Virgin asphalt is produced directly from crude oil, offering consistent quality and durability for high-performance pavement needs. Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) incorporates reclaimed materials from old pavements, reducing costs and environmental impact while maintaining adequate strength for many applications. Selecting between virgin asphalt and RAP depends on project requirements, budget constraints, and sustainability goals.
Table of Comparison
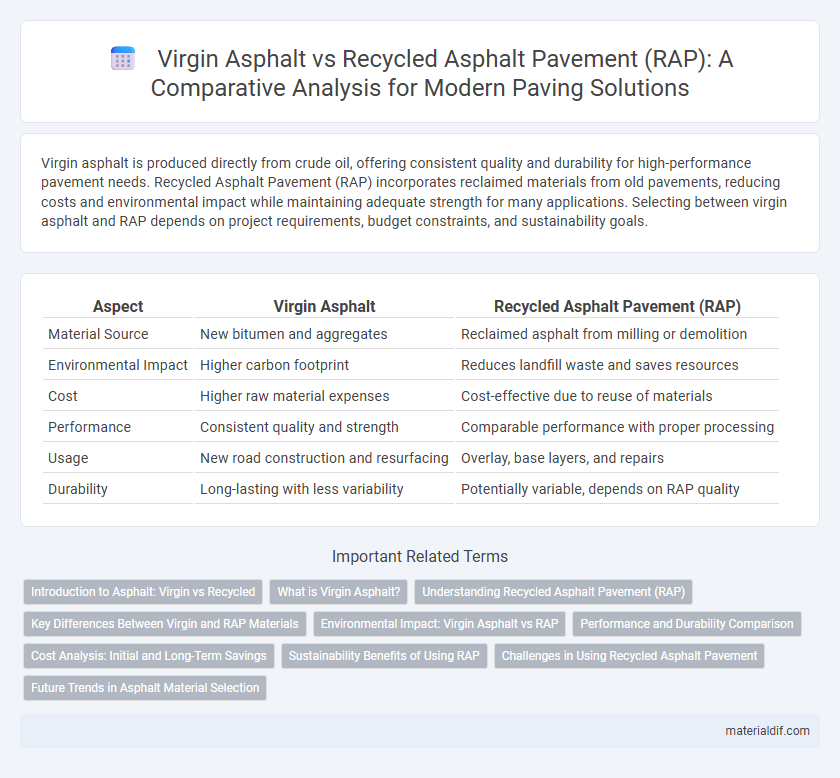
| Aspect | Virgin Asphalt | Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | New bitumen and aggregates | Reclaimed asphalt from milling or demolition |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Reduces landfill waste and saves resources |
| Cost | Higher raw material expenses | Cost-effective due to reuse of materials |
| Performance | Consistent quality and strength | Comparable performance with proper processing |
| Usage | New road construction and resurfacing | Overlay, base layers, and repairs |
| Durability | Long-lasting with less variability | Potentially variable, depends on RAP quality |
Introduction to Asphalt: Virgin vs Recycled
Virgin asphalt consists of freshly refined bitumen combined with new aggregates, delivering high durability and consistent quality in pavement construction. Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) incorporates crushed, reclaimed asphalt materials blended with virgin binder, offering cost-effective and environmentally sustainable alternatives without compromising structural integrity. The selection between virgin asphalt and RAP depends on project specifications, performance requirements, and sustainability goals within infrastructure development.
What is Virgin Asphalt?
Virgin asphalt is a petroleum-based binder used in new pavement construction, characterized by its high purity and consistent performance properties. It is derived from refined bitumen, providing optimal adhesion, flexibility, and durability in asphalt mixtures. Unlike Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP), virgin asphalt contains no aged binder, ensuring superior quality for critical infrastructure projects.
Understanding Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP)
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) consists of reclaimed asphalt materials removed during road milling or demolition and reused in new pavement production, significantly reducing the need for virgin asphalt. RAP contains valuable aggregates and aged bitumen, which, when properly processed and blended, maintain pavement performance while lowering environmental impact and costs. Incorporating RAP into asphalt mixtures supports sustainable construction practices by conserving natural resources and minimizing waste in infrastructure projects.
Key Differences Between Virgin and RAP Materials
Virgin asphalt consists of fresh, unprocessed bitumen and aggregate, offering consistent quality and optimal performance in paving projects. Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) incorporates reclaimed materials from demolished asphalt, reducing costs and environmental impact while potentially varying in binder content and aggregate quality. Key differences lie in material composition, environmental footprint, and performance characteristics, influencing selection based on project specifications and sustainability goals.
Environmental Impact: Virgin Asphalt vs RAP
Virgin asphalt production demands significant energy consumption and emits higher levels of greenhouse gases compared to recycled asphalt pavement (RAP), which utilizes reclaimed materials and reduces landfill waste. Using RAP decreases the need for virgin aggregate extraction, thereby conserving natural resources and lowering environmental degradation. Incorporating RAP in pavement mixtures substantially minimizes carbon footprint and supports sustainable infrastructure development.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Virgin asphalt typically offers higher initial performance with superior structural integrity and longer lifespan due to its uniform binder properties and consistency. Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) can achieve comparable durability when properly processed and blended, but may exhibit increased susceptibility to cracking and rutting under heavy traffic conditions. Optimal RAP content and advanced mix designs are critical to enhancing performance and extending pavement service life while reducing environmental impact.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Savings
Virgin asphalt requires higher initial investment due to the cost of raw materials and production, whereas Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) significantly reduces upfront expenses by reusing existing materials. Long-term savings with RAP extend beyond initial costs, as it lowers maintenance expenses and reduces the need for frequent resurfacing by providing durable pavement structure. The cost efficiency of RAP contributes to sustainable project budgets, balancing environmental benefits with economic advantages over the pavement lifecycle.
Sustainability Benefits of Using RAP
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) significantly reduces the demand for virgin aggregates and bitumen, conserving natural resources and lowering environmental impact. Incorporating RAP in asphalt mixes decreases greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing the need for new material extraction and processing. This sustainable practice supports circular economy principles, reduces landfill waste, and promotes energy efficiency in road construction projects.
Challenges in Using Recycled Asphalt Pavement
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) poses challenges such as variability in material quality, which can lead to inconsistent pavement performance compared to virgin asphalt. The presence of aged binder in RAP can affect mixture workability and durability, requiring precise proportioning and adjustment of virgin binder content. Additionally, the incorporation of RAP may demand advanced mixing technologies and quality control measures to ensure proper compaction and longevity of the pavement.
Future Trends in Asphalt Material Selection
Virgin asphalt offers consistent quality and performance, but increasing environmental regulations and sustainability goals drive the rising use of Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) in modern road construction. Emerging technologies enhance RAP processing, improving binder compatibility and extending pavement lifespan while reducing carbon footprints. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards higher RAP content blends combined with bio-based additives for greener, cost-effective asphalt solutions.
Virgin Asphalt vs Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com