Glassphalt incorporates recycled glass into the asphalt mix, enhancing surface reflectivity and skid resistance while promoting sustainability. Rubberized asphalt integrates crumb rubber from recycled tires, improving flexibility, crack resistance, and noise reduction for longer pavement life. Comparing both, glassphalt prioritizes eco-friendly aesthetics and traction, whereas rubberized asphalt excels in durability and performance under traffic stress.
Table of Comparison
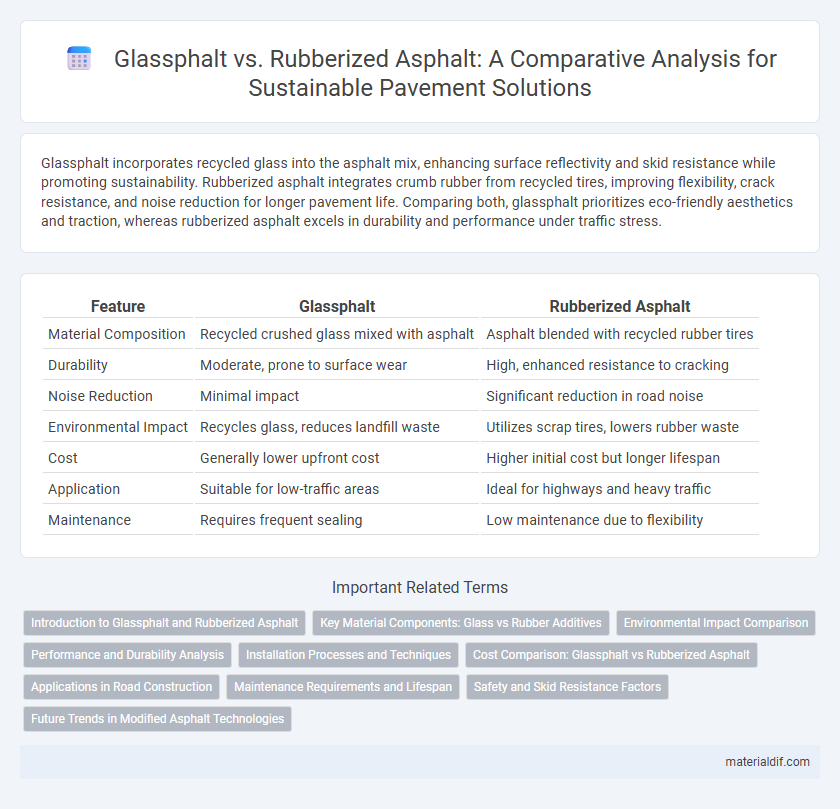
| Feature | Glassphalt | Rubberized Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled crushed glass mixed with asphalt | Asphalt blended with recycled rubber tires |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to surface wear | High, enhanced resistance to cracking |
| Noise Reduction | Minimal impact | Significant reduction in road noise |
| Environmental Impact | Recycles glass, reduces landfill waste | Utilizes scrap tires, lowers rubber waste |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
| Application | Suitable for low-traffic areas | Ideal for highways and heavy traffic |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent sealing | Low maintenance due to flexibility |
Introduction to Glassphalt and Rubberized Asphalt
Glassphalt is a sustainable pavement material that incorporates recycled glass into asphalt mixtures, improving skid resistance and reducing landfill waste. Rubberized asphalt blends crumb rubber from recycled tires into the asphalt binder, enhancing flexibility, durability, and noise reduction. Both materials contribute to environmentally friendly road construction by repurposing waste products while offering distinct performance benefits.
Key Material Components: Glass vs Rubber Additives
Glassphalt incorporates finely crushed recycled glass as its primary additive, enhancing skid resistance and promoting sustainable material reuse. Rubberized asphalt utilizes ground tire rubber from scrap tires, which improves flexibility, reduces cracking, and enhances durability in road surfaces. Both materials leverage recycled components but differ fundamentally in their additive types, affecting performance characteristics and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Glassphalt incorporates recycled glass, reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources, but may release contaminants if not properly processed. Rubberized asphalt utilizes recycled tire rubber, enhancing pavement durability and reducing microplastic pollution, while also diverting significant tire waste from landfills. Both materials promote sustainability, but rubberized asphalt typically offers greater environmental benefits through improved longevity and waste reduction.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Glassphalt incorporates recycled glass particles that enhance skid resistance but may cause increased brittleness, affecting pavement durability under heavy traffic loads. Rubberized asphalt, blending recycled rubber from tires, offers superior flexibility and crack resistance, significantly improving pavement lifespan and performance in diverse temperature conditions. Comparative studies indicate rubberized asphalt outperforms glassphalt in durability metrics, particularly for mitigating fatigue cracking and thermal stresses.
Installation Processes and Techniques
Glassphalt installation requires careful handling of crushed recycled glass mixed with asphalt binder, using standard paving equipment adapted to prevent glass particle loss and ensure uniform distribution. Rubberized asphalt involves blending crumb rubber from recycled tires into the asphalt mixture at specific elevated temperatures, enhancing flexibility and durability; specialized mixers and precise temperature control are essential to maintain rubber integrity during the paving process. Both techniques demand modifications to traditional paving procedures, with Glassphalt emphasizing particle stability and Rubberized Asphalt focusing on temperature management for optimal performance.
Cost Comparison: Glassphalt vs Rubberized Asphalt
Glassphalt typically incurs lower initial installation costs compared to rubberized asphalt due to the use of recycled glass aggregates, which are more affordable than specialized rubber materials. Rubberized asphalt, while more expensive upfront, offers enhanced durability and longer lifespan, potentially reducing maintenance expenses over time. Cost analysis should consider both initial investment and life-cycle savings, factoring in local material availability and project scale.
Applications in Road Construction
Glassphalt incorporates recycled glass aggregates, providing enhanced skid resistance and improved aesthetics, making it suitable for urban roads and pedestrian pathways. Rubberized asphalt uses crumb rubber from scrap tires, offering superior noise reduction and increased durability, ideal for highways and heavy-traffic roads. Both materials contribute to sustainable road construction, but rubberized asphalt excels in high-stress applications due to its elasticity and resilience.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Glassphalt typically requires more frequent maintenance due to its susceptibility to surface wear and cracking, which can reduce its lifespan to around 10-15 years. Rubberized asphalt provides enhanced durability and flexibility, resulting in lower maintenance needs and an extended lifespan of up to 20-25 years. The elastomeric properties of rubberized asphalt improve resistance to thermal cracking and deformation, making it a more sustainable choice for long-term pavement performance.
Safety and Skid Resistance Factors
Glassphalt incorporates recycled glass, enhancing surface texture and improving skid resistance, which leads to greater safety in wet conditions by reducing hydroplaning risks. Rubberized asphalt integrates crumb rubber from tires, offering superior flexibility and elasticity that improves tire grip and minimizes road noise, contributing to safer driving experiences. Studies indicate rubberized asphalt generally outperforms glassphalt in maintaining consistent skid resistance over time, especially under heavy traffic and extreme weather conditions.
Future Trends in Modified Asphalt Technologies
Future trends in modified asphalt technologies emphasize increased sustainability and durability, with Glassphalt incorporating recycled glass to enhance skid resistance and reduce environmental impact. Rubberized asphalt leverages recycled tires to improve flexibility and crack resistance, extending roadway lifespan under heavy traffic conditions. Innovations combining glass and rubber additives aim to optimize performance, offering eco-friendly solutions aligned with evolving infrastructure demands.
Glassphalt vs Rubberized Asphalt Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com