Cutback asphalt is a mixture of asphalt cement and petroleum solvents, allowing it to remain liquid at lower temperatures for easier application but releasing volatile organic compounds during drying. Emulsion asphalt combines asphalt cement with water and an emulsifying agent, offering a safer, more environmentally friendly option with slower curing times suitable for various paving conditions. Both types have specific uses depending on project requirements, temperature conditions, and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
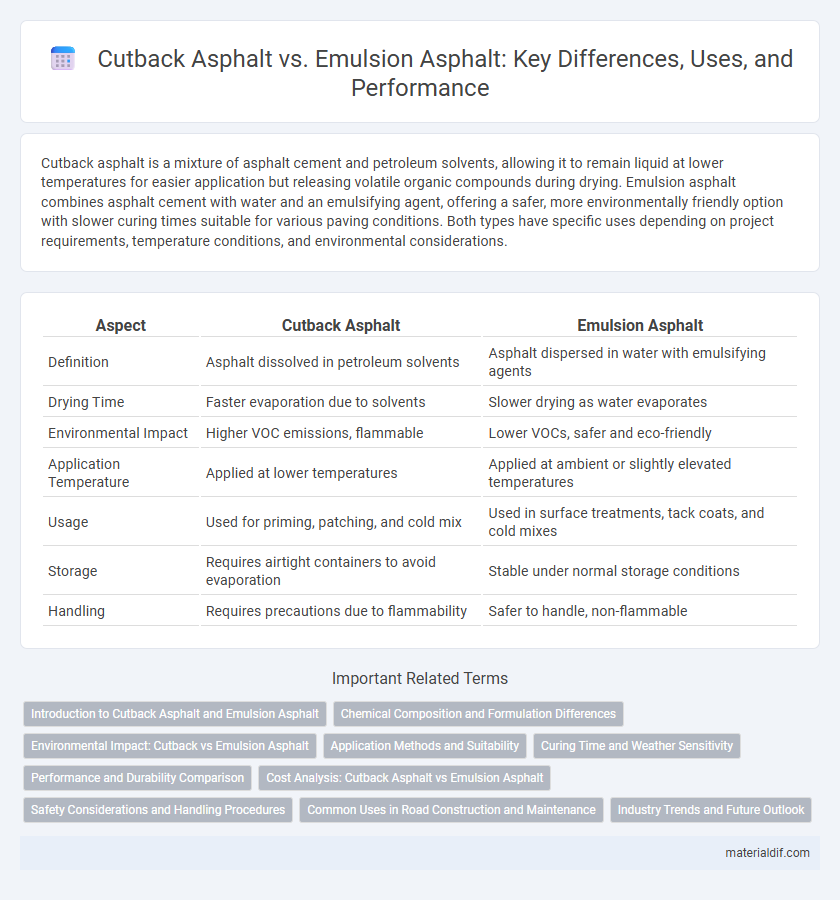
| Aspect | Cutback Asphalt | Emulsion Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Asphalt dissolved in petroleum solvents | Asphalt dispersed in water with emulsifying agents |
| Drying Time | Faster evaporation due to solvents | Slower drying as water evaporates |
| Environmental Impact | Higher VOC emissions, flammable | Lower VOCs, safer and eco-friendly |
| Application Temperature | Applied at lower temperatures | Applied at ambient or slightly elevated temperatures |
| Usage | Used for priming, patching, and cold mix | Used in surface treatments, tack coats, and cold mixes |
| Storage | Requires airtight containers to avoid evaporation | Stable under normal storage conditions |
| Handling | Requires precautions due to flammability | Safer to handle, non-flammable |
Introduction to Cutback Asphalt and Emulsion Asphalt
Cutback asphalt is a liquid asphalt binder dissolved in petroleum solvents to reduce viscosity for easier application in road construction and maintenance, offering fast curing times but higher volatility. Emulsion asphalt consists of asphalt droplets suspended in water with the help of emulsifying agents, providing safer handling, reduced VOC emissions, and better adhesion to damp aggregates. Both types serve distinct purposes based on environmental conditions and project requirements in pavement engineering.
