Fine-graded asphalt mix features a higher proportion of smaller aggregates, providing a smoother surface with increased durability and resistance to water infiltration. Coarse-graded mix contains larger aggregates, offering superior stability and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy traffic areas. Choosing between fine-graded and coarse-graded mixes depends on the specific performance requirements and environmental conditions of the pavement.
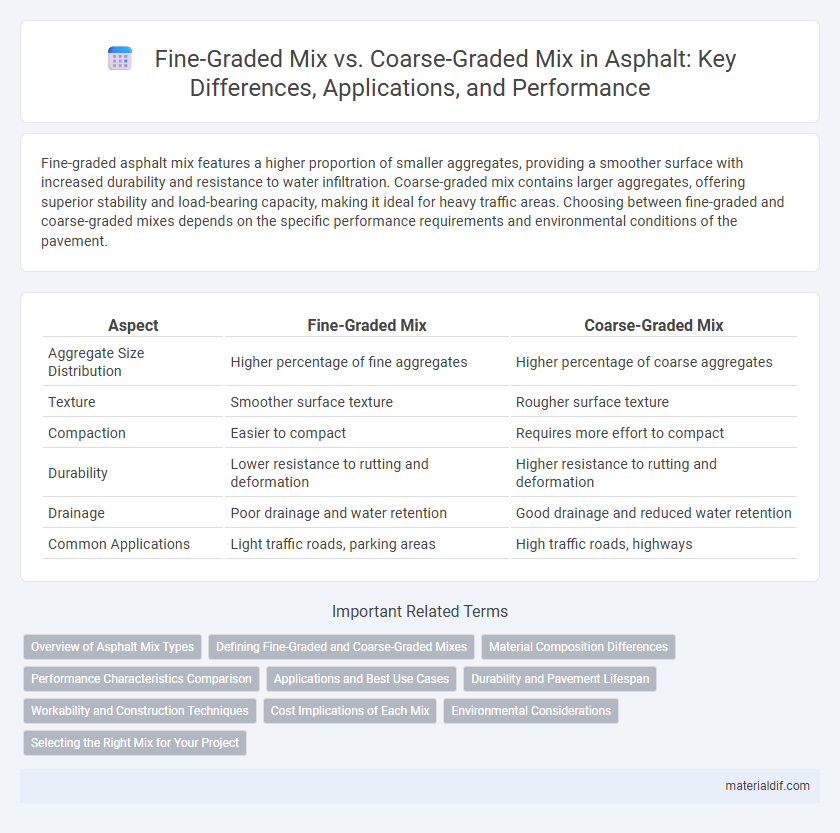
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fine-Graded Mix | Coarse-Graded Mix |
|---|---|---|
| Aggregate Size Distribution | Higher percentage of fine aggregates | Higher percentage of coarse aggregates |
| Texture | Smoother surface texture | Rougher surface texture |
| Compaction | Easier to compact | Requires more effort to compact |
| Durability | Lower resistance to rutting and deformation | Higher resistance to rutting and deformation |
| Drainage | Poor drainage and water retention | Good drainage and reduced water retention |
| Common Applications | Light traffic roads, parking areas | High traffic roads, highways |
Overview of Asphalt Mix Types
Fine-graded asphalt mixes consist of smaller aggregate particles, creating a dense and smooth surface ideal for lighter traffic and improved ride quality. Coarse-graded mixes contain larger aggregates, providing enhanced structural strength and durability for heavy traffic and high-stress environments. Selecting the appropriate asphalt mix type depends on traffic load, climate conditions, and pavement performance requirements.
Defining Fine-Graded and Coarse-Graded Mixes
Fine-graded asphalt mixes consist predominantly of smaller aggregates, typically less than 4.75 mm, which enhance the workability and provide a smooth surface finish ideal for urban pavements and overlays. Coarse-graded mixes feature larger aggregates ranging from 9.5 mm to 25 mm, offering improved structural integrity and skid resistance, making them suitable for high-traffic highways and heavy load conditions. The aggregate gradation directly influences the mix's density, void content, and overall performance, with fine-graded mixes optimizing surface texture and coarse-graded mixes prioritizing load-bearing capacity.
