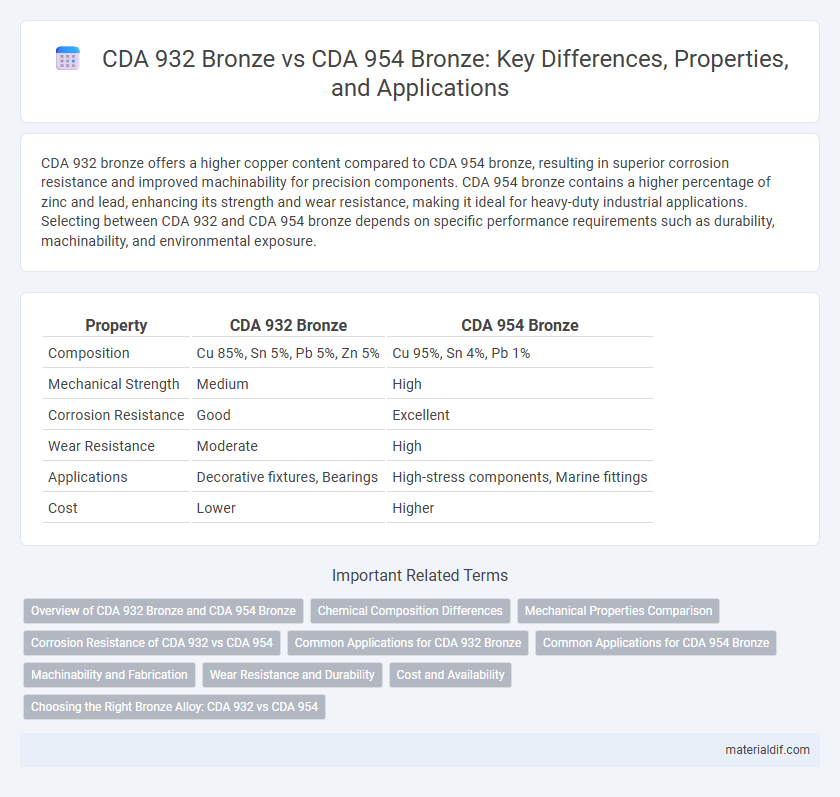
CDA 932 bronze offers a higher copper content compared to CDA 954 bronze, resulting in superior corrosion resistance and improved machinability for precision components. CDA 954 bronze contains a higher percentage of zinc and lead, enhancing its strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. Selecting between CDA 932 and CDA 954 bronze depends on specific performance requirements such as durability, machinability, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | CDA 932 Bronze | CDA 954 Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cu 85%, Sn 5%, Pb 5%, Zn 5% | Cu 95%, Sn 4%, Pb 1% |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Decorative fixtures, Bearings | High-stress components, Marine fittings |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Overview of CDA 932 Bronze and CDA 954 Bronze
CDA 932 Bronze is a high-strength copper alloy containing around 90% copper, 9% zinc, and 1% tin, known for excellent corrosion resistance and machinability, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications. CDA 954 Bronze comprises approximately 88% copper, 10% tin, and 2% zinc, offering superior wear resistance and strength, commonly used in bearing and bushing components. Both alloys provide distinct advantages in durability and mechanical properties, with CDA 932 favoring machinability and CDA 954 excelling in wear resistance.
Chemical Composition Differences
CDA 932 Bronze primarily consists of approximately 88% copper, 10% tin, and 2% lead, offering enhanced machinability and wear resistance. In contrast, CDA 954 Bronze contains about 89% copper, 10% tin, and 1% zinc, emphasizing improved corrosion resistance and strength. The substitution of lead in CDA 932 with zinc in CDA 954 significantly influences their mechanical properties and typical applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
CDA 932 bronze exhibits higher tensile strength, typically around 65,000 psi, compared to CDA 954 bronze, which usually ranges near 55,000 psi. CDA 932 offers better wear resistance due to its higher tin content, enhancing durability in high-friction applications. In contrast, CDA 954 provides improved machinability and toughness, making it suitable for components requiring moderate strength with easier fabrication.
Corrosion Resistance of CDA 932 vs CDA 954
CDA 932 bronze, primarily composed of copper, tin, and lead, offers moderate corrosion resistance suited for marine and industrial environments. CDA 954 bronze contains higher tin and nickel content, significantly improving its resistance to corrosion, especially in seawater and acidic conditions. The enhanced alloying elements in CDA 954 make it a preferred choice for applications requiring superior durability and longevity against corrosive agents.
Common Applications for CDA 932 Bronze
CDA 932 Bronze is widely used in architectural hardware, marine fittings, and industrial components due to its excellent corrosion resistance and superior machinability compared to other bronzes. This alloy contains approximately 9-11% tin, enhancing its strength and durability, making it ideal for gears, bearings, and valve applications. In contrast, CDA 954 Bronze, with higher tin content and added elements, is primarily chosen for heavy-duty applications requiring greater wear resistance and mechanical strength.
Common Applications for CDA 954 Bronze
CDA 954 Bronze, known for its superior corrosion resistance and strength due to higher copper and nickel content, is commonly used in marine hardware, electrical connectors, and precision machined parts requiring durability in harsh environments. It offers enhanced wear resistance compared to CDA 932 Bronze, making it ideal for applications such as valve components, pump parts, and bearings. This alloy's excellent machinability and resistance to dezincification extend the lifespan of critical industrial and marine components.
Machinability and Fabrication
CDA 932 Bronze offers superior machinability due to its higher lead content, making it ideal for precision machining and components requiring intricate detailing. CDA 954 Bronze, with increased tin and zinc, provides enhanced strength and corrosion resistance but is less suited for complex machining processes. Fabrication of CDA 932 involves easier cutting and shaping, whereas CDA 954 demands more robust tooling and techniques to achieve desired forms.
Wear Resistance and Durability
CDA 932 Bronze offers superior wear resistance due to its higher tin content, making it ideal for bearing and bushing applications subjected to heavy loads and friction. CDA 954 Bronze, with added aluminum and iron, provides enhanced overall durability and strength but slightly less wear resistance compared to CDA 932. Selecting between these alloys depends on the specific balance needed between wear resistance and mechanical strength in demanding industrial environments.
Cost and Availability
CDA 932 bronze is generally more cost-effective than CDA 954 bronze due to its simpler alloy composition and widespread production. CDA 932 offers excellent machinability with good corrosion resistance, making it readily available for industrial applications. In contrast, CDA 954 bronze, with higher tin content, provides enhanced strength and wear resistance but comes at a higher price and reduced availability.
Choosing the Right Bronze Alloy: CDA 932 vs CDA 954
CDA 932 bronze, also known as 85-5-5-5, contains approximately 85% copper, 5% tin, 5% lead, and 5% zinc, offering excellent machinability and moderate corrosion resistance, making it ideal for precision components. CDA 954 bronze, with around 94% copper and 6% tin, provides superior strength and wear resistance due to its higher copper and tin content, suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications. Selecting between CDA 932 and CDA 954 depends on balancing machinability with strength and corrosion resistance requirements in specific engineering contexts.
CDA 932 Bronze vs CDA 954 Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com