Dezincification-resistant brass contains special alloying elements such as arsenic or antimony that prevent the selective leaching of zinc, enhancing corrosion resistance in water systems. Regular brass, primarily composed of copper and zinc, is more susceptible to dezincification, which weakens the material and causes premature failure. Using dezincification-resistant brass ensures longer-lasting plumbing components and reduced maintenance costs.
Table of Comparison
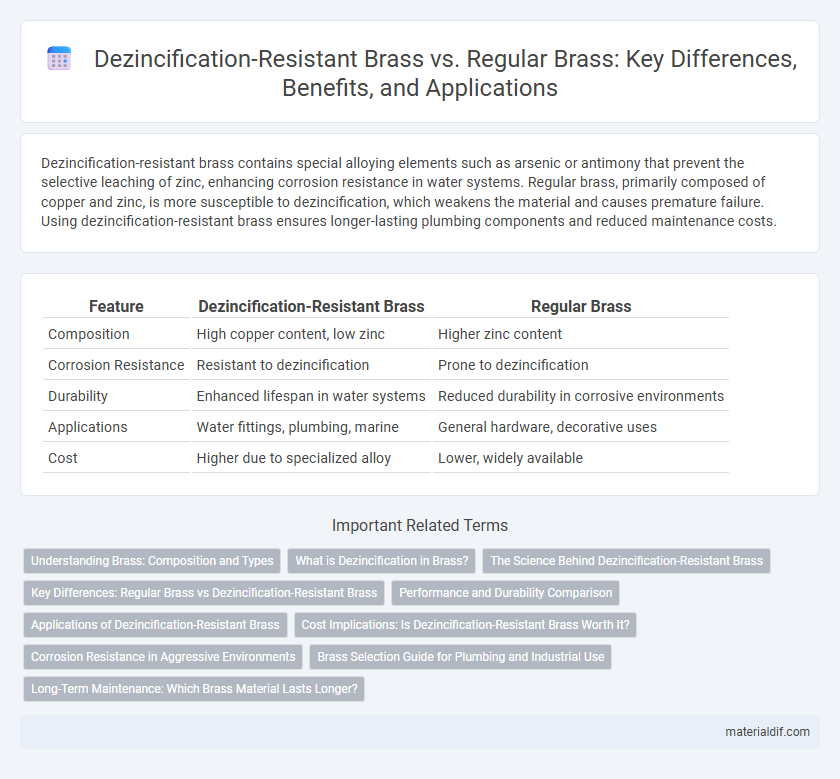
| Feature | Dezincification-Resistant Brass | Regular Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High copper content, low zinc | Higher zinc content |
| Corrosion Resistance | Resistant to dezincification | Prone to dezincification |
| Durability | Enhanced lifespan in water systems | Reduced durability in corrosive environments |
| Applications | Water fittings, plumbing, marine | General hardware, decorative uses |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized alloy | Lower, widely available |
Understanding Brass: Composition and Types
Dezincification-resistant brass contains added elements like arsenic, antimony, or phosphorus to inhibit zinc leaching, maintaining strength and corrosion resistance in plumbing applications. Regular brass primarily consists of copper and zinc, susceptible to dezincification which weakens the material in corrosive environments. Understanding the distinct compositions helps in selecting the appropriate brass type for durability and reliability in water systems.
What is Dezincification in Brass?
Dezincification in brass is a form of corrosion where zinc is selectively leached out from the alloy, weakening its structural integrity and causing porous, brittle surfaces. Dezincification-resistant brass features a carefully balanced composition with added elements like arsenic or tin to inhibit zinc loss and maintain durability. Regular brass, primarily composed of copper and zinc, is more prone to this degradation, especially in environments with water exposure or acidic conditions.
The Science Behind Dezincification-Resistant Brass
Dezincification-resistant brass contains a carefully balanced alloy composition, typically enriched with elements like arsenic or antimony, which inhibit the selective leaching of zinc during corrosion. This microstructural adjustment creates a more uniform and stable matrix that reduces the formation of porous, weakened areas common in regular brass exposed to water. The improved corrosion resistance enhances durability and longevity, especially in plumbing and marine applications where dezincification is prevalent.
Key Differences: Regular Brass vs Dezincification-Resistant Brass
Dezincification-resistant brass contains special alloying elements like arsenic or antimony that prevent the selective leaching of zinc, a common issue in regular brass exposed to corrosive environments. Regular brass, primarily composed of copper and zinc, is prone to dezincification, leading to weakened mechanical properties and compromised corrosion resistance. The enhanced durability of dezincification-resistant brass makes it ideal for plumbing, marine applications, and environments where exposure to water and corrosive agents is frequent.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Dezincification-resistant brass exhibits superior performance and durability compared to regular brass due to its enhanced corrosion resistance, particularly in environments with high water exposure or chlorides. This brass alloy maintains structural integrity longer, reducing the risk of dezincification, a common issue in regular brass that leads to weakened mechanical properties and pitting. Consequently, dezincification-resistant brass is preferred for plumbing fittings and marine applications where longevity and reliable performance are critical.
Applications of Dezincification-Resistant Brass
Dezincification-resistant brass is widely used in plumbing, marine hardware, and water fittings where corrosion resistance is critical. Its superior durability against dezincification ensures long-lasting performance in environments with prolonged exposure to water and moisture. This makes it ideal for components such as valves, faucets, and pump parts, outperforming regular brass in maintaining structural integrity and safety.
Cost Implications: Is Dezincification-Resistant Brass Worth It?
Dezincification-resistant brass typically costs 20-30% more than regular brass due to its enhanced copper and alloy composition designed to prevent zinc leaching. Although the initial investment is higher, the longer lifespan and reduced maintenance expenses often lead to lower total ownership costs in applications exposed to corrosive water environments. For industries prioritizing durability and reduced downtime, the cost premium of dezincification-resistant brass proves economically justified over time.
Corrosion Resistance in Aggressive Environments
Dezincification-resistant brass exhibits superior corrosion resistance in aggressive environments by minimizing the selective leaching of zinc, a common issue in regular brass that leads to structural weakening. This alloy's enhanced copper and special alloying elements improve its durability and maintain its mechanical integrity when exposed to seawater, acidic solutions, or industrial chemicals. Consequently, dezincification-resistant brass is preferred in plumbing and marine applications where prolonged exposure to corrosive agents is expected.
Brass Selection Guide for Plumbing and Industrial Use
Dezincification-resistant brass offers enhanced corrosion resistance by minimizing zinc leaching, making it ideal for plumbing systems exposed to aggressive water conditions. Regular brass, composed primarily of copper and zinc, is cost-effective but prone to dezincification, which can compromise valve and fitting integrity over time. Selecting dezincification-resistant brass ensures greater durability and longevity in industrial applications where water quality challenges are a concern.
Long-Term Maintenance: Which Brass Material Lasts Longer?
Dezincification-resistant brass outperforms regular brass in long-term maintenance due to its enhanced corrosion resistance, preventing zinc leaching that weakens the material over time. Regular brass is prone to dezincification, which leads to reduced mechanical strength and increased vulnerability to stress corrosion cracking. Consequently, dezincification-resistant brass ensures superior durability and longer service life, especially in plumbing and marine applications where exposure to corrosive environments is frequent.
Dezincification-Resistant Brass vs Regular Brass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com