Cellophane wrapping offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic wrapping, reducing environmental impact while maintaining product freshness. Unlike plastic wrapping, cellophane is breathable, allowing moisture to escape and preventing condensation, which helps preserve the quality of pet food and treats. The transparency and glossy finish of cellophane enhance product presentation, making it an attractive option for pet care packaging.
Table of Comparison
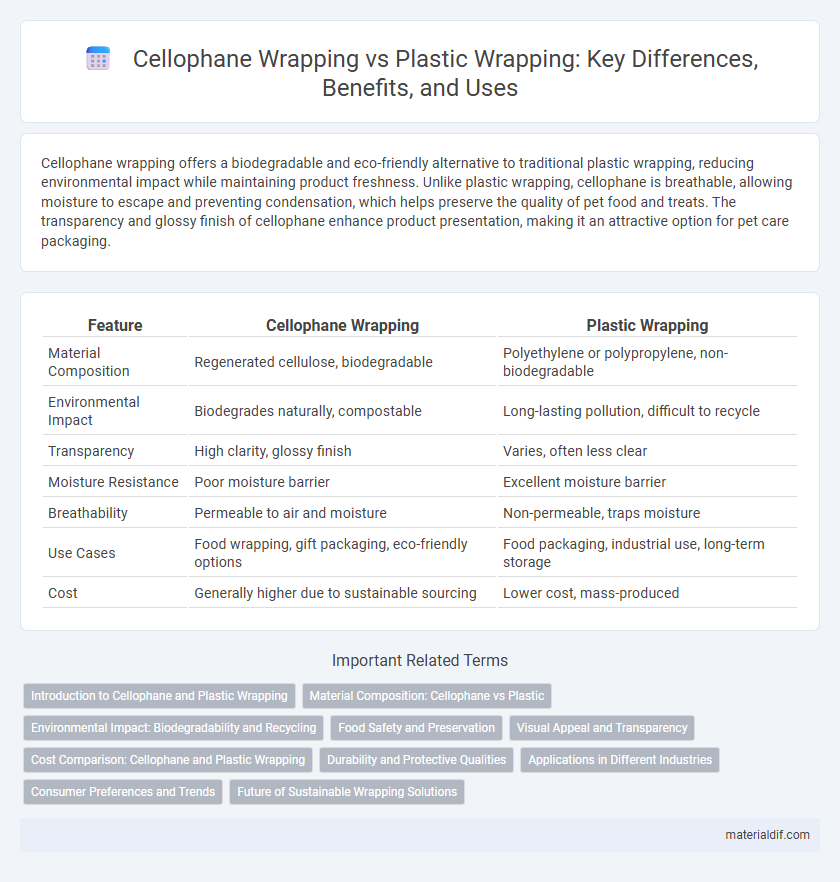
| Feature | Cellophane Wrapping | Plastic Wrapping |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Regenerated cellulose, biodegradable | Polyethylene or polypropylene, non-biodegradable |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegrades naturally, compostable | Long-lasting pollution, difficult to recycle |
| Transparency | High clarity, glossy finish | Varies, often less clear |
| Moisture Resistance | Poor moisture barrier | Excellent moisture barrier |
| Breathability | Permeable to air and moisture | Non-permeable, traps moisture |
| Use Cases | Food wrapping, gift packaging, eco-friendly options | Food packaging, industrial use, long-term storage |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable sourcing | Lower cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Cellophane and Plastic Wrapping
Cellophane is a thin, transparent film made from regenerated cellulose, known for its biodegradability and breathability, making it ideal for food packaging and preserving freshness. Plastic wrapping, typically produced from synthetic polymers like polyethylene, offers superior moisture resistance and durability but presents environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature. Choosing between cellophane and plastic wrapping depends on factors such as product protection needs, sustainability goals, and regulatory requirements.
