Cellophane offers natural biodegradability and excellent breathability, making it ideal for eco-friendly packaging solutions, whereas BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) provides superior moisture resistance and durability, enhancing product shelf life. Cellophane's transparency and compostable properties appeal to sustainable brands, while BOPP's cost-effectiveness and printability suit high-volume commercial applications. Choosing between Cellophane and BOPP depends on balancing environmental impact with performance requirements in packaging design.
Table of Comparison
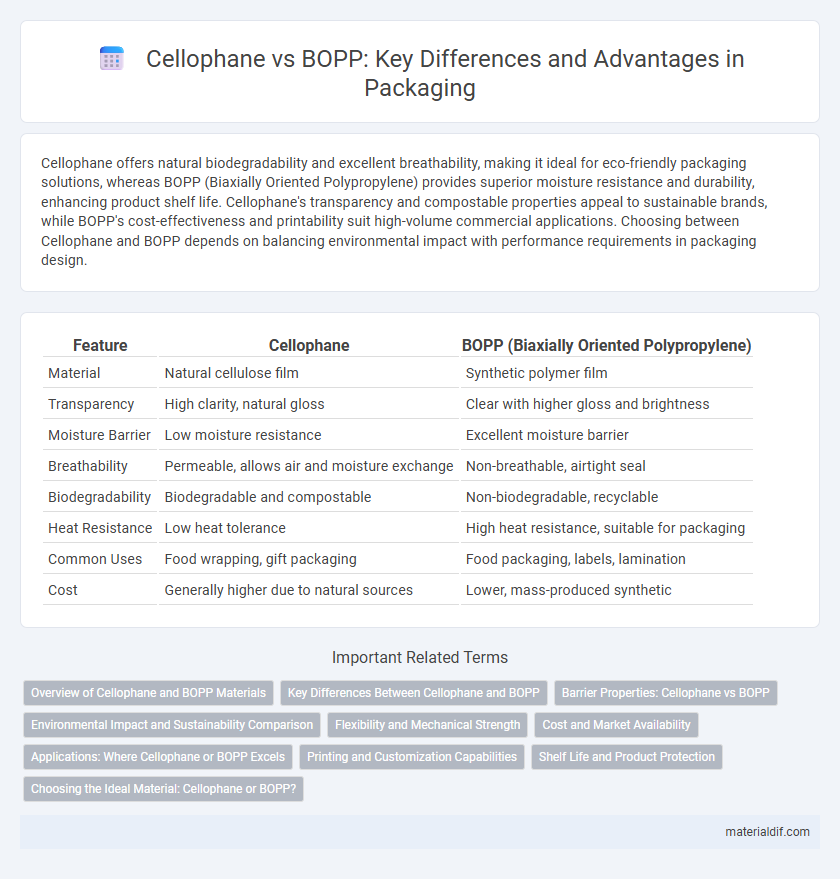
| Feature | Cellophane | BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural cellulose film | Synthetic polymer film |
| Transparency | High clarity, natural gloss | Clear with higher gloss and brightness |
| Moisture Barrier | Low moisture resistance | Excellent moisture barrier |
| Breathability | Permeable, allows air and moisture exchange | Non-breathable, airtight seal |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Heat Resistance | Low heat tolerance | High heat resistance, suitable for packaging |
| Common Uses | Food wrapping, gift packaging | Food packaging, labels, lamination |
| Cost | Generally higher due to natural sources | Lower, mass-produced synthetic |
Overview of Cellophane and BOPP Materials
Cellophane is a thin, transparent film made from regenerated cellulose, known for its biodegradability and excellent moisture permeability. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) is a synthetic film prized for its high tensile strength, moisture resistance, and clarity. While cellophane offers eco-friendly and compostable properties, BOPP provides superior durability and barrier protection for packaging applications.
