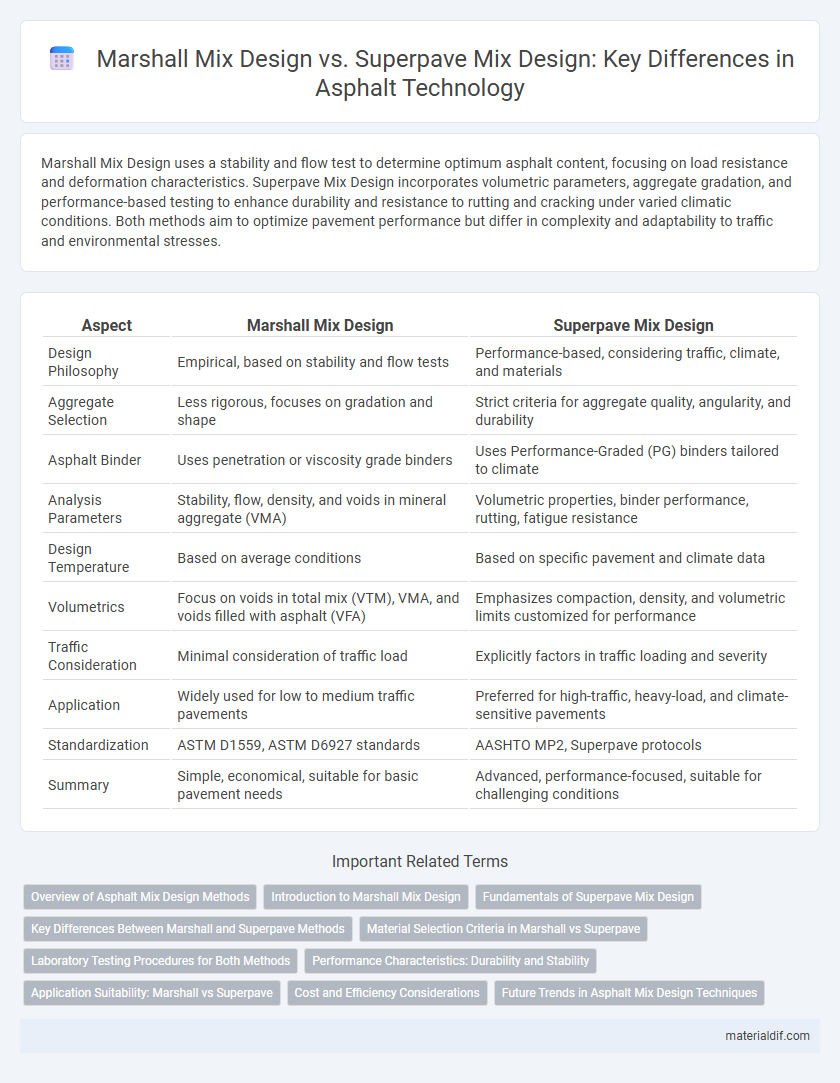
Marshall Mix Design uses a stability and flow test to determine optimum asphalt content, focusing on load resistance and deformation characteristics. Superpave Mix Design incorporates volumetric parameters, aggregate gradation, and performance-based testing to enhance durability and resistance to rutting and cracking under varied climatic conditions. Both methods aim to optimize pavement performance but differ in complexity and adaptability to traffic and environmental stresses.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Marshall Mix Design | Superpave Mix Design |
|---|---|---|
| Design Philosophy | Empirical, based on stability and flow tests | Performance-based, considering traffic, climate, and materials |
| Aggregate Selection | Less rigorous, focuses on gradation and shape | Strict criteria for aggregate quality, angularity, and durability |
| Asphalt Binder | Uses penetration or viscosity grade binders | Uses Performance-Graded (PG) binders tailored to climate |
| Analysis Parameters | Stability, flow, density, and voids in mineral aggregate (VMA) | Volumetric properties, binder performance, rutting, fatigue resistance |
| Design Temperature | Based on average conditions | Based on specific pavement and climate data |
| Volumetrics | Focus on voids in total mix (VTM), VMA, and voids filled with asphalt (VFA) | Emphasizes compaction, density, and volumetric limits customized for performance |
| Traffic Consideration | Minimal consideration of traffic load | Explicitly factors in traffic loading and severity |
| Application | Widely used for low to medium traffic pavements | Preferred for high-traffic, heavy-load, and climate-sensitive pavements |
| Standardization | ASTM D1559, ASTM D6927 standards | AASHTO MP2, Superpave protocols |
| Summary | Simple, economical, suitable for basic pavement needs | Advanced, performance-focused, suitable for challenging conditions |
Overview of Asphalt Mix Design Methods
Marshall Mix Design utilizes a stability and flow test to evaluate asphalt mixtures, focusing on achieving optimal density and durability through empirical methods. Superpave Mix Design incorporates performance-based criteria, including volumetric analysis and binder selection tailored to specific climate and traffic conditions. Both methods aim to enhance pavement longevity but differ in their approach to balancing mechanical properties and environmental adaptability.
