Asphalt binder is a viscous, black, sticky material derived from crude oil, serving as the adhesive agent that binds aggregate particles in asphalt concrete. Asphalt concrete is a composite material composed of asphalt binder mixed with aggregates such as sand, gravel, or crushed stone, forming a durable surface for roads and pavements. Understanding the distinction between asphalt binder and asphalt concrete is crucial for selecting appropriate materials and ensuring long-lasting pavement performance.
Table of Comparison
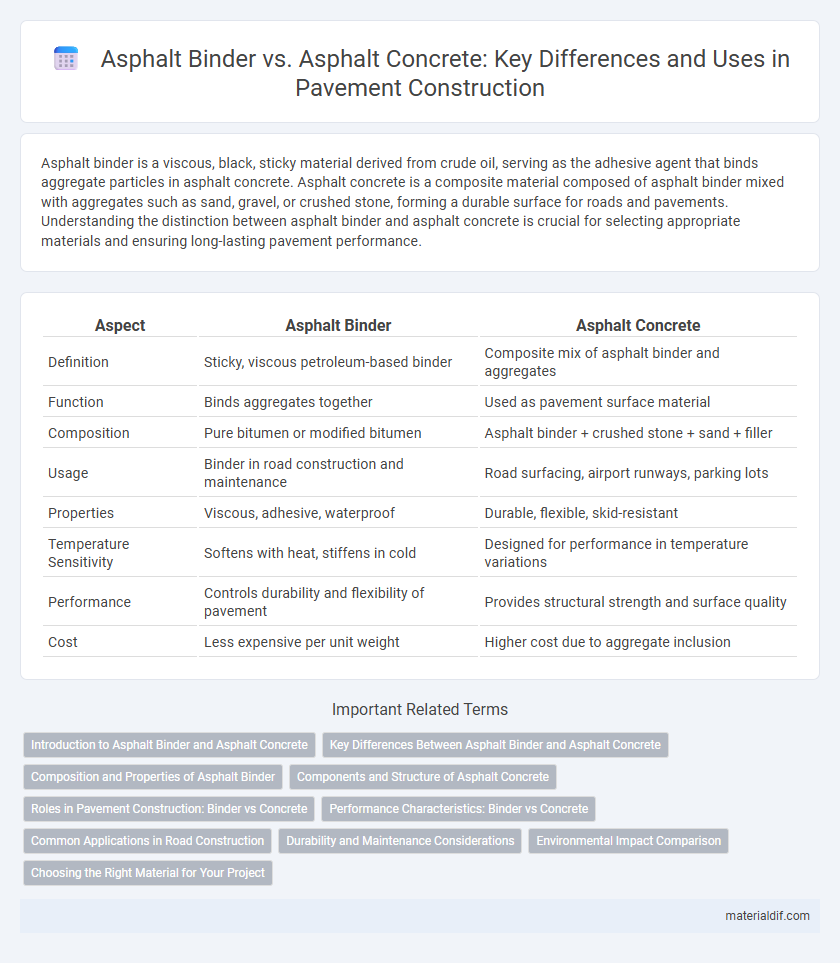
| Aspect | Asphalt Binder | Asphalt Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sticky, viscous petroleum-based binder | Composite mix of asphalt binder and aggregates |
| Function | Binds aggregates together | Used as pavement surface material |
| Composition | Pure bitumen or modified bitumen | Asphalt binder + crushed stone + sand + filler |
| Usage | Binder in road construction and maintenance | Road surfacing, airport runways, parking lots |
| Properties | Viscous, adhesive, waterproof | Durable, flexible, skid-resistant |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Softens with heat, stiffens in cold | Designed for performance in temperature variations |
| Performance | Controls durability and flexibility of pavement | Provides structural strength and surface quality |
| Cost | Less expensive per unit weight | Higher cost due to aggregate inclusion |
Introduction to Asphalt Binder and Asphalt Concrete
Asphalt binder, a viscoelastic material derived from petroleum refining, serves as the adhesive agent that binds aggregate particles in asphalt concrete, providing cohesion and durability. Asphalt concrete is a composite material composed of asphalt binder and mineral aggregates, designed to withstand traffic loads and environmental conditions in road construction. The performance and longevity of asphalt pavements depend on the specific properties of both the asphalt binder and the carefully engineered mixture of aggregates within the asphalt concrete.
