UNS C26800, also known as cartridge brass, contains about 70% copper and 30% zinc, offering excellent corrosion resistance and good ductility for cold working applications. UNS C46400 is a leaded brass with approximately 60% copper and 40% zinc, enhanced with lead for improved machinability, making it ideal for precision components requiring intricate machining. The choice between C26800 and C46400 depends on the balance needed between corrosion resistance, strength, and the ease of fabrication.
Table of Comparison
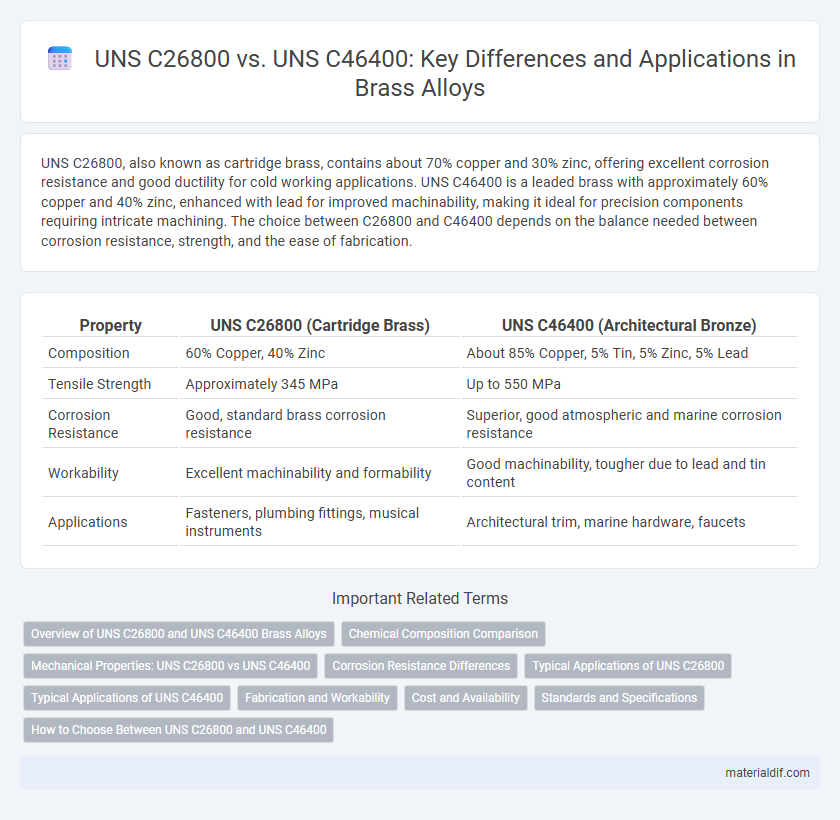
| Property | UNS C26800 (Cartridge Brass) | UNS C46400 (Architectural Bronze) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 60% Copper, 40% Zinc | About 85% Copper, 5% Tin, 5% Zinc, 5% Lead |
| Tensile Strength | Approximately 345 MPa | Up to 550 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, standard brass corrosion resistance | Superior, good atmospheric and marine corrosion resistance |
| Workability | Excellent machinability and formability | Good machinability, tougher due to lead and tin content |
| Applications | Fasteners, plumbing fittings, musical instruments | Architectural trim, marine hardware, faucets |
Overview of UNS C26800 and UNS C46400 Brass Alloys
UNS C26800 brass, commonly known as Cartridge Brass, contains approximately 70% copper and 30% zinc, offering excellent ductility, corrosion resistance, and machinability ideal for ammunition casings and decorative applications. UNS C46400 brass, or Leaded Brass, includes about 60-63% copper, 35-40% zinc, and a small percentage of lead (usually around 2%), enhancing its machinability for precision components such as fittings and valves. Both alloys are widely used in various manufacturing sectors due to their unique mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, but UNS C46400 is preferred where high-speed machining is critical.
