Carbon felt offers superior insulation and thermal stability compared to carbon cloth, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Carbon cloth provides enhanced mechanical strength and flexibility, suitable for structural reinforcement and lightweight composites. Both materials exhibit excellent electrical conductivity, but their choice depends on the specific performance requirements of the application.
Table of Comparison
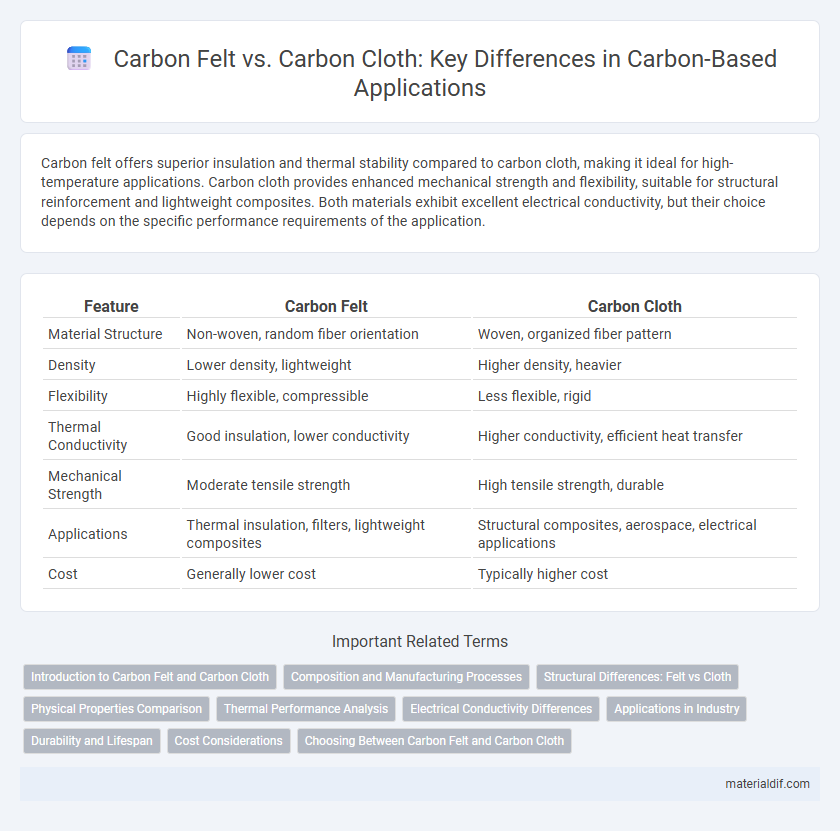
| Feature | Carbon Felt | Carbon Cloth |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Non-woven, random fiber orientation | Woven, organized fiber pattern |
| Density | Lower density, lightweight | Higher density, heavier |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, compressible | Less flexible, rigid |
| Thermal Conductivity | Good insulation, lower conductivity | Higher conductivity, efficient heat transfer |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, durable |
| Applications | Thermal insulation, filters, lightweight composites | Structural composites, aerospace, electrical applications |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
Introduction to Carbon Felt and Carbon Cloth
Carbon felt is a porous material composed of randomly oriented carbon fibers, offering high thermal insulation and excellent chemical resistance, commonly used in high-temperature applications like battery electrodes and filtration. Carbon cloth consists of woven carbon fibers, providing superior electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and flexibility, ideal for use in fuel cells, sensors, and composite reinforcement. Both materials play critical roles in energy storage and thermal management technologies, with their structure significantly influencing performance characteristics.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Carbon felt consists of randomly oriented carbon fibers bonded into a porous, nonwoven mat, offering high thermal insulation and resistance to thermal shock. Carbon cloth is made from woven carbon fibers, resulting in a dense, flexible fabric with enhanced mechanical strength and electrical conductivity. Manufacturing processes for carbon felt involve needling or air laying of fibers followed by high-temperature carbonization, whereas carbon cloth is produced through weaving carbon fiber yarns and subsequent stabilization and carbonization.
Structural Differences: Felt vs Cloth
Carbon felt exhibits a random, three-dimensional fiber arrangement that provides high porosity and thermal insulation, while carbon cloth consists of woven carbon fibers forming a tight, two-dimensional fabric that offers superior mechanical strength and flexibility. The felt's thicker, more open structure enhances gas permeability, making it ideal for filtration and insulation applications, whereas carbon cloth's ordered weave ensures consistent electrical conductivity and durability. Structural differences between carbon felt and carbon cloth directly influence their performance in industries such as energy storage, aerospace, and chemical processing.
Physical Properties Comparison
Carbon felt exhibits a porous, fibrous structure with lower density and higher flexibility compared to the tightly woven, denser, and more rigid carbon cloth. The thermal conductivity of carbon felt is generally lower, making it suitable for insulation, while carbon cloth offers superior electrical conductivity and mechanical strength for structural applications. Carbon cloth's durability and tensile strength surpass carbon felt, which excels in applications requiring lightweight and compressible materials.
Thermal Performance Analysis
Carbon felt exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to carbon cloth due to its porous structure, which reduces heat transfer and enhances thermal resistance. Carbon cloth offers higher thermal conductivity and mechanical strength but allows more heat flow, making it suitable for applications requiring rapid heat dissipation. Thermal performance analysis highlights carbon felt's advantage in applications demanding heat retention and temperature stability, while carbon cloth excels in environments needing efficient heat spreading.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Carbon felt and carbon cloth exhibit distinct electrical conductivity due to their structural differences; carbon cloth's tightly woven fibers promote higher conductivity, ideal for applications requiring efficient electron transport. Carbon felt, with its porous and randomly oriented fiber network, offers lower conductivity but excels in heat dissipation and filtration. The choice between carbon felt and carbon cloth depends on balancing electrical performance and mechanical flexibility for specific industrial uses.
Applications in Industry
Carbon felt offers superior thermal insulation and shock resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial furnaces, heat treatment processes, and filtration systems. Carbon cloth provides excellent flexibility and tensile strength, widely used in aerospace, automotive composites, and structural reinforcement applications. Both materials play critical roles in energy storage devices and chemical processing industries due to their conductivity and durability.
Durability and Lifespan
Carbon felt demonstrates superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to carbon cloth due to its thicker fiber network and higher thermal stability. The porous structure of carbon felt enhances resistance to mechanical wear and thermal cycling, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Carbon cloth, while lightweight and flexible, tends to degrade faster under prolonged stress and heat exposure, limiting its long-term performance.
Cost Considerations
Carbon felt generally offers a lower cost option compared to carbon cloth due to less complex manufacturing processes and lower material density. Carbon cloth, with its higher tensile strength and durability, commands a premium price but can reduce long-term expenses in applications requiring mechanical resilience. Cost considerations between carbon felt and carbon cloth largely depend on specific application requirements such as thermal stability, mechanical performance, and intended lifespan.
Choosing Between Carbon Felt and Carbon Cloth
Choosing between carbon felt and carbon cloth depends on the application's thermal and mechanical requirements. Carbon felt offers superior thermal insulation and porosity, making it ideal for high-temperature filtration and energy storage systems, whereas carbon cloth provides enhanced tensile strength and flexibility suitable for structural reinforcement and composite materials. Evaluating factors such as temperature resistance, mechanical durability, and specific surface area ensures optimal performance in carbon-based applications.
Carbon Felt vs Carbon Cloth Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com