Sand asphalt offers a smoother, more durable surface ideal for urban roads and parking lots due to its fine aggregate composition, which enhances compaction and reduces water infiltration. Gravel asphalt incorporates coarser aggregates that provide better load distribution and improved skid resistance, making it suitable for heavy traffic and rural applications. Choosing between sand and gravel asphalt depends on the specific demands of the pavement environment and desired performance characteristics.
Table of Comparison
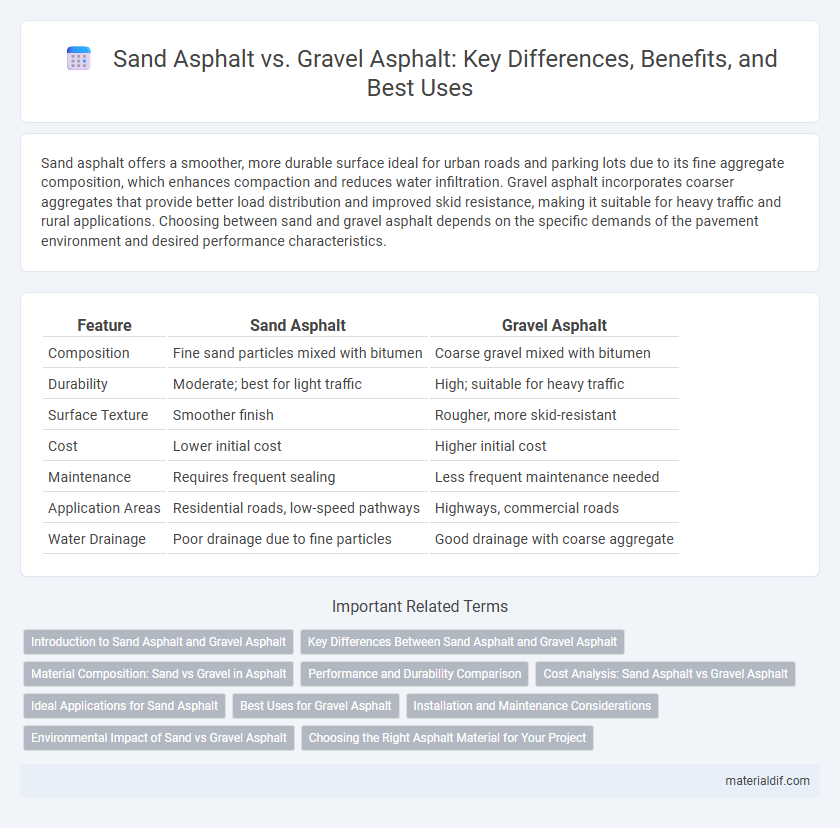
| Feature | Sand Asphalt | Gravel Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine sand particles mixed with bitumen | Coarse gravel mixed with bitumen |
| Durability | Moderate; best for light traffic | High; suitable for heavy traffic |
| Surface Texture | Smoother finish | Rougher, more skid-resistant |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent sealing | Less frequent maintenance needed |
| Application Areas | Residential roads, low-speed pathways | Highways, commercial roads |
| Water Drainage | Poor drainage due to fine particles | Good drainage with coarse aggregate |
Introduction to Sand Asphalt and Gravel Asphalt
Sand asphalt consists of fine sand particles mixed with bitumen, creating a smooth, dense surface ideal for low-traffic areas and decorative purposes. Gravel asphalt incorporates coarser aggregate like crushed stone or gravel, providing enhanced strength and durability for high-traffic roads and heavy load-bearing applications. Choosing between sand asphalt and gravel asphalt depends on the required surface texture, load capacity, and environmental conditions.