Material Composition Differences
Fine-graded asphalt mix contains a higher proportion of smaller aggregates and fillers, enhancing workability and producing a denser pavement surface ideal for smooth finishes and reduced permeability. Coarse-graded mix incorporates larger aggregates with a wider range of particle sizes, improving stability and load distribution while allowing better drainage in road surfaces. The material composition directly affects the mechanical properties and performance characteristics of the pavement under various traffic and environmental conditions.
Performance Characteristics Comparison
Fine-graded asphalt mixes exhibit superior compaction and enhanced resistance to moisture damage due to their dense particle distribution, which improves pavement durability in low to moderate traffic conditions. Coarse-graded mixes provide greater structural strength and skid resistance, making them suitable for heavy-load applications and high-traffic highways. Performance comparison indicates that fine-graded mixes optimize smoothness and fatigue resistance, while coarse-graded mixes excel in rutting resistance and load-bearing capacity.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Fine-graded asphalt mixes, characterized by a higher proportion of smaller aggregates, provide superior smoothness and durability, making them ideal for high-traffic urban roads and airport runways where surface quality is critical. Coarse-graded mixes, containing larger aggregate particles, excel in heavy-duty applications such as highways and industrial pavements due to enhanced load-bearing capacity and resistance to rutting. Selecting between fine-graded and coarse-graded mixes depends on factors like traffic volume, load conditions, and desired pavement longevity, ensuring optimal performance for specific infrastructure needs.
Durability and Pavement Lifespan
Fine-graded asphalt mixes, characterized by a higher proportion of smaller aggregates, tend to offer enhanced durability due to improved compaction and reduced air voids, which minimizes moisture infiltration and cracking. Coarse-graded mixes, with larger aggregates and more interconnected voids, provide better permeability and resistance to rutting but may be more susceptible to oxidation and moisture damage over time. Pavements constructed with fine-graded mixes typically exhibit longer lifespans in low-traffic conditions, whereas coarse-graded mixes are preferred for heavy-load applications where structural strength is critical.
Workability and Construction Techniques
Fine-graded asphalt mixes exhibit superior workability due to their well-distributed aggregate sizes, allowing for easier compaction and better adaptability to complex pavement shapes. Coarse-graded mixes, with larger aggregate sizes, provide improved stability but require advanced compaction equipment and careful temperature control during construction to achieve optimal density. Construction techniques for fine-graded mixes emphasize uniform layer thickness and gradual compaction, while coarse-graded mixes demand aggressive rolling patterns and precise aggregate placement for enhanced load-bearing performance.
Cost Implications of Each Mix
Fine-graded asphalt mixes typically incur higher costs due to increased binder content and enhanced production complexity, leading to improved durability and smoother surface texture. Coarse-graded mixes use larger aggregates, reducing binder demand and overall material expenses, but may result in less uniform compaction and increased maintenance costs over time. Evaluating initial production costs against long-term performance and maintenance needs is crucial in determining the most cost-effective choice for pavement projects.
Environmental Considerations
Fine-graded asphalt mixes reduce air voids, enhancing durability and reducing the need for frequent repairs, which lowers overall environmental impact by conserving raw materials. Coarse-graded mixes improve permeability, helping to manage stormwater runoff and reduce urban heat island effects. Selecting the appropriate gradation influences long-term sustainability goals by balancing material efficiency with environmental performance.
Selecting the Right Mix for Your Project
Fine-graded asphalt mixes provide enhanced compaction and better resistance to water infiltration, making them ideal for surfaces requiring smooth finishes and durability against weathering. Coarse-graded mixes offer superior load distribution and high resistance to deformation, suitable for heavy traffic roads and base layers. Selecting the right mix depends on project-specific factors such as traffic load, climate conditions, and structural requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Fine-Graded Mix vs Coarse-Graded Mix Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com