Chemical Composition Comparison
UNS C26800 (Copper Alloy CDA 268) typically contains about 60% copper and 39% zinc, with small amounts of lead and iron, whereas UNS C46400 (Copper Alloy CDA 464) generally consists of approximately 63% copper, 35% zinc, and a similar trace of lead. The higher copper content in UNS C46400 enhances its corrosion resistance and strength compared to the more zinc-rich UNS C26800. Variations in lead content affect machinability, making UNS C46400 preferred for precision components requiring higher mechanical performance.
Mechanical Properties: UNS C26800 vs UNS C46400
UNS C26800, commonly known as yellow brass, typically exhibits tensile strength around 345 MPa and an elongation of 40%, making it suitable for general-purpose applications with moderate mechanical demands. UNS C46400, or naval brass, offers higher tensile strength, approximately 415 MPa, and improved corrosion resistance, with elongation near 35%, favoring more demanding marine and industrial environments. The superior mechanical properties of UNS C46400 result from its optimized copper-zinc-tin alloy composition, enhancing hardness and durability compared to UNS C26800.
Corrosion Resistance Differences
UNS C26800, commonly known as Cartridge Brass, exhibits moderate corrosion resistance in atmospheric conditions but may suffer dezincification in marine environments. UNS C46400, or Naval Brass, contains tin which significantly enhances its resistance to dezincification and improves performance against stress corrosion cracking in saltwater. Differences in alloy composition make UNS C46400 preferable for applications demanding superior corrosion resistance, especially in harsh chloride-rich environments.
Typical Applications of UNS C26800
UNS C26800 brass, commonly known as Cartridge Brass, is widely used in applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance and good formability, including ammunition casings, electrical connectors, and decorative hardware. This alloy's superior machinability and strength make it ideal for precision components in automotive radiators and plumbing fittings. Unlike UNS C46400, which is favored for high-strength wrought products, UNS C26800 is preferred for stamped or drawn components in electrical and industrial sectors.
Typical Applications of UNS C46400
UNS C46400, known as Naval Brass, is widely used in marine environments due to its excellent resistance to dezincification and corrosion, making it ideal for seawater fittings, pumps, and valves. This alloy is also preferred for architectural applications, including decorative hardware and plumbing fixtures, where both strength and aesthetic appeal are critical. Compared to UNS C26800, UNS C46400 offers superior durability and performance in harsh, saltwater conditions.
Fabrication and Workability
UNS C26800 brass, known as cartridge brass, offers excellent workability due to its high copper and zinc content, making it ideal for deep drawing, forming, and machining processes. UNS C46400, a free-machining brass alloy with added lead, significantly enhances machinability and reduces tool wear, but its lead content can limit certain fabrication methods like brazing or welding. Fabricators often choose UNS C26800 for applications requiring superior forming and UNS C46400 when precision machining and quick production turnaround are priorities.
Cost and Availability
UNS C26800 brass, known as cartridge brass, generally offers a lower cost compared to UNS C46400 due to its higher copper-zinc ratio and widespread production. UNS C46400, a leaded brass, tends to have better machinability but may be less readily available in certain markets, impacting availability and cost efficiency. Manufacturers often choose UNS C26800 for bulk applications where cost-effectiveness and material supply are critical factors.
Standards and Specifications
UNS C26800 brass conforms to ASTM B16 and B36 specifications, known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance in general-purpose applications. UNS C46400 brass, often specified under ASTM B135 and B36, offers higher strength and improved mechanical properties suitable for more demanding structural components. Both alloys adhere to strict industry standards ensuring consistent composition and performance in plumbing and industrial fittings.
How to Choose Between UNS C26800 and UNS C46400
When choosing between UNS C26800 and UNS C46400 brass alloys, consider the application's mechanical strength and corrosion resistance requirements; UNS C46400 offers higher tensile strength and better machinability, making it ideal for precision components. UNS C26800, with its excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity, suits applications in marine environments and heat exchangers. Evaluate factors such as operating conditions, manufacturing processes, and cost constraints to select the optimal brass alloy for your project.
UNS C26800 vs UNS C46400 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com