Key Differences Between Sand Asphalt and Gravel Asphalt
Sand asphalt features finer aggregates, resulting in a smoother surface ideal for pedestrian pathways and residential driveways, while gravel asphalt incorporates larger, coarser aggregates providing greater durability and strength suited for heavy traffic roads and highways. The binder content in sand asphalt is typically higher to ensure strong adhesion of the small particles, contrasting with gravel asphalt which requires less binder due to the natural interlocking of larger stones. Drainage performance also differs, as gravel asphalt allows better water runoff, reducing the risk of surface water retention compared to the denser, less permeable sand asphalt.
Material Composition: Sand vs Gravel in Asphalt
Sand asphalt features fine aggregates that create a smoother, more compact surface ideal for pedestrian paths and light traffic areas. Gravel asphalt incorporates larger, coarse aggregates, providing enhanced strength and durability suited for heavy traffic and road construction. The choice between sand and gravel in asphalt influences the pavement's texture, load-bearing capacity, and overall longevity.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Sand asphalt offers superior compaction and smoother surface texture, enhancing ride quality and reducing noise compared to gravel asphalt. Gravel asphalt provides higher structural strength and better load distribution due to larger aggregate size, making it more suitable for heavy traffic conditions. Durability-wise, gravel asphalt resists rutting and cracking under heavy loads, while sand asphalt excels in flexibility and minor crack resistance in lighter traffic areas.
Cost Analysis: Sand Asphalt vs Gravel Asphalt
Sand asphalt typically incurs higher material costs due to the fine aggregate quality and specialized mixing process, but it offers smoother finishes that reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Gravel asphalt is generally more cost-effective upfront because of the abundant availability and lower price of coarse aggregates, though it may require more frequent repairs in high-traffic areas. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, sand asphalt suits projects prioritizing durability and aesthetics, whereas gravel asphalt is preferable for budget-conscious infrastructure with moderate performance demands.
Ideal Applications for Sand Asphalt
Sand asphalt is best suited for applications requiring a smooth, dense surface with high resistance to water penetration, making it ideal for urban roads, parking lots, and airport runways. Its fine aggregate composition provides excellent compaction and durability under moderate traffic loads, enhancing surface stability and reducing maintenance costs. Sand asphalt performs well in environments where noise reduction and skid resistance are important factors.
Best Uses for Gravel Asphalt
Gravel asphalt is best suited for heavy-load surfaces such as highways, industrial roads, and airport runways due to its superior durability and load-bearing capacity. Its coarse aggregate structure provides enhanced drainage and increased resistance to deformation under traffic stress. This makes gravel asphalt ideal for environments requiring long-lasting, stable pavements with excellent skid resistance.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Sand asphalt offers easier installation due to its fine aggregate composition, allowing for a smoother surface and quicker compaction compared to gravel asphalt, which requires more precise placement of coarse aggregates. Maintenance of sand asphalt typically involves more frequent sealing to prevent surface wear, whereas gravel asphalt benefits from its robust aggregate structure, making it more resistant to rutting and deformation under heavy traffic. Choosing between the two depends on balancing installation complexity with long-term maintenance needs and expected traffic loads.
Environmental Impact of Sand vs Gravel Asphalt
Sand asphalt generally exhibits a lower environmental impact due to its finer aggregate that requires less energy for extraction and transportation compared to gravel asphalt. Gravel asphalt, composed of larger, coarser aggregates, often results in higher carbon emissions during mining and processing stages. Both materials influence stormwater runoff and heat absorption differently, with gravel asphalt typically offering better permeability but potentially greater ecological disturbance at extraction sites.
Choosing the Right Asphalt Material for Your Project
Choosing the right asphalt material depends on project requirements, where sand asphalt offers better smoothness and compaction for residential driveways, while gravel asphalt provides enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity suited for heavy traffic roads. Sand asphalt's fine aggregate creates a denser surface ideal for aesthetics and light use, whereas gravel asphalt's coarse aggregate improves resistance to cracking and wear in commercial or industrial applications. Evaluating factors like traffic volume, environmental conditions, and budget ensures optimal performance and longevity for your asphalt installation.
Sand Asphalt vs Gravel Asphalt Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com