Cellophane film offers superior breathability and biodegradability compared to LDPE film, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging. LDPE film provides excellent moisture resistance and flexibility, ideal for protecting goods requiring airtight seals. Selecting between cellophane and LDPE depends on specific packaging needs like environmental impact, barrier properties, and product shelf life.
Table of Comparison
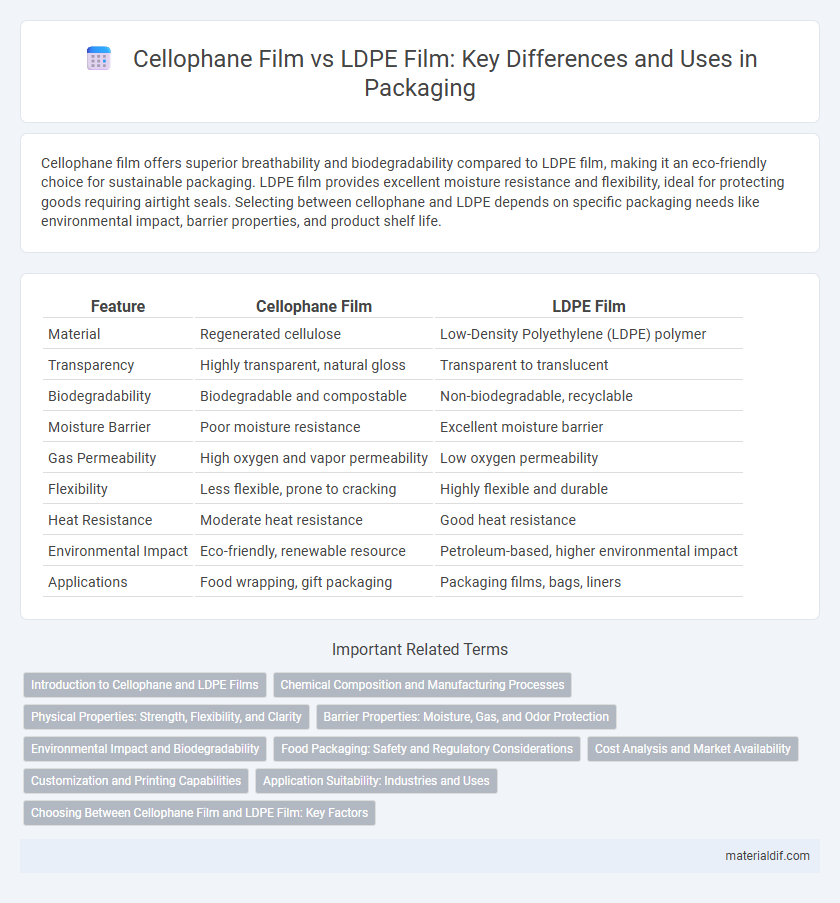
| Feature | Cellophane Film | LDPE Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Regenerated cellulose | Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) polymer |
| Transparency | Highly transparent, natural gloss | Transparent to translucent |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Moisture Barrier | Poor moisture resistance | Excellent moisture barrier |
| Gas Permeability | High oxygen and vapor permeability | Low oxygen permeability |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, prone to cracking | Highly flexible and durable |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | Good heat resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable resource | Petroleum-based, higher environmental impact |
| Applications | Food wrapping, gift packaging | Packaging films, bags, liners |
Introduction to Cellophane and LDPE Films
Cellophane film is a biodegradable, transparent packaging material made from cellulose, known for its excellent breathability and resistance to oils and greases. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) film, a flexible plastic polymer, offers superior moisture barrier properties and puncture resistance, commonly used for food packaging and plastic bags. Both films serve distinct roles in packaging, with cellophane favored for eco-friendly and breathable applications, while LDPE is preferred for durability and moisture protection.
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Cellophane film is primarily made from regenerated cellulose derived from wood pulp or cotton fibers through a viscose process involving chemical treatments with sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide, resulting in a biodegradable material. In contrast, LDPE (low-density polyethylene) film is synthesized from polymerized ethylene molecules via high-pressure polymerization, producing a thermoplastic with hydrocarbon chains lacking natural biodegradability. The manufacturing process for cellophane involves dissolving cellulose, extruding, and regenerating fibers, while LDPE film is produced through extrusion or blown film methods without chemical regeneration.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Clarity
Cellophane film exhibits superior clarity and biodegradability compared to LDPE film, making it ideal for packaging applications where transparency is crucial. While cellophane offers moderate strength and flexibility, LDPE film surpasses it in tensile strength and elasticity, providing enhanced durability and resistance to tearing. The choice between cellophane and LDPE films depends on prioritizing environmental impact, aesthetic clarity, or mechanical robustness in packaging solutions.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Odor Protection
Cellophane film offers superior moisture barrier properties compared to LDPE film, effectively preventing water vapor transmission and maintaining product freshness. In terms of gas barrier capabilities, cellophane significantly limits oxygen permeability, enhancing the shelf life of oxygen-sensitive goods better than LDPE. Additionally, cellophane provides excellent odor protection due to its dense molecular structure, reducing unwanted scent migration more efficiently than LDPE film.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Cellophane film, derived from cellulose, is biodegradable and compostable, breaking down naturally without releasing harmful microplastics, making it a more environmentally friendly option compared to LDPE film. LDPE film, made from polyethylene, is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to plastic pollution due to its persistence in landfills and marine environments. The biodegradable nature of cellophane reduces the ecological footprint of packaging, promoting sustainable practices in industries reliant on plastic films.
Food Packaging: Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Cellophane film offers superior breathability and biodegradability compared to LDPE film, making it ideal for eco-friendly food packaging solutions. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA approve cellophane for direct food contact due to its natural cellulose composition and low risk of chemical migration. LDPE film, while providing excellent moisture barrier properties, often raises concerns regarding environmental impact and potential chemical leaching in food safety compliance.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Cellophane film generally incurs higher production costs due to its natural cellulose composition and energy-intensive manufacturing process compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film, which utilizes cheaper petrochemical raw materials. Market availability favors LDPE film, as its mass production and wider application in packaging industries ensure abundant supply and lower prices. Cost analysis reveals that while LDPE offers affordability and broad accessibility, cellophane film appeals to niche markets prioritizing biodegradability and product visibility despite its premium cost.
Customization and Printing Capabilities
Cellophane film offers superior customization options compared to LDPE film, allowing for tailored thickness, width, and length to meet specific packaging needs. Its smooth, non-porous surface enhances printing capabilities, supporting high-resolution graphics and vibrant colors ideal for branding and product information. In contrast, LDPE film's printable surface is less receptive to detailed prints, often limiting customization in appearance and design quality.
Application Suitability: Industries and Uses
Cellophane film is highly suitable for food packaging in industries requiring moisture and grease resistance, such as confectionery and fresh produce, due to its excellent breathability and biodegradability. LDPE film is preferred in industrial and retail sectors for its superior flexibility, puncture resistance, and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for heavy-duty wrapping and frozen food packaging. Both films serve essential roles in packaging but are selected based on specific application demands like environmental impact and mechanical strength.
Choosing Between Cellophane Film and LDPE Film: Key Factors
Choosing between cellophane film and LDPE film depends on the specific packaging needs, such as moisture barrier properties, biodegradability, and clarity. Cellophane film offers superior biodegradability and excellent oxygen permeability, ideal for environmentally conscious packaging and product visibility. LDPE film provides stronger moisture resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for products requiring airtight sealing and durability.
Cellophane Film vs LDPE Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com