Cellophane offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to PVC film, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum resources and poses environmental concerns. Unlike PVC, cellophane provides excellent breathability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging perishable goods. Its natural translucency enhances product visibility without the chemical additives often found in PVC films.
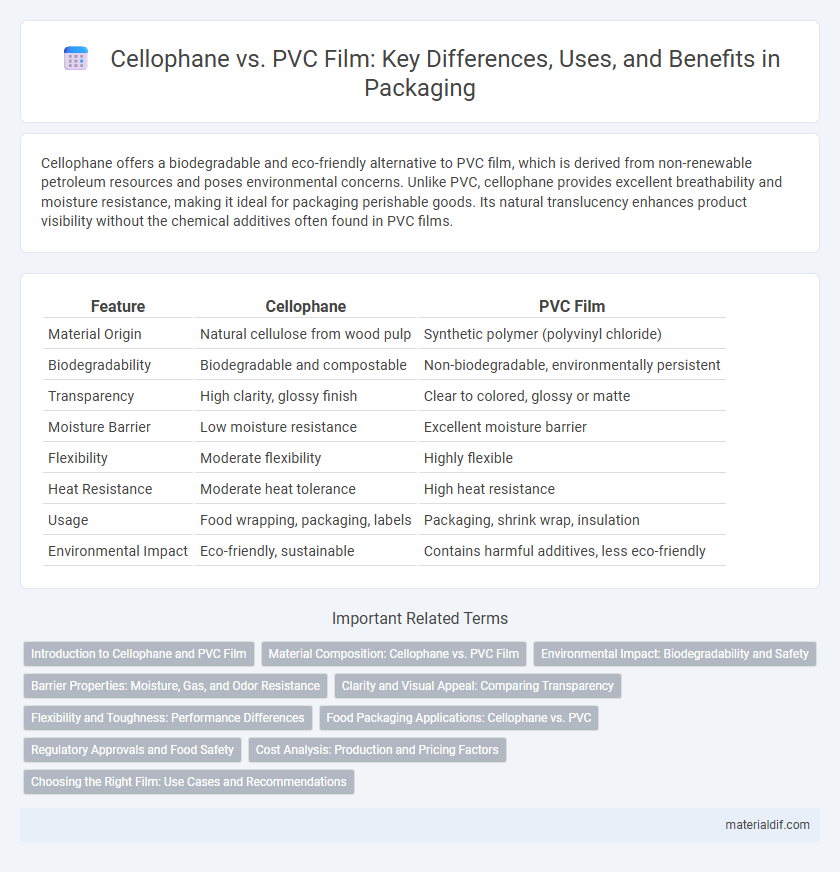
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellophane | PVC Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Natural cellulose from wood pulp | Synthetic polymer (polyvinyl chloride) |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Non-biodegradable, environmentally persistent |
| Transparency | High clarity, glossy finish | Clear to colored, glossy or matte |
| Moisture Barrier | Low moisture resistance | Excellent moisture barrier |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Highly flexible |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat tolerance | High heat resistance |
| Usage | Food wrapping, packaging, labels | Packaging, shrink wrap, insulation |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable | Contains harmful additives, less eco-friendly |
Introduction to Cellophane and PVC Film
Cellophane is a transparent, biodegradable film made from cellulose derived from wood pulp, valued for its eco-friendly properties and breathability. PVC film, on the other hand, is a synthetic plastic made from polyvinyl chloride, known for its durability, flexibility, and water resistance but less environmentally sustainable. Both materials serve packaging purposes, but cellophane is preferred for its natural origins and compostability, while PVC film is chosen for its strength and moisture barrier capabilities.
Material Composition: Cellophane vs. PVC Film
Cellophane is made from regenerated cellulose derived from natural wood pulp, making it biodegradable and breathable, whereas PVC film consists of synthetic polyvinyl chloride, a plastic polymer with added plasticizers for flexibility. The cellulose structure in cellophane allows water vapor permeability, contrasting with PVC film's impermeable and moisture-resistant properties. These material compositions influence environmental impact, with cellophane being more eco-friendly due to its natural origin and biodegradability compared to the petroleum-based, non-biodegradable PVC film.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Safety
Cellophane, derived from cellulose, is fully biodegradable and compostable, breaking down naturally within weeks, whereas PVC film, made from polyvinyl chloride, persists in the environment for decades due to its synthetic polymer nature. PVC film production involves hazardous chemicals and releases dioxins, posing significant risks to human health and ecosystems, unlike cellophane's production which is less toxic and more environmentally friendly. The safety profile of cellophane makes it a preferable option for sustainable packaging, reducing landfill waste and minimizing chemical pollution.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Odor Resistance
Cellophane offers superior moisture barrier properties compared to PVC film, making it ideal for packaging products requiring low water vapor transmission rates. In contrast, PVC film provides enhanced gas resistance, particularly against oxygen and carbon dioxide, benefiting applications where extended shelf life is critical. Odor resistance is generally higher in cellophane due to its natural cellulose composition, whereas PVC tends to have higher permeability to volatile compounds.
Clarity and Visual Appeal: Comparing Transparency
Cellophane offers superior clarity and natural transparency compared to PVC film, providing a more visually appealing and glossy finish that enhances product presentation. Its biodegradable composition maintains high light transmission without the plastic haze often found in PVC, making it ideal for eco-conscious packaging with clear visibility. While PVC film can be clear, cellophane's distinct crispness and smooth surface deliver sharper visual appeal, especially for premium retail packaging.
Flexibility and Toughness: Performance Differences
Cellophane offers moderate flexibility but is more prone to tearing under stress compared to PVC film, which exhibits superior toughness and resistance to punctures. PVC film's enhanced elasticity allows it to withstand bending and stretching without losing integrity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability. The combination of cellophane's biodegradable nature and PVC's mechanical strength often drives material choice based on performance and environmental considerations.
Food Packaging Applications: Cellophane vs. PVC
Cellophane offers superior biodegradability and breathability compared to PVC film, making it ideal for fresh produce and bakery packaging where moisture control is crucial. PVC film provides excellent clarity and moisture resistance, better suited for products requiring extended shelf life and high barrier protection against oxygen and contaminants. Food packaging applications benefit from choosing cellophane for environmentally friendly options and PVC for durability and enhanced protective performance.
Regulatory Approvals and Food Safety
Cellophane is favored over PVC film in food packaging due to its natural cellulose base, which is biodegradable and generally recognized as safe by regulatory bodies like the FDA and EFSA. Unlike PVC film, cellophane does not release harmful chemicals such as phthalates or chlorine-based compounds, ensuring food safety and compliance with stringent food contact regulations. Its superior breathability and moisture permeability also make cellophane a preferred choice for preserving freshness while meeting global food safety standards.
Cost Analysis: Production and Pricing Factors
Cellophane production involves renewable cellulose fibers, resulting in higher costs compared to PVC film, which is synthesized from petrochemicals and benefits from large-scale manufacturing economies. PVC film's lower raw material expenses and faster production cycles contribute to its competitive pricing in packaging applications. However, cellophane's biodegradability and premium market positioning allow for higher price points despite elevated production costs.
Choosing the Right Film: Use Cases and Recommendations
Cellophane offers superior breathability and biodegradability compared to PVC film, making it ideal for packaging fresh produce and food items requiring moisture control. PVC film provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance, suitable for industrial applications and long-lasting protective wraps. Selecting the right film depends on factors like environmental impact, required flexibility, and product preservation needs.
Cellophane vs PVC Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com