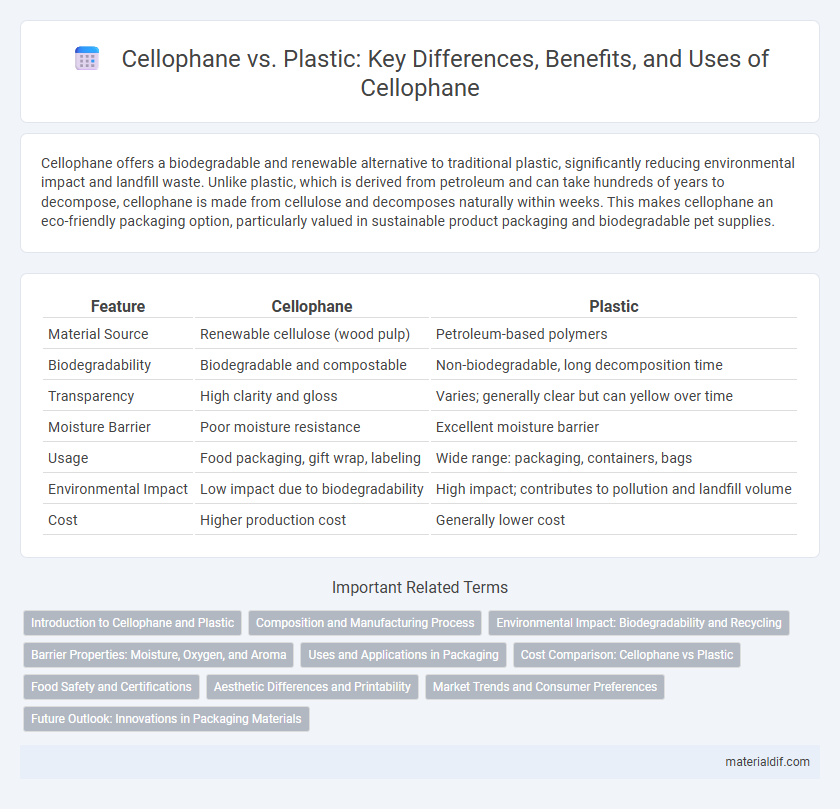
Cellophane offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to traditional plastic, significantly reducing environmental impact and landfill waste. Unlike plastic, which is derived from petroleum and can take hundreds of years to decompose, cellophane is made from cellulose and decomposes naturally within weeks. This makes cellophane an eco-friendly packaging option, particularly valued in sustainable product packaging and biodegradable pet supplies.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellophane | Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable cellulose (wood pulp) | Petroleum-based polymers |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Non-biodegradable, long decomposition time |
| Transparency | High clarity and gloss | Varies; generally clear but can yellow over time |
| Moisture Barrier | Poor moisture resistance | Excellent moisture barrier |
| Usage | Food packaging, gift wrap, labeling | Wide range: packaging, containers, bags |
| Environmental Impact | Low impact due to biodegradability | High impact; contributes to pollution and landfill volume |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Cellophane and Plastic
Cellophane, a biodegradable film made from cellulose, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic, which is derived from petroleum-based polymers. While plastic provides durability and flexibility, cellophane excels in breathability and transparency, making it ideal for packaging perishable goods. The environmental impact of cellophane is significantly lower due to its renewable source and biodegradability compared to synthetic plastics.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Cellophane is composed primarily of regenerated cellulose derived from wood pulp or cotton fibers, whereas traditional plastic is made from synthetic polymers such as polyethylene or polypropylene. The manufacturing process of cellophane involves dissolving cellulose in alkali and carbon disulfide to form viscose, which is then extruded and regenerated into a thin, transparent film; plastic is produced through polymerization or polymer processing techniques like extrusion and molding from petrochemical feedstocks. These distinct compositions and manufacturing methods result in cellophane being biodegradable and more environmentally friendly compared to conventional plastics.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Recycling
Cellophane is derived from cellulose, making it fully biodegradable and compostable within weeks, contrasting sharply with traditional plastics that can take centuries to decompose and often contribute to long-term environmental pollution. Unlike many plastics, cellophane breaks down into natural elements without releasing harmful microplastics, reducing soil and water contamination. Recycling efforts for cellophane are more environmentally friendly but less widespread compared to plastic recycling, partly due to limited infrastructure and collection channels.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Oxygen, and Aroma
Cellophane offers excellent moisture barrier properties due to its dense cellulose structure, effectively preventing water vapor transmission better than many traditional plastics. Its oxygen barrier is superior in dry conditions but can diminish in high humidity, whereas some plastics like polyethylene provide more consistent oxygen resistance regardless of moisture levels. In terms of aroma retention, cellophane excels by limiting aroma diffusion, making it ideal for packaging sensitive food products where preserving flavor is critical.
Uses and Applications in Packaging
Cellophane, a biodegradable and breathable film derived from cellulose, excels in packaging fresh produce, bakery products, and pharmaceuticals by maintaining moisture balance and preserving freshness. Plastic packaging, typically made from petroleum-based polymers, offers superior durability and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for long-term storage of processed foods and liquids. While plastic dominates in versatility and strength, cellophane's eco-friendly nature is increasingly favored for sustainable packaging applications.
Cost Comparison: Cellophane vs Plastic
Cellophane typically costs more to produce than conventional plastic due to its natural cellulose base and biodegradable properties, making it a premium option in packaging. Plastic, derived from petroleum, remains cheaper because of mass production and established supply chains. Despite higher costs, cellophane offers environmental benefits that may justify its price for eco-conscious consumers and businesses.
Food Safety and Certifications
Cellophane, derived from cellulose, is biodegradable and free from harmful chemicals, making it a safer option for food packaging compared to conventional plastic, which can leach toxic substances like BPA and phthalates. Cellophane often holds certifications such as FDA approval and compostability labels, ensuring compliance with strict food safety standards. Plastic packaging typically lacks these eco-friendly certifications and poses greater risks of chemical contamination during food storage.
Aesthetic Differences and Printability
Cellophane offers a smooth, glossy finish that enhances color vibrancy and clarity in printing, making it ideal for high-resolution graphics and intricate designs, unlike plastic films which often have a more matte or uneven surface that can dull printed images. The natural transparency of cellophane allows for sharper contrast and brighter visuals, while plastic materials may produce a muted or less crisp appearance due to their varied textures. Printability on cellophane benefits from better ink adhesion and quicker drying times, enabling detailed, vivid packaging aesthetics preferred in premium product presentations.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Cellophane is gaining market traction as consumers increasingly prioritize biodegradable and compostable packaging over conventional plastic due to environmental concerns. Market trends demonstrate a shift towards sustainable alternatives, with cellophane's renewable cellulose base appealing to eco-conscious buyers seeking reduced plastic waste. Despite plastic's cost-effectiveness and durability, the rising demand for transparent, biodegradable packaging solutions is propelling cellophane's growth in food and retail sectors.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Packaging Materials
Cellophane, derived from renewable cellulose, offers a biodegradable alternative to traditional plastic packaging, addressing escalating environmental concerns and regulatory pressures worldwide. Innovations in cellophane production, such as water-resistant coatings and enhanced barrier properties, are expanding its application potential across food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods sectors. Future packaging trends emphasize sustainable, compostable materials like cellophane to reduce plastic pollution, supporting circular economies and achieving global plastic reduction targets.
Cellophane vs Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com