Material Composition: Cellophane vs Plastic
Cellophane is a biodegradable film made from regenerated cellulose derived from wood pulp or cotton fibers, offering natural breathability and moisture resistance. In contrast, plastic wrapping is typically produced from synthetic polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene, which are petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. The material composition of cellophane makes it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastic wrapping, reducing environmental impact through faster decomposition and compostability.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Recycling
Cellophane wrapping, derived from cellulose, is biodegradable and compostable, breaking down naturally within weeks and reducing landfill waste compared to plastic wrapping, which can take hundreds of years to decompose. Plastic wrapping is often non-biodegradable and poses significant recycling challenges due to mixed polymer types and contamination issues, whereas cellophane can be recycled more efficiently through industrial composting facilities. The environmental impact of cellophane is therefore lower, making it a sustainable choice for packaging aiming to minimize ecological footprint and pollution.
Food Safety and Preservation
Cellophane wrapping offers superior breathability and biodegradability compared to plastic wrapping, reducing moisture buildup that can cause food spoilage. This natural cellulose film acts as a barrier to contaminants while allowing oxygen exchange, which helps maintain the freshness and extends the shelf-life of perishable items. In contrast, plastic wrapping often traps moisture and creates an anaerobic environment that can accelerate bacterial growth and compromise food safety.
Visual Appeal and Transparency
Cellophane wrapping offers superior visual appeal through its high clarity and natural gloss, making products look fresh and attractive on shelves. Unlike plastic wrapping, cellophane provides excellent transparency without the cloudy or matte finish often seen in plastics, enhancing product visibility. This clear, shiny surface also reflects light more effectively, adding to the aesthetic quality of packaged goods.
Cost Comparison: Cellophane and Plastic Wrapping
Cellophane wrapping generally incurs higher initial costs compared to plastic wrapping due to its production from natural cellulose, making it more expensive to manufacture. Plastic wrapping, often made from polyethylene or polypropylene, offers lower material and production expenses, contributing to its widespread use in cost-sensitive packaging applications. Despite the higher price, cellophane's biodegradability and eco-friendly properties can reduce long-term environmental costs and align with sustainability goals.
Durability and Protective Qualities
Cellophane wrapping offers moderate durability with excellent breathability, making it ideal for preserving freshness in perishable goods, but it is less resistant to moisture and punctures compared to plastic wrapping. Plastic wrapping provides superior durability and moisture resistance, offering enhanced protection against contaminants and physical damage, particularly in harsh environments. The choice between cellophane and plastic wrapping depends on the specific protective requirements, balancing biodegradability with barrier strength.
Applications in Different Industries
Cellophane wrapping is widely used in the food industry for packaging fresh produce, baked goods, and confectionery due to its biodegradability and moisture permeability, enhancing product freshness. In contrast, plastic wrapping dominates the electronics and automotive sectors where durability, moisture resistance, and protective barrier properties are critical for safeguarding sensitive components. Both materials enable visibility of products but serve distinct applications based on environmental impact considerations and functional performance requirements.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor cellophane wrapping over traditional plastic due to its biodegradability and eco-friendly image. Market trends indicate a growing demand for sustainable packaging in food and retail sectors, with cellophane providing a clear, breathable barrier that enhances product visibility and freshness. Sustainability-conscious consumers prioritize packaging that reduces environmental impact, making cellophane a preferred choice amidst rising plastic pollution concerns.
Future of Sustainable Wrapping Solutions
Cellophane wrapping, made from cellulose derived from wood pulp, is biodegradable and compostable, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional plastic wrapping that relies on non-renewable petroleum-based materials and contributes significantly to environmental pollution. Innovations in cellophane production are enhancing its barrier properties and durability, making it increasingly suitable for food packaging and other applications where performance has traditionally favored plastic. The future of sustainable wrapping solutions leans towards cellophane's ecological benefits combined with advances in manufacturing technology that reduce carbon footprint and improve recyclability compared to plastic wrapping.
Cellophane Wrapping vs Plastic Wrapping Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com