Introduction to Marshall Mix Design
Marshall Mix Design is a widely used method for designing asphalt concrete mixes by determining the optimum binder content through stability and flow tests. It evaluates the mix's resistance to deformation and flow under load, ensuring adequate strength and flexibility for road pavement applications. This empirical approach emphasizes simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and practical field application, making it popular in various regions for pavement performance evaluation.
Fundamentals of Superpave Mix Design
Superpave Mix Design is grounded in the analysis of aggregate properties, asphalt binder performance, and traffic loading conditions to optimize pavement durability. It employs the Superpave Gyratory Compactor to simulate field compaction and achieves target air voids for enhanced rutting and fatigue resistance. This method incorporates climate-specific binder selection and volumetric criteria to ensure optimized performance across varying environmental and loading scenarios.
Key Differences Between Marshall and Superpave Methods
Marshall Mix Design involves compacting asphalt samples with a standardized hammer to evaluate stability and flow, focusing primarily on aggregate gradation and asphalt content. Superpave Mix Design uses advanced volumetric and performance criteria, incorporating climate and traffic data to optimize pavement durability and resistance to rutting and cracking. Key differences include Superpave's emphasis on performance grading and aggregate selectivity versus Marshall's simplicity and widespread use in routine highway projects.
Material Selection Criteria in Marshall vs Superpave
Marshall Mix Design prioritizes stability and flow values to select aggregate gradation and asphalt binder content, focusing on empirical performance under static loading conditions. Superpave Mix Design incorporates criteria such as aggregate angularity, fine aggregate angularity, and dust-to-binder ratio, emphasizing volumetric properties and performance under dynamic, environmental, and traffic-related stresses. Key distinctions include Superpave's use of traffic loading data and climate for binder selection, ensuring higher durability and resistance to rutting and cracking compared to the Marshall method.
Laboratory Testing Procedures for Both Methods
Marshall Mix Design employs stability and flow tests by compacting asphalt samples with a standard hammer to evaluate resistance to plastic deformation, focusing on optimum binder content through volumetric analysis. Superpave Mix Design utilizes gyratory compaction to simulate actual field conditions more closely, assessing parameters like air voids, permeability, and durability under varying temperatures and loading cycles. Both methods conduct moisture susceptibility and aging tests, but Superpave's procedure integrates advanced mechanical conditioning to better predict pavement performance.
Performance Characteristics: Durability and Stability
Marshall Mix Design provides reliable stability measurements through a simple compaction method, delivering good performance for standard traffic loads but may exhibit limitations under high-temperature conditions and heavy traffic. Superpave Mix Design incorporates detailed performance criteria based on climatic data and traffic load levels, enhancing durability against rutting, fatigue cracking, and thermal cracking in diverse environments. The Superpave system's use of volumetric properties and performance tests results in superior long-term pavement performance and increased resistance to deformation compared to the Marshall method.
Application Suitability: Marshall vs Superpave
Marshall Mix Design is best suited for low to medium traffic roads due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in flexible pavements with consistent material properties. Superpave Mix Design excels in high-traffic and heavy-load conditions by incorporating climatic factors and traffic data for enhanced durability and performance. The selection between Marshall and Superpave depends on specific project requirements, traffic volume, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal pavement longevity.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
Marshall Mix Design offers a cost-effective method with simpler testing procedures, reducing laboratory time and equipment expenses, making it ideal for projects with budget constraints. Superpave Mix Design, while more complex and initially costly due to advanced performance testing and specialized equipment, enhances long-term efficiency by optimizing mixtures for specific traffic and climate conditions, thereby reducing maintenance expenses. Choosing between the two depends on balancing upfront costs with expected lifecycle performance and durability requirements.
Future Trends in Asphalt Mix Design Techniques
Emerging trends in asphalt mix design emphasize sustainability and performance with increasing adoption of Superpave Mix Design for enhanced rutting and fatigue resistance compared to traditional Marshall Mix Design. Advances in binder modification, warm mix asphalt technologies, and incorporation of recycled materials align with Superpave's performance-based criteria to optimize durability under diverse loading and climate conditions. Future research prioritizes intelligent compaction techniques and mechanistic-empirical models to refine mix designs, ensuring long-term pavement resilience and cost-effectiveness.
Marshall Mix Design vs Superpave Mix Design Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com