C95800 bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent strength, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications. C93200 bronze provides better machinability and wear resistance, suited for valve components and bearings. Choosing between C95800 and C93200 depends on balancing durability with ease of manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
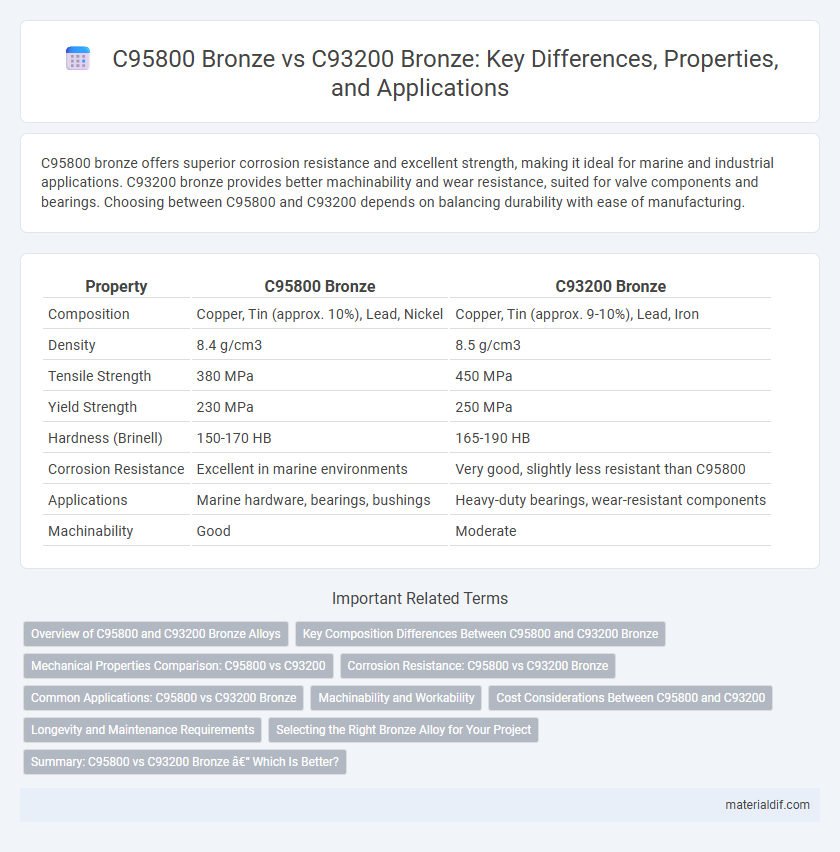
| Property | C95800 Bronze | C93200 Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, Tin (approx. 10%), Lead, Nickel | Copper, Tin (approx. 9-10%), Lead, Iron |
| Density | 8.4 g/cm3 | 8.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 380 MPa | 450 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 230 MPa | 250 MPa |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 150-170 HB | 165-190 HB |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in marine environments | Very good, slightly less resistant than C95800 |
| Applications | Marine hardware, bearings, bushings | Heavy-duty bearings, wear-resistant components |
| Machinability | Good | Moderate |
Overview of C95800 and C93200 Bronze Alloys
C95800 bronze, also known as manganese bronze, contains approximately 60% copper, 1.5% manganese, and 10% zinc, offering excellent strength and corrosion resistance for marine and industrial applications. C93200 bronze, or aluminum bronze, typically comprises about 85% copper and 11% aluminum, providing superior wear resistance and protection against corrosion in harsh environments. Both alloys are widely used in heavy-duty bearing and valve components, with C95800 favored for its high mechanical strength and C93200 preferred for its enhanced durability in corrosive conditions.
Key Composition Differences Between C95800 and C93200 Bronze
C95800 Bronze primarily consists of approximately 9-11% tin, 0.5-1.5% iron, and small amounts of phosphorus, offering strong corrosion and wear resistance. C93200 Bronze contains around 7-9% tin, 1-2% lead, and 0.3-1.0% iron, which enhances machinability but reduces corrosion resistance compared to C95800. The presence of lead in C93200 significantly improves its machinability, whereas C95800's higher tin content provides superior strength and tarnish resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: C95800 vs C93200
C95800 bronze exhibits higher tensile strength and superior fatigue resistance compared to C93200 bronze, making it ideal for applications requiring robust mechanical durability. C93200 bronze, while slightly lower in tensile strength, offers excellent corrosion resistance and better machinability, suited for precision components. Both alloys feature good wear resistance, but C95800's enhanced mechanical properties support more demanding industrial environments.
Corrosion Resistance: C95800 vs C93200 Bronze
C95800 Bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to C93200 Bronze, making it ideal for marine and chemical environments. The high nickel and tin content in C95800 enhances its ability to withstand oxidizing and reducing acids, while C93200, though corrosion-resistant, performs better in less aggressive conditions. Industries requiring long-term exposure to seawater and corrosive fluids often prefer C95800 for its enhanced durability and minimal maintenance requirements.
Common Applications: C95800 vs C93200 Bronze
C95800 Bronze, known for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, is commonly used in marine hardware, valve components, and pump parts where durability and resistance to seawater are critical. C93200 Bronze, characterized by superior machinability and wear resistance, is frequently applied in bearings, bushings, and precision connectors within automotive and industrial machinery. Both alloys serve vital roles in environments demanding robust mechanical performance, but selection depends heavily on specific operational stresses and exposure conditions.
Machinability and Workability
C95800 bronze exhibits superior machinability compared to C93200 bronze due to its higher lead content, which reduces tool wear and improves chip formation. Both alloys demonstrate excellent workability, but C95800's composition allows for easier machining processes and finer surface finishes. The enhanced machinability of C95800 makes it a preferred choice for complex components requiring precision and efficiency in manufacturing.
Cost Considerations Between C95800 and C93200
C95800 bronze generally costs more than C93200 bronze due to its higher nickel content, which enhances corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. The price difference impacts budget decisions in marine and industrial applications where performance requirements must balance with material expenses. Choosing between C95800 and C93200 involves weighing initial cost against long-term durability and maintenance savings.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
C95800 bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance and higher tensile strength compared to C93200 bronze, resulting in enhanced longevity in harsh environments. Maintenance requirements for C95800 are generally lower due to its improved resistance to wear and oxidation, reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements. In contrast, C93200 bronze demands more frequent inspections and maintenance to prevent surface degradation and mechanical failure over time.
Selecting the Right Bronze Alloy for Your Project
Selecting the right bronze alloy, such as C95800 or C93200, depends on the specific requirements of your project including corrosion resistance, machinability, and strength. C95800 bronze, often known as manganese bronze, provides excellent wear resistance and strength, making it ideal for marine and heavy-duty applications. In contrast, C93200 bronze offers superior machinability and is commonly used for general engineering purposes where moderate strength and good corrosion resistance are needed.
Summary: C95800 vs C93200 Bronze – Which Is Better?
C95800 bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and tensile strength compared to C93200 bronze, making it ideal for demanding marine and industrial applications. C93200 bronze provides better machinability and is more cost-effective, suitable for general-purpose components requiring moderate strength. Choosing between C95800 and C93200 depends on balancing performance needs with budget constraints, with C95800 favored for durability and C93200 for economic machining.
C95800 Bronze vs C93200 Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com