Antimicrobial brass contains copper and other elements that inhibit the growth of bacteria and viruses on its surface, making it a superior choice for hygiene-sensitive environments compared to conventional brass. Conventional brass lacks these antimicrobial properties, allowing microbes to thrive longer on its surface, which can increase the risk of contamination. Using antimicrobial brass reduces the spread of infections, enhancing safety in healthcare, public spaces, and household fixtures.
Table of Comparison
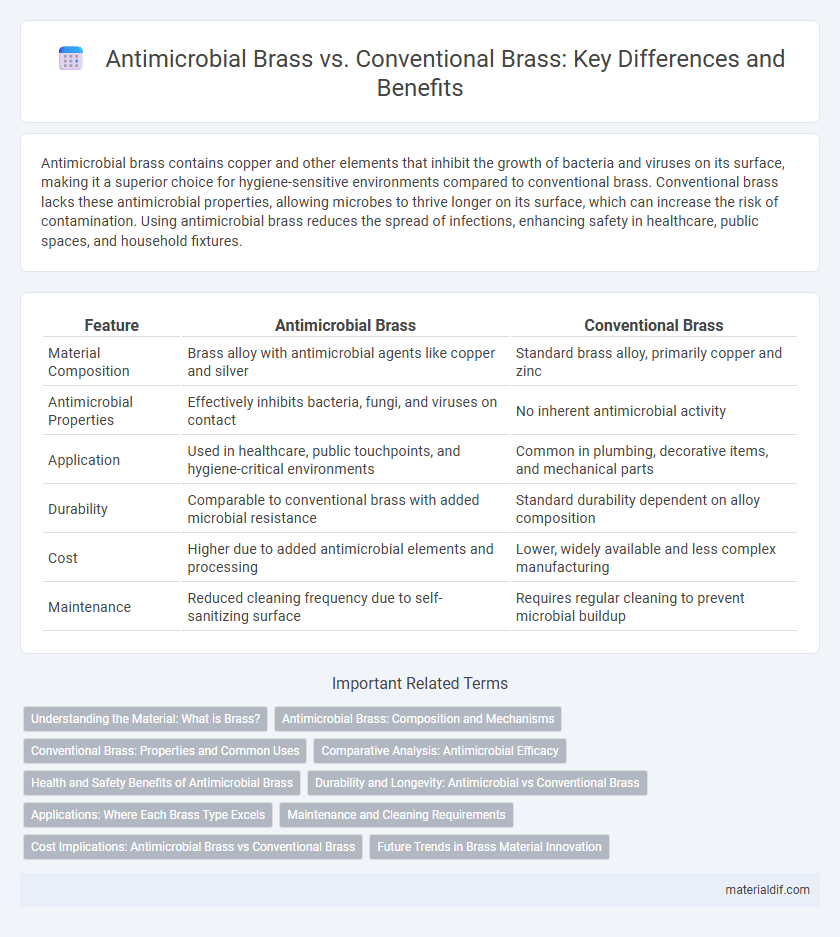
| Feature | Antimicrobial Brass | Conventional Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Brass alloy with antimicrobial agents like copper and silver | Standard brass alloy, primarily copper and zinc |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Effectively inhibits bacteria, fungi, and viruses on contact | No inherent antimicrobial activity |
| Application | Used in healthcare, public touchpoints, and hygiene-critical environments | Common in plumbing, decorative items, and mechanical parts |
| Durability | Comparable to conventional brass with added microbial resistance | Standard durability dependent on alloy composition |
| Cost | Higher due to added antimicrobial elements and processing | Lower, widely available and less complex manufacturing |
| Maintenance | Reduced cleaning frequency due to self-sanitizing surface | Requires regular cleaning to prevent microbial buildup |
Understanding the Material: What is Brass?
Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. Antimicrobial brass incorporates additional elements like silver or copper ions to inhibit bacterial growth on its surface, enhancing hygiene in high-touch environments. Conventional brass lacks these antimicrobial properties but remains widely used for its durability and aesthetic appeal in plumbing, musical instruments, and decorative applications.