Key Differences Between Asphalt Binder and Asphalt Concrete
Asphalt binder is a viscous, sticky material made primarily from bitumen used to bind aggregates in asphalt concrete, while asphalt concrete is a composite construction material consisting of asphalt binder mixed with aggregates like sand, gravel, or crushed stone. Key differences include asphalt binder's role as a binding agent versus asphalt concrete's function as the durable, load-bearing pavement surface. Asphalt binder affects flexibility and resistance to temperature changes, whereas asphalt concrete determines the structural strength and skid resistance of roads.
Composition and Properties of Asphalt Binder
Asphalt binder is a viscous, black, sticky substance composed primarily of bitumen, a complex mixture of hydrocarbons derived from crude oil refining. It acts as a binder in asphalt concrete, providing adhesion and flexibility to the aggregate particles, which are composed of sand, gravel, or crushed stone. The properties of asphalt binder, such as viscosity, elasticity, and temperature susceptibility, significantly influence the durability, performance, and resistance to deformation of the asphalt concrete pavement.
Components and Structure of Asphalt Concrete
Asphalt binder is a viscous, black material derived from crude oil used to coat aggregates in asphalt concrete, acting as the adhesive that binds the components together. Asphalt concrete consists of a mixture of mineral aggregates such as crushed stone, sand, and gravel, combined with the asphalt binder to form a durable pavement material. The structure of asphalt concrete features tightly packed aggregates held in place by the binder, providing strength, flexibility, and resistance to weathering and traffic loads.
Roles in Pavement Construction: Binder vs Concrete
Asphalt binder serves as the adhesive material that holds the aggregate particles together, providing flexibility and durability in pavement construction, while asphalt concrete is the composite material made from the binder and aggregates that forms the structural layer of the pavement. The binder ensures resistance to deformation and weathering, enhancing the pavement's lifespan, whereas asphalt concrete distributes traffic loads and maintains surface integrity. Effective pavement design relies on optimizing the properties of both binder and concrete to achieve performance and longevity.
Performance Characteristics: Binder vs Concrete
Asphalt binder is a viscous, adhesive material designed to bind aggregate particles together, providing flexibility and resistance to deformation under temperature changes and traffic loads. Asphalt concrete consists of a mixture of asphalt binder and aggregates, delivering enhanced structural strength, durability, and load-bearing capacity required for pavement surfaces. Performance characteristics of binder focus on adhesion, temperature susceptibility, and elasticity, while asphalt concrete emphasizes compressive strength, fatigue resistance, and skid resistance for long-term roadway performance.
Common Applications in Road Construction
Asphalt binder is a viscous material acting as the glue that holds aggregate particles together in asphalt concrete, which is extensively used for road pavements, highways, and airport runways. Asphalt concrete combines asphalt binder with a mixture of mineral aggregates to provide a durable, flexible, and weather-resistant surface optimized for heavy traffic loads and climate variations. Common applications in road construction include base, binder, and surface layers, where varying asphalt binder grades are selected to enhance performance characteristics such as rutting resistance and cracking prevention.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Asphalt binder acts as the adhesive component in asphalt concrete, significantly influencing the pavement's durability by enhancing resistance to cracking and deformation under heavy traffic loads. Asphalt concrete, composed of aggregates bonded by the asphalt binder, requires regular maintenance to address surface wear and prevent water infiltration that can compromise its structural integrity. Selecting high-quality asphalt binder improves the long-term performance and reduces the frequency of maintenance interventions for asphalt concrete pavements.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Asphalt binder, primarily a petroleum-derived product, significantly contributes to greenhouse gas emissions during its extraction and refinement, whereas asphalt concrete incorporates recycled materials, reducing overall environmental footprint. Asphalt concrete's use of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) enhances sustainability by diverting waste from landfills and lowering raw material demand. Life cycle assessments reveal that asphalt concrete offers superior environmental benefits through reduced energy consumption and emissions compared to using virgin asphalt binder alone.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Asphalt binder, a viscous petroleum product, acts as the adhesive that binds aggregate particles in asphalt concrete, determining the pavement's durability and flexibility. Selecting the right asphalt binder grade based on climatic conditions and traffic load ensures optimal performance and resistance to rutting or cracking. Asphalt concrete combines this binder with aggregates to form a robust surface suitable for roads, driveways, and parking lots, where the specific mix design tailors strength and skid resistance for project requirements.
Asphalt Binder vs Asphalt Concrete Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com