Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) offers a sustainable alternative to Virgin Asphalt by reusing reclaimed materials, reducing the need for new aggregates and lowering environmental impact. RAP provides comparable durability and performance when properly processed and mixed, making it a cost-effective choice for road construction and maintenance. Utilizing RAP conserves natural resources and decreases greenhouse gas emissions associated with asphalt production.
Table of Comparison
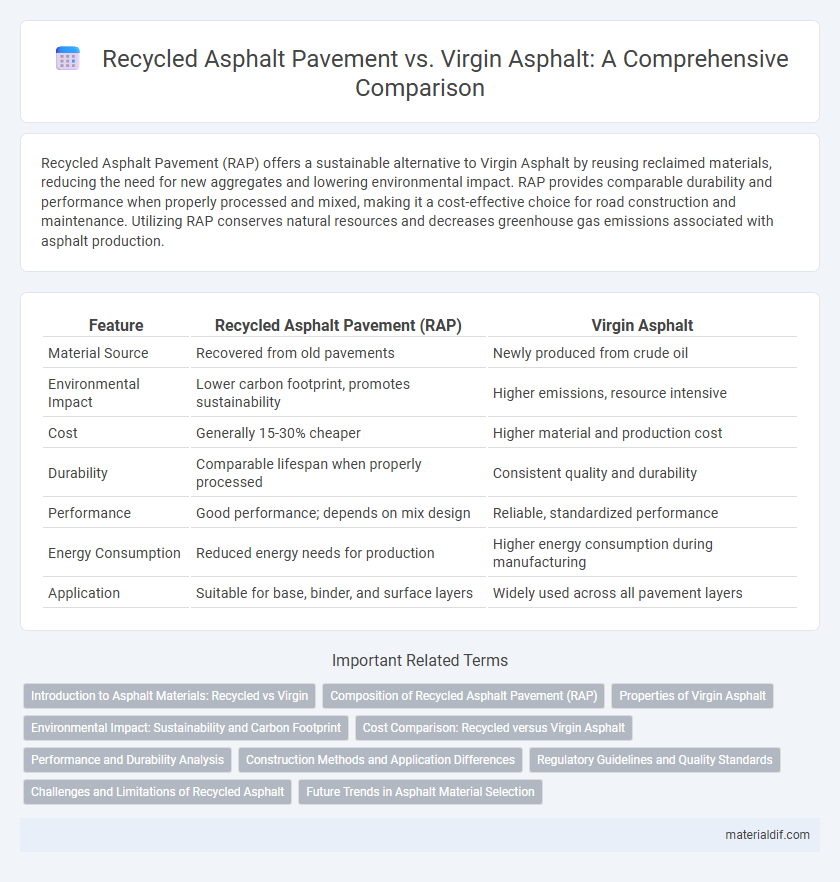
| Feature | Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) | Virgin Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Recovered from old pavements | Newly produced from crude oil |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, promotes sustainability | Higher emissions, resource intensive |
| Cost | Generally 15-30% cheaper | Higher material and production cost |
| Durability | Comparable lifespan when properly processed | Consistent quality and durability |
| Performance | Good performance; depends on mix design | Reliable, standardized performance |
| Energy Consumption | Reduced energy needs for production | Higher energy consumption during manufacturing |
| Application | Suitable for base, binder, and surface layers | Widely used across all pavement layers |
Introduction to Asphalt Materials: Recycled vs Virgin
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) consists of reclaimed asphalt removed from old road surfaces, processed, and reused, offering sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to Virgin Asphalt, which is produced from new petroleum-based bitumen and aggregates. RAP conserves natural resources and reduces landfill waste while maintaining comparable performance in pavement durability and stability. The selection between recycled and virgin asphalt materials depends on project specifications, environmental goals, and budget considerations.
Composition of Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP)
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) primarily consists of reclaimed asphalt binder, aggregates, and residual asphalt cement from previously used pavement materials. The composition typically includes 20-25% aged binder adhered to 75-80% high-quality aggregates, which contribute to the structural integrity and durability of new pavement mixes. Incorporating RAP reduces the demand for virgin aggregates and asphalt binder, promoting sustainability and cost efficiency in asphalt pavement production.
Properties of Virgin Asphalt
Virgin asphalt exhibits superior binding properties and consistent consistency, providing enhanced durability and flexibility in pavement applications compared to recycled asphalt pavement. Its chemical composition remains stable, ensuring optimal resistance to temperature fluctuations and environmental stressors. The high-quality aggregates in virgin asphalt contribute to improved load-bearing capacity and longer lifespan of road surfaces.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Carbon Footprint
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing the need for new raw materials and decreasing landfill waste, contributing to sustainable road construction practices. Virgin asphalt production involves extensive energy consumption and higher carbon emissions due to the extraction and processing of raw aggregates and bitumen. Incorporating RAP lowers the carbon footprint of paving projects by up to 30%, promoting resource conservation and reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with asphalt manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Recycled versus Virgin Asphalt
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) significantly reduces costs by lowering raw material expenses since it reuses existing asphalt materials instead of relying solely on new aggregates and bitumen found in virgin asphalt. Studies show that projects incorporating RAP can experience savings of 20-40% in material costs compared to those using 100% virgin asphalt. Maintenance and life-cycle costs also tend to be lower for RAP mixtures, offering an economically advantageous option for sustainable pavement construction.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) often demonstrates comparable performance to virgin asphalt in terms of load-bearing capacity and resistance to rutting, making it a viable sustainable alternative for road construction. Durability analysis shows that RAP mixtures maintain structural integrity under repeated traffic loads, although their aging properties can vary based on the percentage of recycled content and blending methods. Optimizing RAP content and mixture design is crucial to achieving performance parity with virgin asphalt while benefiting from cost savings and environmental advantages.
Construction Methods and Application Differences
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) involves milling and reprocessing existing asphalt materials, reducing the need for new aggregates and bitumen, which lowers environmental impact and material costs. Virgin Asphalt uses freshly mined aggregates and refined bitumen, typically resulting in higher initial performance but increased production energy and resource consumption. Construction methods differ as RAP requires specialized equipment for crushing and mixing reclaimed material, while Virgin Asphalt follows conventional mixing and laying techniques, influencing project timelines and sustainability outcomes.
Regulatory Guidelines and Quality Standards
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) must comply with regulatory guidelines set by agencies like the EPA and state DOTs, ensuring it meets environmental and safety standards to minimize contaminants and maintain pavement durability. Virgin asphalt adheres to stringent quality standards outlined by organizations such as ASTM and AASHTO, which specify performance criteria including binder grade and aggregate properties for optimal road longevity. Both materials require rigorous testing protocols to verify compliance with specifications that affect leachate control, compaction, and resistance to rutting and cracking under traffic loads.
Challenges and Limitations of Recycled Asphalt
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) presents challenges such as inconsistent material properties and potential contamination that affect pavement performance and durability. The variability in binder quality and aggregate gradation requires careful quality control and mix design adjustments. Environmental factors and aging of recycled binder can limit the reuse rate compared to virgin asphalt, necessitating supplementary virgin materials for optimal road construction.
Future Trends in Asphalt Material Selection
Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) is gaining prominence due to its environmental benefits and cost-efficiency, driving future trends toward sustainable road construction practices. Innovations in processing RAP improve its performance, making it increasingly comparable to Virgin Asphalt in durability and flexibility. Emerging technologies such as warm-mix asphalt and bio-based binders combined with recycled materials are shaping the future landscape of asphalt material selection.
Recycled Asphalt Pavement vs Virgin Asphalt Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com