Centrifugal casting produces higher-quality bronze components by using centrifugal force to distribute molten metal evenly within a mold, resulting in fewer impurities and improved density compared to sand casting. Sand casting is more versatile and cost-effective for complex shapes and smaller production runs but often leads to coarser grain structures and higher porosity in bronze parts. Choosing between centrifugal and sand casting methods depends on the desired mechanical properties, surface finish, and production volume for bronze applications.
Table of Comparison
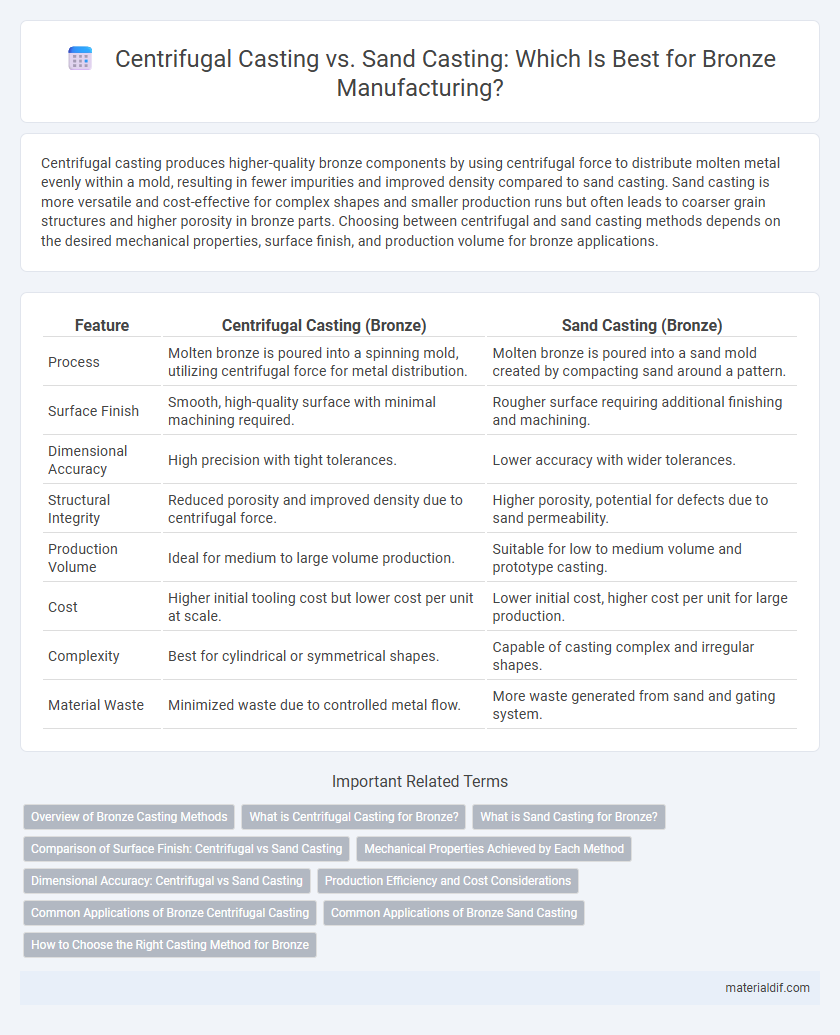
| Feature | Centrifugal Casting (Bronze) | Sand Casting (Bronze) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Molten bronze is poured into a spinning mold, utilizing centrifugal force for metal distribution. | Molten bronze is poured into a sand mold created by compacting sand around a pattern. |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, high-quality surface with minimal machining required. | Rougher surface requiring additional finishing and machining. |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High precision with tight tolerances. | Lower accuracy with wider tolerances. |
| Structural Integrity | Reduced porosity and improved density due to centrifugal force. | Higher porosity, potential for defects due to sand permeability. |
| Production Volume | Ideal for medium to large volume production. | Suitable for low to medium volume and prototype casting. |
| Cost | Higher initial tooling cost but lower cost per unit at scale. | Lower initial cost, higher cost per unit for large production. |
| Complexity | Best for cylindrical or symmetrical shapes. | Capable of casting complex and irregular shapes. |
| Material Waste | Minimized waste due to controlled metal flow. | More waste generated from sand and gating system. |
Overview of Bronze Casting Methods
Bronze casting methods primarily include centrifugal casting and sand casting, each offering distinct advantages for producing high-quality bronze components. Centrifugal casting uses high-speed rotation to distribute molten bronze evenly within a mold, resulting in dense, defect-free parts ideal for cylindrical shapes and applications requiring superior strength and wear resistance. Sand casting involves pouring molten bronze into a sand mold, providing design flexibility and cost-effectiveness for complex geometries or low-volume production, but it may produce parts with rougher surfaces and less dimensional accuracy compared to centrifugal casting.
