Cellophane bags offer superior biodegradability compared to polyethylene bags, making them an eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging. Their natural cellulose composition allows for better breathability, preserving the freshness of products such as food and flowers more effectively than polyethylene. While polyethylene bags provide higher durability and moisture resistance, cellophane bags excel in environmental impact and aesthetic appeal due to their crystal-clear transparency.
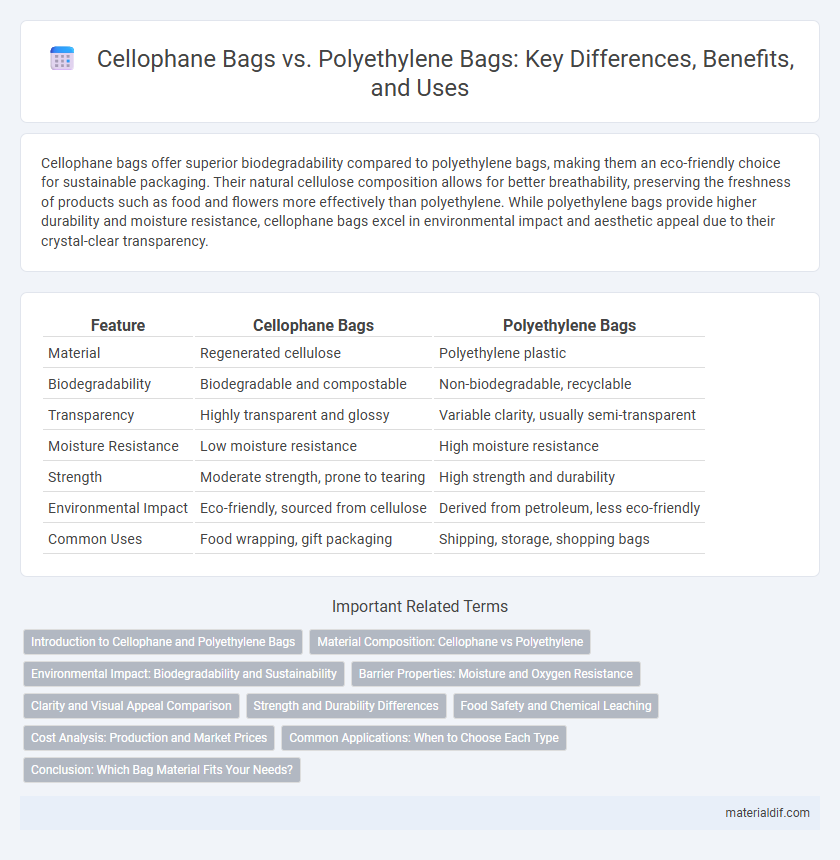
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellophane Bags | Polyethylene Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Regenerated cellulose | Polyethylene plastic |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Transparency | Highly transparent and glossy | Variable clarity, usually semi-transparent |
| Moisture Resistance | Low moisture resistance | High moisture resistance |
| Strength | Moderate strength, prone to tearing | High strength and durability |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sourced from cellulose | Derived from petroleum, less eco-friendly |
| Common Uses | Food wrapping, gift packaging | Shipping, storage, shopping bags |
Introduction to Cellophane and Polyethylene Bags
Cellophane bags, made from regenerated cellulose, offer biodegradability and a glossy, transparent appearance ideal for packaging fresh produce and gifts. Polyethylene bags, derived from petroleum-based polymers, provide superior moisture resistance, flexibility, and durability for heavy-duty packaging and industrial use. Differences in material composition and environmental impact define their distinct applications and consumer preferences.
