Bearing bronze offers superior load-bearing capacity and durability, making it ideal for high-stress applications with heavy radial loads. Bushing bronze, while also strong, provides excellent friction resistance and is typically used for lighter, low-speed rotational movements. Both materials deliver corrosion resistance and wear properties, but selecting between them depends on the specific mechanical demands and operational environment.
Table of Comparison
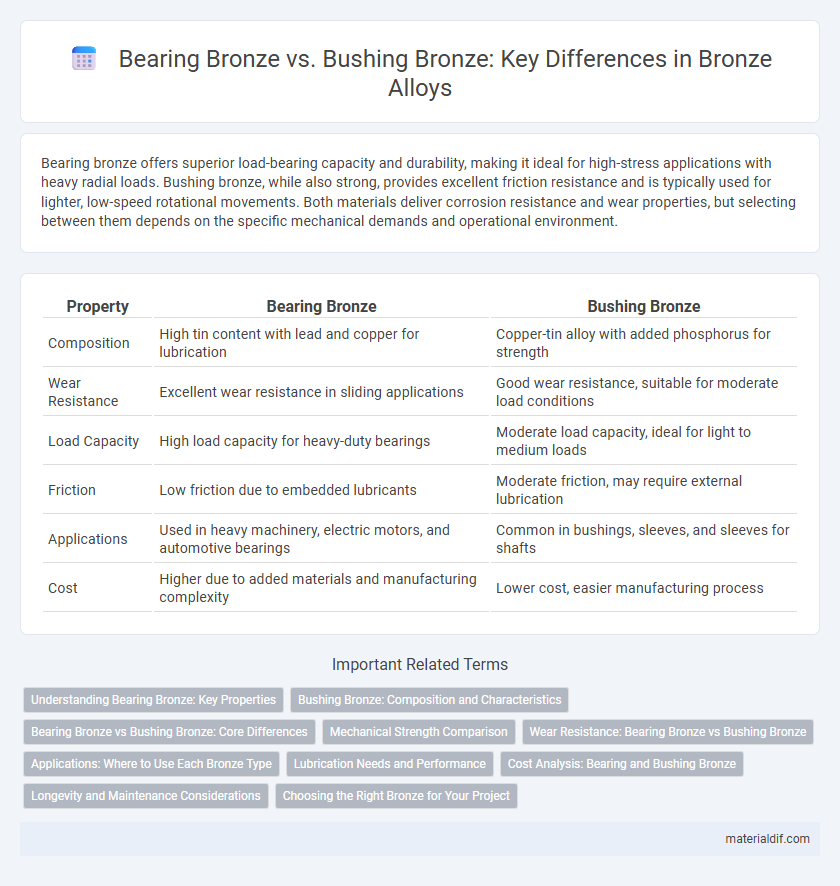
| Property | Bearing Bronze | Bushing Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High tin content with lead and copper for lubrication | Copper-tin alloy with added phosphorus for strength |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear resistance in sliding applications | Good wear resistance, suitable for moderate load conditions |
| Load Capacity | High load capacity for heavy-duty bearings | Moderate load capacity, ideal for light to medium loads |
| Friction | Low friction due to embedded lubricants | Moderate friction, may require external lubrication |
| Applications | Used in heavy machinery, electric motors, and automotive bearings | Common in bushings, sleeves, and sleeves for shafts |
| Cost | Higher due to added materials and manufacturing complexity | Lower cost, easier manufacturing process |
Understanding Bearing Bronze: Key Properties
Bearing bronze exhibits high strength, excellent wear resistance, and superior fatigue endurance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications involving rotating shafts and heavy loads. Its composition typically includes around 8-10% tin, which enhances its hardness and anti-friction properties, crucial for efficient performance in bearings. Bearing bronze's low coefficient of friction and ability to withstand extreme pressures ensure long service life and reduced maintenance in industrial machinery.
Bushing Bronze: Composition and Characteristics
Bushing bronze typically consists of a copper-tin alloy with small amounts of lead or phosphorus to enhance lubrication and wear resistance, making it ideal for bearing surfaces exposed to moderate loads and speeds. Its microstructure allows it to maintain strength and reduce friction, ensuring long service life in applications such as automotive bushings and industrial machinery. The combination of high fatigue resistance and excellent corrosion tolerance distinguishes bushing bronze from other bearing materials.
Bearing Bronze vs Bushing Bronze: Core Differences
Bearing bronze typically contains higher levels of tin and lead, enhancing its wear resistance and load-carrying capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty bearing applications. Bushing bronze often incorporates more aluminum and iron, providing superior strength and corrosion resistance suited for bushings operating under moderate loads and varying environments. The core difference lies in their alloy composition and mechanical properties, with bearing bronze optimized for high-load rotational components and bushing bronze engineered for versatile, durable sliding support.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Bearing bronze typically exhibits higher mechanical strength compared to bushing bronze due to its alloy composition with additional elements like tin and lead, which enhance its durability and load-bearing capacity. Mechanical strength in bearing bronze manifests as superior hardness and wear resistance, making it more suitable for heavy-duty applications subjected to high stress and friction. Bushing bronze, while still durable, prioritizes corrosion resistance and machinability, resulting in comparatively lower tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
Wear Resistance: Bearing Bronze vs Bushing Bronze
Bearing bronze typically exhibits superior wear resistance compared to bushing bronze due to its higher hardness and alloy composition, often including elements such as lead and tin that enhance durability. Bushing bronze, while offering good wear properties, is generally softer and better suited for applications requiring low friction rather than maximum wear resistance. The enhanced wear resistance of bearing bronze makes it ideal for high-load, high-speed conditions where extended service life is critical.
Applications: Where to Use Each Bronze Type
Bearing bronze is ideal for high-load mechanical applications such as gears, crankshafts, and heavy-duty bearings where strength and wear resistance are critical. Bushing bronze is commonly used in lower-load environments like automotive suspension components, door hinges, and machinery bushings, providing excellent friction reduction and corrosion resistance. Selecting between bearing and bushing bronze depends on operational load, speed, and exposure to corrosive elements in the application.
Lubrication Needs and Performance
Bearing bronze typically requires minimal external lubrication due to its inherent oil-retaining properties, allowing for self-lubrication under various load conditions. Bushing bronze, often designed with porous structures, necessitates regular lubrication to maintain optimal performance and reduce wear in high-friction applications. Both materials offer excellent durability, but bearing bronze excels in low-maintenance environments, whereas bushing bronze benefits from consistent lubrication to enhance lifespan and operational efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Bearing and Bushing Bronze
Bearing bronze typically incurs higher material and manufacturing costs due to its superior load-bearing and wear-resistant properties, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Bushing bronze offers a more cost-effective solution with adequate performance in lower-load environments, reducing overall expenses while maintaining durability. Evaluating the specific operational demands and lifespan requirements helps determine the optimal investment between bearing bronze and bushing bronze.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Bearing bronze typically offers superior longevity due to its high load-carrying capacity and excellent wear resistance compared to bushing bronze. Maintenance considerations favor bearing bronze as it often requires less frequent lubrication and replacement cycles, contributing to reduced downtime in industrial applications. Bushing bronze, while generally easier to manufacture, may need more regular maintenance to prevent premature wear in high-stress environments.
Choosing the Right Bronze for Your Project
Bearing bronze offers superior wear resistance and load-carrying capacity due to its tin and lead content, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Bushing bronze, typically composed of phosphor bronze, provides excellent corrosion resistance and is better suited for low-friction, light-load scenarios. Selecting the right bronze depends on factors like operating conditions, load requirements, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Bearing Bronze vs Bushing Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com