Antimicrobial Brass: Composition and Mechanisms
Antimicrobial brass typically contains copper, zinc, and small amounts of elements like silver or nickel that enhance its antimicrobial properties. The copper ions in antimicrobial brass disrupt microbial cell membranes and generate reactive oxygen species, effectively inhibiting bacterial growth and biofilm formation. This composition and mechanism make antimicrobial brass a preferred material in healthcare and food contact surfaces due to its ability to reduce the risk of contamination.
Conventional Brass: Properties and Common Uses
Conventional brass, an alloy composed primarily of copper and zinc, offers excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for a wide range of industrial and decorative applications. Its inherent antimicrobial properties, although less enhanced than antimicrobial brass, still provide some resistance to bacterial growth, commonly utilized in plumbing fittings, musical instruments, and architectural hardware. The alloy's versatility and durability contribute to its extensive use in manufacturing valves, gears, locks, and electrical connectors.
Comparative Analysis: Antimicrobial Efficacy
Antimicrobial brass demonstrates significantly higher efficacy in reducing microbial load compared to conventional brass, effectively inhibiting the growth of bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Zinc and copper ion release in antimicrobial brass disrupts bacterial cell membranes, leading to rapid inactivation, whereas conventional brass lacks this enhanced ion leaching capacity. Studies indicate up to a 99.9% reduction in microbial populations on antimicrobial brass surfaces within hours, contrasting with persistent contamination found on traditional brass alloys.
Health and Safety Benefits of Antimicrobial Brass
Antimicrobial brass contains copper alloys with proven antimicrobial properties that reduce the survival of harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi on contact surfaces, significantly lowering the risk of infection transmission in healthcare and public settings. Conventional brass lacks these enhanced properties, allowing pathogens to persist longer on surfaces, increasing health hazards. Using antimicrobial brass in high-touch areas like door handles and fixtures promotes better hygiene, reduces microbial contamination, and enhances overall health and safety.
Durability and Longevity: Antimicrobial vs Conventional Brass
Antimicrobial brass exhibits enhanced durability and longevity due to its unique copper and zinc alloy composition combined with antimicrobial agents that inhibit microbial growth and reduce corrosion. Conventional brass, while durable, is more susceptible to tarnishing and microbial degradation, leading to accelerated wear over time. This increased resistance in antimicrobial brass translates to extended product lifespan and reduced maintenance costs in high-contact environments.
Applications: Where Each Brass Type Excels
Antimicrobial brass excels in healthcare and food processing applications, where its ability to reduce microbial contamination enhances hygiene and safety. Conventional brass is preferred in plumbing and decorative hardware due to its superior machinability and cost-effectiveness. Both types find use in electrical components, but antimicrobial brass offers added benefits in environments requiring stringent cleanliness standards.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Antimicrobial brass features a copper-rich alloy composition that naturally inhibits bacterial growth, reducing the need for frequent cleaning compared to conventional brass, which requires regular maintenance to prevent tarnishing and bacterial buildup. Conventional brass surfaces often demand chemical cleaners and polishing agents to maintain their appearance and hygiene, increasing labor and material costs over time. The lower maintenance requirements of antimicrobial brass make it an ideal choice for high-touch areas in healthcare and public environments, promoting sustained cleanliness with minimal effort.
Cost Implications: Antimicrobial Brass vs Conventional Brass
Antimicrobial brass typically incurs a higher upfront cost compared to conventional brass due to its specialized alloy composition and production process. Despite the increased initial expense, antimicrobial brass can reduce long-term maintenance and healthcare costs by minimizing bacterial growth and associated contamination risks. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that antimicrobial brass may offer greater value in environments demanding enhanced hygiene standards.
Future Trends in Brass Material Innovation
Antimicrobial brass is gaining momentum due to its inherent ability to inhibit microbial growth, making it ideal for healthcare and high-touch environments. Future trends in brass material innovation emphasize enhancing copper content and integrating nanosilver particles to boost antimicrobial efficacy without compromising durability. Advancements in surface treatments and alloy compositions are expected to drive broader adoption of antimicrobial brass in public infrastructure and consumer goods.
Antimicrobial Brass vs Conventional Brass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com