Material Composition: Cellophane vs Polyethylene
Cellophane bags are made from cellulose, a natural polymer derived from wood pulp or cotton fibers, making them biodegradable and compostable. Polyethylene bags consist of synthetic polymers created through the polymerization of ethylene, a petroleum-based product, resulting in durable, flexible, and moisture-resistant packaging. The distinct material composition affects environmental impact, with cellophane offering a more eco-friendly alternative compared to traditional polyethylene plastics.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Sustainability
Cellophane bags are made from cellulose derived from wood pulp, making them biodegradable and compostable within weeks under proper conditions, thus reducing long-term environmental pollution. Polyethylene bags, composed of non-renewable petroleum-based plastics, persist in the environment for hundreds of years and contribute significantly to plastic pollution and microplastic contamination. The sustainability of cellophane bags is further enhanced by their renewable resource base and lower carbon footprint compared to polyethylene bags, which rely heavily on fossil fuels and energy-intensive production processes.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Oxygen Resistance
Cellophane bags exhibit excellent moisture barrier properties due to their dense cellulose structure, making them suitable for products requiring protection from humidity. However, their oxygen resistance is moderate, which may limit shelf life for oxygen-sensitive goods. Polyethylene bags, in contrast, offer superior oxygen resistance but lower moisture barrier performance, making them ideal for applications demanding extended oxygen protection but less critical moisture control.
Clarity and Visual Appeal Comparison
Cellophane bags offer superior clarity with their transparent, glossy finish, making them ideal for showcasing products with vibrant colors or intricate details, while polyethylene bags typically have a hazier, matte appearance that can obscure contents. The high transparency of cellophane enhances visual appeal for retail packaging, gift wrapping, and food presentation, attracting consumer attention through clear product visibility. Polyethylene bags prioritize durability and moisture resistance but compromise on visual clarity, making cellophane the preferred choice for marketing items where aesthetics are crucial.
Strength and Durability Differences
Cellophane bags, made from regenerated cellulose, offer moderate strength but are generally less durable compared to polyethylene bags, which are crafted from versatile plastic polymers known for their high tensile strength and resistance to punctures. Polyethylene bags provide superior durability under stress, moisture, and extended usage, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications, whereas cellophane bags excel in breathability and biodegradability but are more prone to tearing and degradation when exposed to moisture. The structural integrity of polyethylene bags consistently outperforms cellophane bags in scenarios demanding robust protection and longevity.
Food Safety and Chemical Leaching
Cellophane bags, made from regenerated cellulose, provide superior breathability and are compostable, minimizing chemical leaching risks when storing food compared to polyethylene bags, which are petroleum-based and may release harmful additives under heat or prolonged contact. Studies indicate that polyethylene bags can leach plasticizers and antioxidants affecting food safety, whereas cellophane's natural composition reduces such concerns, making it a safer choice for direct food contact. The biodegradability and non-toxic nature of cellophane align with stringent food safety standards, promoting chemical-free food packaging solutions.
Cost Analysis: Production and Market Prices
Cellophane bags generally incur higher production costs due to the use of cellulose-based materials and more energy-intensive manufacturing processes compared to polyethylene bags made from cheaper petroleum derivatives. Market prices for cellophane bags reflect these increased costs, often positioning them at a premium rate, while polyethylene bags benefit from lower raw material expenses and economies of scale, resulting in more competitive pricing. Businesses considering packaging solutions evaluate these cost differences alongside environmental impact and product requirements to optimize cost-effectiveness and sustainability.
Common Applications: When to Choose Each Type
Cellophane bags excel in packaging fresh produce, baked goods, and gift items due to their biodegradable nature and excellent moisture resistance, making them ideal for environmentally conscious brands. Polyethylene bags dominate in heavy-duty uses such as grocery packaging, industrial storage, and freezer bags, offering superior durability and flexibility at a lower cost. Choosing cellophane is optimal for sustainable packaging with high clarity, while polyethylene suits applications requiring strength and moisture barrier in bulk handling.
Conclusion: Which Bag Material Fits Your Needs?
Cellophane bags offer biodegradability and a natural, transparent look ideal for eco-conscious packaging and fresh product display, while polyethylene bags provide greater durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness suited for heavy-duty or long-term storage. Selecting between cellophane and polyethylene depends on priorities such as environmental impact, product protection, and budget constraints. For sustainable packaging with visual appeal, cellophane is preferable; for strength and moisture barrier, polyethylene is the optimal choice.
Cellophane Bags vs Polyethylene Bags Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com