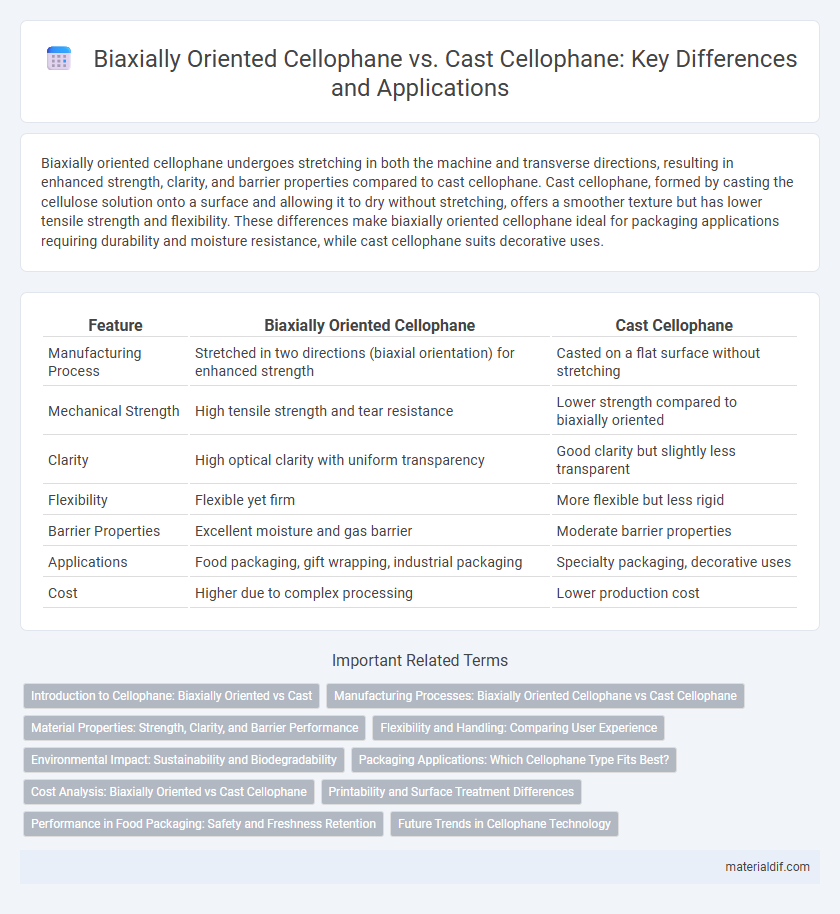
Biaxially oriented cellophane undergoes stretching in both the machine and transverse directions, resulting in enhanced strength, clarity, and barrier properties compared to cast cellophane. Cast cellophane, formed by casting the cellulose solution onto a surface and allowing it to dry without stretching, offers a smoother texture but has lower tensile strength and flexibility. These differences make biaxially oriented cellophane ideal for packaging applications requiring durability and moisture resistance, while cast cellophane suits decorative uses.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biaxially Oriented Cellophane | Cast Cellophane |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Stretched in two directions (biaxial orientation) for enhanced strength | Casted on a flat surface without stretching |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and tear resistance | Lower strength compared to biaxially oriented |
| Clarity | High optical clarity with uniform transparency | Good clarity but slightly less transparent |
| Flexibility | Flexible yet firm | More flexible but less rigid |
| Barrier Properties | Excellent moisture and gas barrier | Moderate barrier properties |
| Applications | Food packaging, gift wrapping, industrial packaging | Specialty packaging, decorative uses |
| Cost | Higher due to complex processing | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Cellophane: Biaxially Oriented vs Cast
Biaxially oriented cellophane undergoes a stretching process in both machine and transverse directions, enhancing its strength, clarity, and barrier properties compared to cast cellophane, which is produced by casting the cellulose solution into thin films without mechanical stretching. The biaxial orientation improves moisture resistance and mechanical durability, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring higher performance. Cast cellophane typically offers a softer texture and flexibility but lacks the enhanced dimensional stability and tensile strength of biaxially oriented variants.
