High-tin bronze contains a higher percentage of tin, typically above 15%, resulting in increased hardness, wear resistance, and brittleness, making it ideal for applications like bearings and heavy-duty machinery. Low-tin bronze has less tin, usually below 10%, offering greater ductility, corrosion resistance, and ease of casting, which suits decorative items and electrical components. Choosing between high-tin and low-tin bronze depends on the required balance between strength and malleability for the specific industrial use.
Table of Comparison
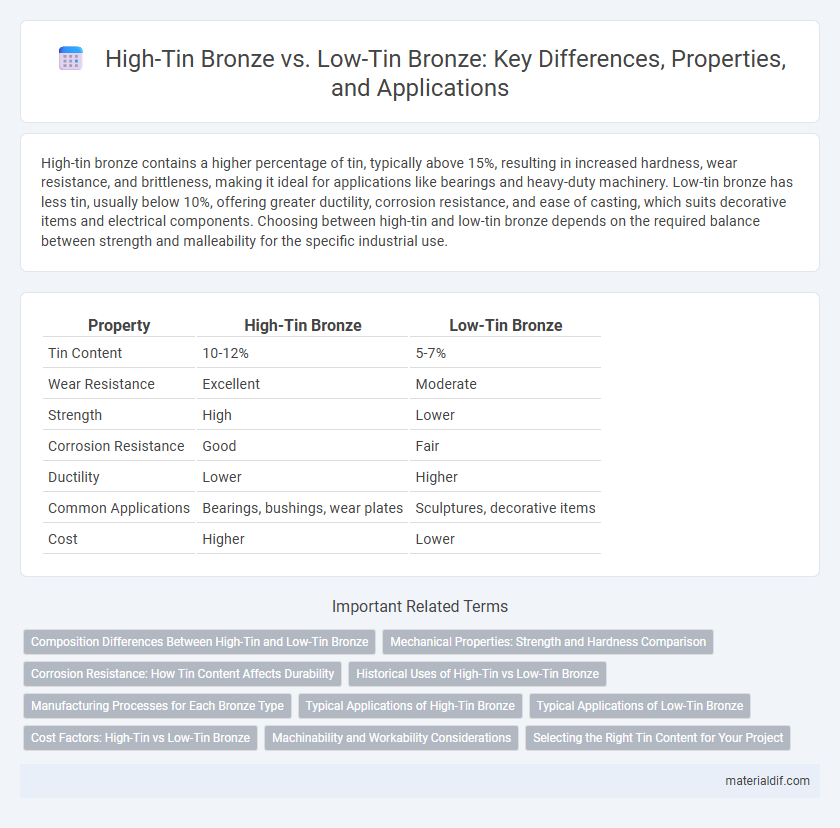
| Property | High-Tin Bronze | Low-Tin Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Tin Content | 10-12% | 5-7% |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Strength | High | Lower |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Fair |
| Ductility | Lower | Higher |
| Common Applications | Bearings, bushings, wear plates | Sculptures, decorative items |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Composition Differences Between High-Tin and Low-Tin Bronze
High-tin bronze typically contains between 10% to 20% tin, increasing hardness and wear resistance compared to low-tin bronze, which generally has less than 10% tin content. The higher tin percentage in high-tin bronze enhances corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and friction resistance. Low-tin bronze, with its lower tin concentration, offers greater ductility and ease of casting but sacrifices some hardness and corrosion resistance relative to high-tin bronze.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Hardness Comparison
High-tin bronze exhibits superior strength and hardness compared to low-tin bronze due to its increased tin content, typically ranging from 15% to 20%, which enhances its wear resistance and tensile strength. Low-tin bronze, with tin content below 10%, offers greater ductility and corrosion resistance but lower mechanical strength, making it more suitable for applications requiring flexibility over hardness. The hardness of high-tin bronze alloys often surpasses 150 HB, whereas low-tin bronzes generally measure below 100 HB on the Brinell scale, reflecting their significant differences in mechanical performance.
Corrosion Resistance: How Tin Content Affects Durability
High-tin bronze alloys, containing approximately 15-20% tin, exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to low-tin bronze with tin content below 10%. The increased tin content enhances the formation of a protective oxide layer on the metal surface, significantly reducing oxidation and wear in marine and industrial environments. This durability makes high-tin bronze ideal for applications requiring extended exposure to corrosive elements, such as ship propellers and bearings.
Historical Uses of High-Tin vs Low-Tin Bronze
High-tin bronze, containing over 20% tin, was historically favored for tools and weapons due to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, seen prominently in ancient Chinese and European artifacts. Low-tin bronze, with less than 12% tin, was preferred for decorative objects, vessels, and sculptures because of its greater malleability and ease of casting, common in Mediterranean civilizations. Archaeological findings demonstrate the strategic selection of high-tin bronze for functional durability and low-tin bronze for artistic expression throughout Bronze Age cultures.
Manufacturing Processes for Each Bronze Type
High-tin bronze manufacturing involves precise alloying with 10-20% tin, requiring controlled melting and casting techniques to ensure hardness and wear resistance. Low-tin bronze, containing less than 10% tin, is typically produced using simpler casting processes and mechanical working methods that enhance ductility and corrosion resistance. Both types benefit from heat treatment, but high-tin bronze demands more stringent temperature control to avoid brittleness during manufacturing.
Typical Applications of High-Tin Bronze
High-tin bronze, containing 7-11% tin, exhibits excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for bearing bushings, valve components, and marine hardware applications. Its superior hardness and reduced friction are favored in heavy-load machinery and industrial equipment, where durability under continuous stress is critical. Low-tin bronze, with less than 7% tin, is commonly used in architectural fittings and decorative items due to its greater malleability and ease of casting.
Typical Applications of Low-Tin Bronze
Low-tin bronze is commonly used in applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance and good tensile strength, such as marine hardware, electrical connectors, and bearing components. Its lower tin content compared to high-tin bronze results in better machinability and ductility, making it ideal for producing intricate parts like valves and pump components. Industries such as automotive and aerospace often select low-tin bronze for bushings and wear-resistant fittings due to its balance of strength and ease of fabrication.
Cost Factors: High-Tin vs Low-Tin Bronze
High-tin bronze typically incurs higher material costs due to the increased tin content, which enhances corrosion resistance and strength but raises alloy expenses. Low-tin bronze offers a more economical option with lower tin percentages, resulting in reduced raw material costs but potentially compromising durability in certain applications. Manufacturing processes and casting complexity further influence the overall cost difference between high-tin and low-tin bronze alloys.
Machinability and Workability Considerations
High-tin bronze alloys, containing tin content typically above 10%, exhibit superior wear resistance and hardness but present challenges in machinability due to increased brittleness and tool wear. Low-tin bronzes, with tin percentages around 5% or less, offer enhanced ductility and ease of machining, making them preferable for complex shapes requiring extensive turning or milling. Selecting the appropriate tin concentration balances workability and durability, with high-tin variants suited for heavy load applications and low-tin types favored for intricate machining tasks.
Selecting the Right Tin Content for Your Project
High-tin bronze, typically containing 10-20% tin, offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty bearings and marine applications. Low-tin bronze, with tin content below 10%, provides enhanced ductility and ease of machining, suitable for decorative items and components requiring moderate strength. Selecting the right tin content depends on the balance needed between mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and workability for your specific project's requirements.
High-Tin Bronze vs Low-Tin Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com