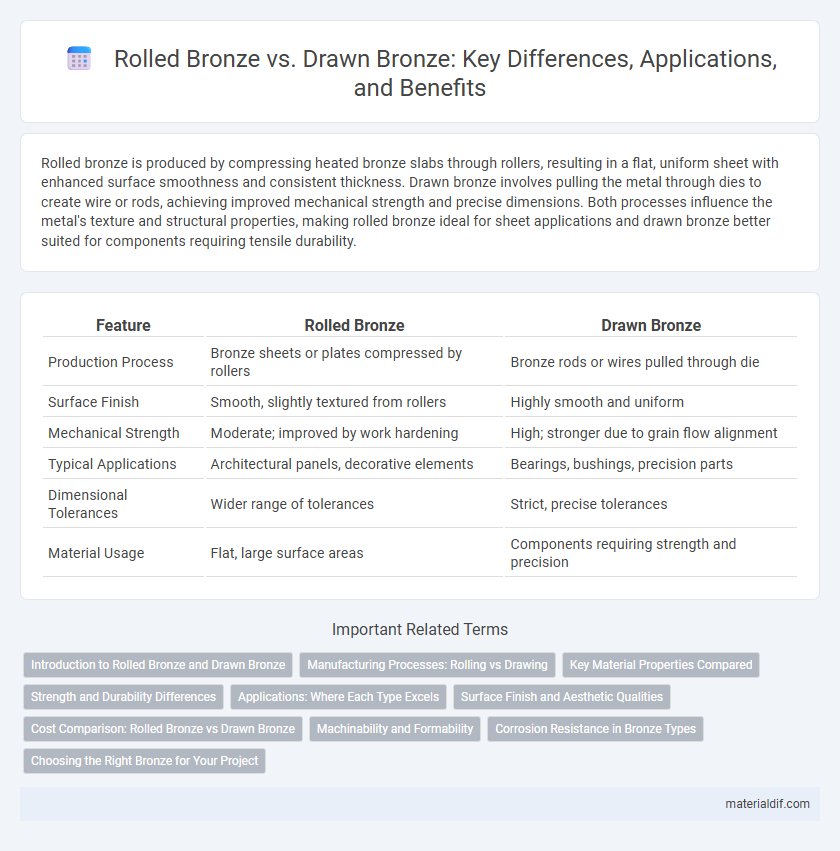
Rolled bronze is produced by compressing heated bronze slabs through rollers, resulting in a flat, uniform sheet with enhanced surface smoothness and consistent thickness. Drawn bronze involves pulling the metal through dies to create wire or rods, achieving improved mechanical strength and precise dimensions. Both processes influence the metal's texture and structural properties, making rolled bronze ideal for sheet applications and drawn bronze better suited for components requiring tensile durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rolled Bronze | Drawn Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Production Process | Bronze sheets or plates compressed by rollers | Bronze rods or wires pulled through die |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, slightly textured from rollers | Highly smooth and uniform |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate; improved by work hardening | High; stronger due to grain flow alignment |
| Typical Applications | Architectural panels, decorative elements | Bearings, bushings, precision parts |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Wider range of tolerances | Strict, precise tolerances |
| Material Usage | Flat, large surface areas | Components requiring strength and precision |
Introduction to Rolled Bronze and Drawn Bronze
Rolled bronze is produced by passing bronze alloy slabs through rollers to achieve a uniform thickness and smooth surface, making it ideal for architectural and decorative applications. Drawn bronze involves pulling bronze rods or wires through dies to create precise shapes with enhanced mechanical properties, commonly used in electrical and industrial components. Both processes optimize the metal's strength and flexibility but differ in production methods and final product characteristics.
Manufacturing Processes: Rolling vs Drawing
Rolled bronze involves passing heated bronze slabs through rollers to achieve desired thickness, resulting in uniform thickness and improved grain structure. Drawn bronze is produced by pulling bronze alloy through dies, which enhances tensile strength and surface finish due to work hardening. Rolling offers efficient bulk processing, while drawing provides precise dimensional control for thinner, more refined bronze components.
Key Material Properties Compared
Rolled bronze exhibits a more uniform grain structure and enhanced surface finish, resulting in superior wear resistance and mechanical strength compared to drawn bronze. Drawn bronze, processed through cold drawing, typically has higher tensile strength and improved dimensional accuracy but may possess increased residual stresses affecting ductility. Both processes influence corrosion resistance differently, with rolled bronze generally offering better resistance due to its homogenized microstructure.
Strength and Durability Differences
Rolled bronze exhibits greater strength due to its dense, compact grain structure formed through the rolling process, which enhances resistance to wear and deformation. Drawn bronze, while offering improved dimensional accuracy and surface finish, generally has lower tensile strength because the drawing process elongates the grains, reducing its overall hardness. For applications requiring maximum durability and impact resistance, rolled bronze is typically preferred over drawn bronze.
Applications: Where Each Type Excels
Rolled bronze is ideal for architectural and decorative applications due to its smooth surface finish and excellent malleability, making it perfect for intricate designs and large sheets. Drawn bronze excels in mechanical and electrical components, benefiting from its superior tensile strength and precise dimensional accuracy. Each type's production method tailors its properties to specific uses, with rolled bronze favored in aesthetic and form-intensive roles, while drawn bronze suits high-stress, precision-dependent applications.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
Rolled bronze exhibits a smoother, more uniform surface finish due to the compressive forces applied during rolling, resulting in enhanced aesthetic appeal with subtle sheen and consistent texture. Drawn bronze, shaped through tensile forces, often shows a slightly rougher surface with visible grain direction, imparting a rustic and handcrafted look that some designers prefer for its natural character. The choice between rolled and drawn bronze directly impacts the visual qualities and tactile experience of finished products, influencing their suitability for decorative or functional applications.
Cost Comparison: Rolled Bronze vs Drawn Bronze
Rolled bronze typically costs more than drawn bronze due to the intensive manufacturing process involving heating and pressing, which enhances its strength and surface finish. Drawn bronze, produced by pulling the metal through dies, offers a more cost-effective option with moderate mechanical properties suitable for less demanding applications. Choosing between rolled and drawn bronze depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements in specific industrial uses.
Machinability and Formability
Rolled bronze exhibits superior machinability due to its uniform grain structure, allowing precise cutting and shaping with minimal tool wear. Drawn bronze offers enhanced formability attributed to its elongated grain orientation, enabling it to be easily bent or stretched without cracking. Choosing between rolled and drawn bronze depends on whether the application prioritizes intricate machining or complex forming processes.
Corrosion Resistance in Bronze Types
Rolled bronze typically exhibits enhanced corrosion resistance due to its refined grain structure achieved through mechanical working, reducing pathways for corrosive agents. Drawn bronze, formed by pulling the metal through dies, may have anisotropic properties that influence localized corrosion behavior differently. Understanding these differences is crucial for applications requiring longevity in marine or industrial environments where bronze's resistance to oxidation and saltwater is paramount.
Choosing the Right Bronze for Your Project
Rolled bronze offers a smoother surface finish and greater dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for applications requiring precise tolerances and aesthetic appeal. Drawn bronze, characterized by enhanced strength and uniform grain structure, suits projects demanding superior mechanical properties and durability. Selecting the right bronze depends on balancing factors like surface finish, strength requirements, and machining capabilities to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Rolled Bronze vs Drawn Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com