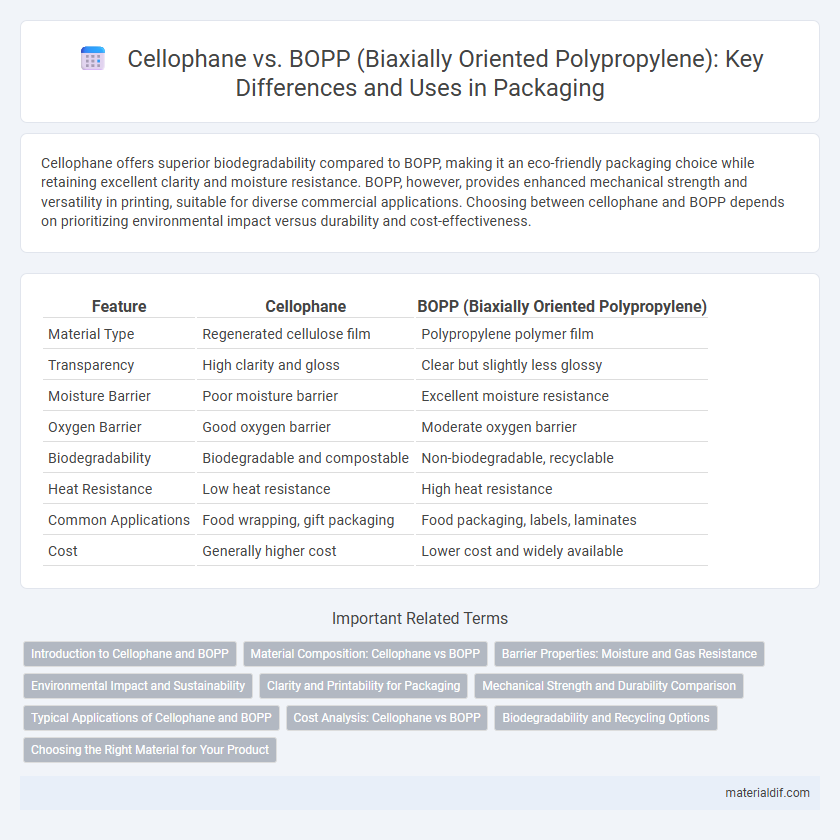
Cellophane offers superior biodegradability compared to BOPP, making it an eco-friendly packaging choice while retaining excellent clarity and moisture resistance. BOPP, however, provides enhanced mechanical strength and versatility in printing, suitable for diverse commercial applications. Choosing between cellophane and BOPP depends on prioritizing environmental impact versus durability and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellophane | BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Regenerated cellulose film | Polypropylene polymer film |
| Transparency | High clarity and gloss | Clear but slightly less glossy |
| Moisture Barrier | Poor moisture barrier | Excellent moisture resistance |
| Oxygen Barrier | Good oxygen barrier | Moderate oxygen barrier |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Heat Resistance | Low heat resistance | High heat resistance |
| Common Applications | Food wrapping, gift packaging | Food packaging, labels, laminates |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Lower cost and widely available |
Introduction to Cellophane and BOPP
Cellophane is a thin, transparent film made from regenerated cellulose, valued for its biodegradability and excellent gas and aroma barrier properties. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) is a synthetic polymer film known for its high tensile strength, moisture resistance, and clarity, commonly used in flexible packaging. Both materials serve distinct roles in packaging, with cellophane favored for eco-friendly applications and BOPP preferred for durability and moisture barrier performance.
Material Composition: Cellophane vs BOPP
Cellophane is a biodegradable film made from cellulose derived from wood pulp or cotton, offering natural transparency and breathability. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) consists of a synthetic polymer formed by biaxial orientation of polypropylene, providing stronger resistance to moisture and chemicals. The material composition differences impact environmental sustainability, with cellophane being eco-friendly and BOPP valued for durability and moisture barrier properties.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Resistance
Cellophane offers excellent moisture barrier properties due to its dense cellulose structure, making it highly effective in preserving food freshness by preventing water vapor transmission. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) provides superior gas resistance, especially against oxygen, which helps extend shelf life and maintain product quality. While cellophane excels in moisture resistance, BOPP is typically preferred for applications requiring enhanced oxygen and gas barrier performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellophane, derived from cellulose, is biodegradable and compostable, making it a more environmentally sustainable packaging option compared to BOPP, which is a petroleum-based plastic and slower to degrade. Cellophane's production relies on renewable resources, whereas BOPP contributes to plastic pollution due to its resistance to natural decomposition. The choice of cellophane over BOPP significantly reduces long-term ecological impact and supports circular economy principles.
Clarity and Printability for Packaging
Cellophane offers superior clarity with a natural, glossy finish that enhances product visibility in packaging, making it ideal for high-end or organic product displays. BOPP film provides excellent printability due to its smoother surface and compatibility with various printing techniques, enabling vibrant, sharp graphics and branding. While cellophane excels in transparency, BOPP is preferred for detailed, colorful packaging designs requiring consistent print quality.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Cellophane offers moderate mechanical strength but tends to be less durable than BOPP, which exhibits superior tensile strength and puncture resistance due to its biaxially oriented polypropylene structure. BOPP's enhanced durability makes it more resistant to tears, moisture, and temperature variations, providing longer-lasting packaging solutions. In contrast, cellophane is more biodegradable but requires careful handling to prevent damage during transport and use.
Typical Applications of Cellophane and BOPP
Cellophane is commonly used in food packaging, such as candy wrappers, bakery item covers, and produce bags due to its excellent moisture barrier and biodegradability. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) finds typical applications in snack packaging, labels, and adhesive tapes because of its high tensile strength, clarity, and resistance to oils and fats. Both materials serve packaging needs but differ in environmental impact and performance characteristics, influencing their specific industrial uses.
Cost Analysis: Cellophane vs BOPP
Cellophane generally costs more than BOPP due to its cellulose-based composition and eco-friendly manufacturing process, which require higher resource input. BOPP, made from polypropylene, benefits from lower raw material expenses and efficient production methods, resulting in a more cost-effective solution for packaging. Price differences influence selection based on budget constraints and sustainability priorities in packaging applications.
Biodegradability and Recycling Options
Cellophane is a biodegradable film made from cellulose, allowing it to decompose naturally under composting conditions, unlike BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene), which is a petroleum-based plastic that resists biodegradation. Recycling options for cellophane are limited but environmentally favorable due to its compostability, while BOPP offers better mechanical recycling but contributes to microplastic pollution when not properly managed. Choosing between cellophane and BOPP depends on prioritizing biodegradability and composting benefits versus conventional plastic recycling infrastructure and durability.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Product
Cellophane offers superior biodegradability and excellent moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for eco-conscious packaging needs, especially for food products requiring breathability. BOPP, with its higher tear resistance, clarity, and cost-effectiveness, excels in durability and aesthetic appeal for retail packaging and labels. Selecting between cellophane and BOPP hinges on product shelf life, environmental impact goals, and packaging performance requirements.
Cellophane vs BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com