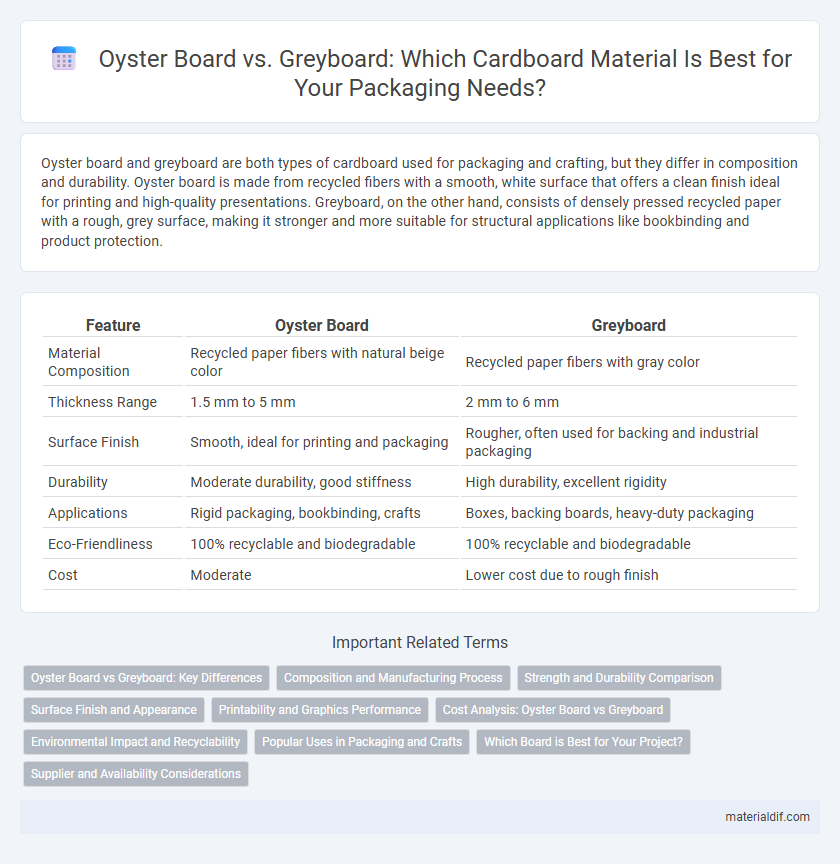
Oyster board and greyboard are both types of cardboard used for packaging and crafting, but they differ in composition and durability. Oyster board is made from recycled fibers with a smooth, white surface that offers a clean finish ideal for printing and high-quality presentations. Greyboard, on the other hand, consists of densely pressed recycled paper with a rough, grey surface, making it stronger and more suitable for structural applications like bookbinding and product protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oyster Board | Greyboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled paper fibers with natural beige color | Recycled paper fibers with gray color |
| Thickness Range | 1.5 mm to 5 mm | 2 mm to 6 mm |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ideal for printing and packaging | Rougher, often used for backing and industrial packaging |
| Durability | Moderate durability, good stiffness | High durability, excellent rigidity |
| Applications | Rigid packaging, bookbinding, crafts | Boxes, backing boards, heavy-duty packaging |
| Eco-Friendliness | 100% recyclable and biodegradable | 100% recyclable and biodegradable |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower cost due to rough finish |
Oyster Board vs Greyboard: Key Differences
Oyster board features a smooth, bleached white surface ideal for high-quality printing, while greyboard consists of recycled paper fibers with a rougher texture and a natural grey color. Oyster board offers superior stiffness and brightness, making it preferable for premium packaging and luxury presentations, whereas greyboard is commonly used for economical applications like backing and book covers. The moisture resistance and aesthetic appeal of oyster board outperform greyboard, which prioritizes cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability due to its recycled content.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Oyster board consists of recycled paper fibers pressed into layers, combining moisture resistance with stiffness, whereas greyboard is composed of recycled gray paper pulp and is more porous and less durable. The manufacturing process of oyster board involves rigorous pressing and chemical treatment to enhance firmness and water resistance, while greyboard is produced by compressing recycled fibers without additional coatings, resulting in a cheaper, less robust material. Oyster board is preferred for packaging that requires durability and moisture protection, while greyboard is commonly used for backing and simple packaging applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Oyster board offers superior strength and durability compared to greyboard due to its higher density and moisture-resistant properties, making it ideal for protective packaging and heavy-duty applications. Greyboard, while more lightweight and cost-effective, tends to absorb moisture and is less rigid, which can lead to bending or warping under stress or prolonged use. For projects requiring long-term structural integrity and resistance to environmental factors, oyster board provides a more reliable and durable solution.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Oyster board features a smooth, clean surface with a white or light-colored finish ideal for high-quality printing and vibrant graphics, making it popular in luxury packaging and premium presentation materials. Greyboard has a rougher, untreated surface, primarily gray in color, which offers a more utilitarian and recycled look suited for structural support rather than aesthetic appeal. The superior surface finish of oyster board provides enhanced printability and a polished appearance compared to the coarse texture and matte finish of greyboard.
Printability and Graphics Performance
Oyster board offers superior printability with a smooth, coated surface that enhances color vibrancy and sharpness in graphics, making it ideal for high-quality packaging and promotional materials. Greyboard, composed of recycled fibers, has a rougher texture that limits detailed printing and results in muted colors, thus better suited for structural applications rather than visually intensive printing. For projects requiring exceptional graphic performance, oyster board delivers a premium finish with consistent ink absorption and excellent reproduction of fine details.
Cost Analysis: Oyster Board vs Greyboard
Oyster board generally costs 15-25% less than greyboard due to its simpler manufacturing process and lower raw material expenses. Greyboard features higher density and stiffness, resulting in increased production costs that reflect in its price. Businesses balancing budget and durability often choose oyster board for cost-effective packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Oyster board features a lower environmental impact due to its use of recycled fibers and minimal chemical additives, enhancing its sustainability compared to traditional greyboard. Greyboard typically contains higher amounts of virgin fiber and fillers, which can complicate recycling processes and increase environmental burdens. Both materials are recyclable, but oyster board's composition allows for easier reprocessing and reduced landfill waste.
Popular Uses in Packaging and Crafts
Oyster board is commonly used in premium packaging for cosmetics and luxury food items due to its smooth surface and high stiffness, which enhances print quality and product presentation. Greyboard, known for its durability and recycled content, is widely utilized in bookbinding, backing for pads, and protective packaging for electronics and household goods. Both materials offer distinct advantages depending on the balance between aesthetic appeal and structural strength required in packaging and craft applications.
Which Board is Best for Your Project?
Oyster board offers a smooth, durable surface ideal for high-quality printing and packaging, while greyboard is thicker and more rigid, perfect for structural support and heavy-duty packaging. Choosing between oyster board and greyboard depends on your project's needs: opt for oyster board for elegant presentation and finer finishes, whereas greyboard suits projects requiring strength and durability. Evaluating the balance between aesthetics and functionality will ensure the best board selection for your packaging or crafting project.
Supplier and Availability Considerations
Oyster board is typically sourced from specialized manufacturers with limited production volumes, resulting in higher costs and variable availability compared to greyboard. Greyboard, commonly produced by major suppliers, benefits from widespread availability and competitive pricing due to its standardized manufacturing processes. Businesses should assess supplier reliability, delivery timelines, and stock consistency when choosing between oyster board and greyboard for packaging or printing applications.
Oyster board vs Greyboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com