Key Differences Between Cellophane and BOPP
Cellophane is a biodegradable, transparent film made from cellulose, offering excellent breathability and moisture control, whereas BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) is a synthetic, non-biodegradable plastic known for its strength, clarity, and moisture barrier properties. Cellophane is preferred for eco-friendly packaging due to its compostability, while BOPP provides superior resistance to water, grease, and chemicals, making it ideal for food packaging requiring extended shelf life. The key differences lie in their environmental impact, moisture permeability, and mechanical strength, influencing their applications in sustainable versus durable packaging solutions.
Barrier Properties: Cellophane vs BOPP
Cellophane offers superior oxygen and aroma barrier properties compared to BOPP, making it ideal for packaging sensitive food products. BOPP excels in moisture resistance but allows more oxygen permeability than cellophane, which affects the shelf life of oxygen-sensitive goods. Selecting between cellophane and BOPP depends on specific barrier requirements, with cellophane favored for oxygen-sensitive items and BOPP preferred for moisture protection.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Comparison
Cellophane, made from cellulose, is biodegradable and compostable, offering a more environmentally friendly option compared to BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene), which is derived from fossil fuels and resistant to natural degradation. The production of cellophane involves renewable raw materials and generates fewer carbon emissions, while BOPP's reliance on petrochemicals contributes to higher environmental pollution and landfill accumulation. Choosing cellophane reduces plastic waste and supports sustainable packaging solutions due to its renewable sourcing and lower ecological footprint.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Cellophane offers moderate flexibility but is generally less pliable than BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene), which provides superior flexibility suitable for diverse packaging applications. In terms of mechanical strength, BOPP outperforms cellophane with higher tensile strength and puncture resistance, making it more durable for heavy-duty uses. The trade-off between cellophane's biodegradability and BOPP's enhanced mechanical properties depends on packaging requirements and environmental considerations.
Cost and Market Availability
Cellophane generally incurs higher production costs than BOPP due to its more complex manufacturing process and biodegradable characteristics, affecting its pricing in various markets. BOPP films dominate the packaging industry with their lower cost and widespread availability, providing cost-effective solutions for mass production and distribution. Market availability of cellophane remains limited mainly to niche sectors prioritizing environmental sustainability, while BOPP's extensive supply chain supports diverse applications globally.
Applications: Where Cellophane or BOPP Excels
Cellophane excels in applications requiring biodegradability and moisture permeability, commonly used for wrapping fresh produce, bakery goods, and confectionery to maintain freshness while allowing breathability. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) is preferred for packaging that demands high clarity, moisture resistance, and durability, making it ideal for snack packaging, labels, and flexible packaging films. Both materials serve distinct niches: Cellophane is favored in eco-friendly packaging, whereas BOPP dominates in high-performance, water-resistant, and printable packaging solutions.
Printing and Customization Capabilities
Cellophane offers excellent print clarity and vibrant colors due to its natural cellulose base, making it highly suitable for high-quality graphic printing. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) provides superior customization flexibility with various finishes such as matte, gloss, and satin, supporting diverse printing techniques including flexographic and rotogravure. While BOPP excels in durability and scratch resistance, cellophane's eco-friendly and biodegradable properties appeal to brands emphasizing sustainable packaging solutions.
Shelf Life and Product Protection
Cellophane offers superior breathability compared to BOPP, allowing moisture vapor to pass through, which helps maintain the freshness of perishable goods but may reduce shelf life for moisture-sensitive products. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) provides enhanced barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants, significantly extending shelf life and protecting products from environmental damage. For long-term storage and maximum product protection, BOPP is often preferred, whereas cellophane is ideal for applications requiring natural biodegradability and aroma preservation.
Choosing the Ideal Material: Cellophane or BOPP?
Cellophane offers superior biodegradability and breathability, making it ideal for eco-conscious packaging and products requiring moisture control. BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) excels in strength, clarity, and moisture barrier properties, preferred for durable, water-resistant packaging applications. Selecting between cellophane and BOPP depends on balancing environmental impact with packaging performance requirements.
Cellophane vs BOPP Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com