What is Centrifugal Casting for Bronze?
Centrifugal casting for bronze involves pouring molten bronze into a rapidly spinning mold, using centrifugal force to distribute the metal evenly and reduce impurities. This process produces dense, high-quality bronze components with superior mechanical properties and fine surface finishes compared to sand casting. It is particularly suited for manufacturing cylindrical parts such as bushings, bearings, and pipes where uniformity and structural integrity are critical.
What is Sand Casting for Bronze?
Sand casting for bronze involves creating a mold from a mixture of sand and binders, which shapes the molten bronze as it cools and solidifies. This method is valued for its versatility and cost-effectiveness, particularly in producing complex shapes and large components. The porous nature of the sand mold allows gases to escape, reducing defects and ensuring high-quality bronze castings.
Comparison of Surface Finish: Centrifugal vs Sand Casting
Centrifugal casting of bronze typically produces a smoother, denser surface finish with fewer porosities compared to sand casting, which often results in a rougher texture due to the granular nature of the sand mold. The centrifugal force in centrifugal casting helps in minimizing impurities and enhancing the metal's microstructure, leading to improved mechanical properties and better casting surface quality. Sand casting bronze, while more economical for complex shapes, may require additional machining and surface finishing to achieve similar aesthetics and tolerances found in centrifugal cast components.
Mechanical Properties Achieved by Each Method
Bronze components produced through centrifugal casting exhibit superior mechanical properties, including higher tensile strength and improved wear resistance due to their refined microstructure and reduced porosity. Sand casting of bronze, while versatile and cost-effective, typically results in components with lower mechanical strength and higher porosity, affecting durability and fatigue resistance. The denser grain structure achieved in centrifugal casting enhances hardness and elongation, making it ideal for high-performance bronze parts requiring enhanced mechanical integrity.
Dimensional Accuracy: Centrifugal vs Sand Casting
Centrifugal casting of bronze offers superior dimensional accuracy due to the rotational force that evenly distributes the molten metal, minimizing shrinkage and reducing porosity. In contrast, sand casting typically results in less dimensional precision because the sand mold can deform slightly and allow for more variation in metal flow and cooling. The enhanced control in centrifugal casting makes it ideal for components requiring tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes.
Production Efficiency and Cost Considerations
Centrifugal casting of bronze offers higher production efficiency by reducing porosity and enabling thinner walls, resulting in superior mechanical properties and less machining compared to sand casting. While initial setup costs for centrifugal casting are higher due to specialized equipment, the overall cost per unit decreases with volume production because of faster cycle times and minimal finishing requirements. Sand casting remains more cost-effective for low-volume runs and complex shapes but generally involves longer lead times and increased labor costs due to mold preparation and post-casting processes.
Common Applications of Bronze Centrifugal Casting
Bronze centrifugal casting is commonly used to produce high-performance components such as bushings, bearings, valve bodies, and pump impellers, where uniformity and superior mechanical properties are critical. The process excels in manufacturing parts requiring complex shapes and excellent corrosion resistance, often found in marine, aerospace, and industrial machinery applications. Compared to sand casting, centrifugal casting offers improved density and reduced porosity, making it ideal for functional bronze parts subjected to wear and stress.
Common Applications of Bronze Sand Casting
Bronze sand casting is extensively used in the manufacturing of decorative art pieces, marine components, and industrial fittings due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ability to capture intricate details. Common applications include statues, pump housings, valve bodies, and bearing shells, where durability and precision are critical. The porous nature of sand molds also facilitates casting of large, complex shapes that require minimal machining post-production.
How to Choose the Right Casting Method for Bronze
Choosing the right casting method for bronze depends on factors such as desired dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and production volume. Centrifugal casting offers superior mechanical properties and minimal impurities, making it ideal for high-performance, precision parts in cylindrical shapes. Sand casting is more versatile and cost-effective for complex geometries and lower-volume production, but may require additional machining due to rougher surface finish and lower tolerances.
Centrifugal Casting vs Sand Casting (Bronze) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com