Manufacturing Processes: Biaxially Oriented Cellophane vs Cast Cellophane
Biaxially oriented cellophane is manufactured by mechanically stretching regenerated cellulose film in both machine and transverse directions, enhancing strength, clarity, and barrier properties. Cast cellophane is produced by casting a cellulose solution onto a rotating drum, resulting in a smoother, more uniform film with superior moisture resistance. The key distinction lies in the mechanical orientation of biaxially oriented cellophane versus the solvent casting technique of cast cellophane, influencing their respective applications and performance characteristics.
Material Properties: Strength, Clarity, and Barrier Performance
Biaxially oriented cellophane exhibits higher tensile strength and improved dimensional stability due to the stretching process in two perpendicular directions, enhancing its durability compared to cast cellophane. Cast cellophane, produced by casting the cellulose solution onto a metal drum, offers superior clarity with a smoother surface finish but lower mechanical strength. In terms of barrier performance, biaxially oriented cellophane provides better resistance to moisture and oxygen transmission, making it more suitable for packaging applications requiring longer shelf life.
Flexibility and Handling: Comparing User Experience
Biaxially Oriented Cellophane (BOC) offers superior flexibility due to its stretching process in both machine and transverse directions, enhancing its tensile strength and resistance to tearing. Cast Cellophane, produced by casting cellulose solution onto a flat surface, tends to be stiffer and less pliable, leading to a less smooth handling experience. Users find BOC more adaptable for complex packaging requirements, while Cast Cellophane suits applications where rigidity and dimensional stability are prioritized.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Biodegradability
Biaxially Oriented Cellophane (BOC) demonstrates enhanced strength and barrier properties compared to Cast Cellophane, enabling thinner packaging with reduced material usage and lower environmental footprint. Both BOC and Cast Cellophane are biodegradable and compostable, derived from renewable cellulose sources, which makes them preferable alternatives to fossil-based plastics in sustainable packaging. The production process of BOC, however, requires more energy due to biaxial stretching, but its extended shelf life reduces food waste, balancing its overall environmental impact.
Packaging Applications: Which Cellophane Type Fits Best?
Biaxially Oriented Cellophane (BOC) offers enhanced strength, clarity, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for food packaging requiring durability and visual appeal, such as confectionery and baked goods. Cast Cellophane provides superior barrier properties against oxygen and aroma, suitable for packaging products like coffee and tea where preservation of freshness is critical. Selecting between BOC and Cast Cellophane depends on the packaging need for mechanical strength versus barrier performance.
Cost Analysis: Biaxially Oriented vs Cast Cellophane
Biaxially oriented cellophane (BOC) typically incurs higher production costs due to its complex stretching process, resulting in superior strength and clarity. Cast cellophane offers a more cost-effective alternative with a simpler manufacturing technique but may lack the mechanical properties and optical quality of BOC. Cost analysis reveals BOC as a premium choice for high-performance packaging, while cast cellophane suits budget-sensitive applications.
Printability and Surface Treatment Differences
Biaxially oriented cellophane (BOC) offers superior printability due to its enhanced surface smoothness and dimensional stability achieved through stretching in two directions, allowing for high-resolution printing and vibrant color reproduction. In contrast, cast cellophane possesses a more uneven surface as it is formed by casting the cellulose solution onto a drum, resulting in lower print quality and less ink adhesion. Surface treatment methods for BOC typically involve corona or plasma treatments to improve ink receptivity, whereas cast cellophane often requires additional coatings to enhance its printability and surface uniformity.
Performance in Food Packaging: Safety and Freshness Retention
Biaxially Oriented Cellophane (BOC) offers superior mechanical strength and barrier properties compared to Cast Cellophane, enhancing food safety by effectively preventing contamination and moisture ingress. BOC's enhanced oxygen and aroma barrier characteristics significantly contribute to extended freshness retention in packaged food products. Cast Cellophane, while more flexible, provides lower protection levels, making BOC the preferred choice for high-performance food packaging applications.
Future Trends in Cellophane Technology
Biaxially oriented cellophane offers superior mechanical strength and clarity compared to cast cellophane, making it ideal for advanced packaging applications. Future trends in cellophane technology emphasize enhanced biodegradability and improved barrier properties through nanocomposite integration. Innovations in eco-friendly coatings and sustainable production processes are driving increased adoption of cellophane in global markets focused on reducing plastic waste.
Biaxially Oriented Cellophane vs Cast Cellophane Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com