Chemical Composition and Formulation Differences
Cutback asphalt is formulated by dissolving asphalt cement in petroleum solvents such as kerosene or naphtha, enabling easier application at lower temperatures due to its liquid state. Emulsion asphalt differs chemically, consisting of asphalt cement dispersed in water with emulsifying agents like cationic, anionic, or nonionic surfactants, creating a stable mixture suitable for environmentally friendly and quick-setting applications. The primary formulation distinction lies in cutback asphalt's solvent-based composition versus emulsion asphalt's water-based system stabilized by emulsifiers.
Environmental Impact: Cutback vs Emulsion Asphalt
Cutback asphalt releases higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) due to its solvent-based composition, increasing air pollution and health risks during application. Emulsion asphalt, made by mixing asphalt with water and an emulsifying agent, significantly reduces VOC emissions, making it a more environmentally friendly choice. The lower toxicity and reduced environmental footprint of emulsion asphalt contribute to sustainable paving practices and compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Application Methods and Suitability
Cutback asphalt uses petroleum solvents to keep it in a liquid state, allowing for easy application by spraying or mixing with aggregates on various surfaces, making it suitable for cold weather and base courses. Emulsion asphalt, composed of asphalt droplets suspended in water, is applied primarily by spraying or mixing at ambient temperatures, reducing environmental hazards and providing better adhesion on damp surfaces. Cutback asphalt is favored for quick-drying applications while emulsion asphalt excels in eco-friendly road construction and maintenance where controlled curing and lower emissions are required.
Curing Time and Weather Sensitivity
Cutback asphalt cures faster than emulsion asphalt due to its rapid solvent evaporation, making it suitable for quick-setting applications. Emulsion asphalt has a longer curing time as water slowly evaporates, allowing better performance in cooler or damp weather conditions. Cutback asphalt is more sensitive to temperature extremes, while emulsion asphalt offers greater flexibility and weather resistance during curing.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Cutback asphalt, known for its rapid curing due to petroleum solvents, offers excellent workability in lower temperatures but tends to be less durable over time because of its susceptibility to oil evaporation and environmental damage. Emulsion asphalt, utilizing water as the solvent, provides enhanced environmental safety and longer-lasting performance, with better resistance to aging, cracking, and moisture damage, making it suitable for moderate to high-stress pavements. Performance tests indicate that emulsion asphalt generally outperforms cutback asphalt in durability metrics such as resistance to rutting and oxidative aging.
Cost Analysis: Cutback Asphalt vs Emulsion Asphalt
Cutback asphalt generally incurs higher costs due to the use of petroleum solvents, which require careful handling and longer curing times, increasing labor expenses. Emulsion asphalt offers a more cost-effective alternative by utilizing water-based emulsions that cure faster and reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, lowering environmental compliance costs. Choosing between cutback and emulsion asphalt depends on project scale, environmental regulations, and long-term maintenance budgets.
Safety Considerations and Handling Procedures
Cutback asphalt contains volatile solvents that require careful handling to prevent fire hazards and health risks, necessitating proper ventilation and protective equipment during application. Emulsion asphalt, being water-based, poses fewer flammability risks but still demands appropriate storage to avoid freezing and separation, along with personal protective gear to minimize skin and eye contact. Safety protocols must address the specific chemical properties of each asphalt type to ensure environmental compliance and worker well-being.
Common Uses in Road Construction and Maintenance
Cutback asphalt is commonly used for patching, prime coats, and cold mix applications in road construction due to its rapid curing properties and strong adhesion to aggregates. Emulsion asphalt is favored for surface treatments, chip seals, and cold recycling because it emulsifies asphalt in water, allowing safer handling and lower curing temperatures. Both materials optimize performance in maintenance, with cutback asphalt suited for faster setting repairs and emulsion asphalt supporting environmentally friendly and cost-effective road rehabilitation.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Cutback asphalt, known for its quick curing and ease of application, faces declining use due to environmental regulations favoring low-VOC materials like emulsion asphalt. Emulsion asphalt, prized for its water-based composition and improved sustainability, dominates industry trends as governments and contractors prioritize eco-friendly paving solutions. Future outlook indicates increased adoption of emulsion asphalt driven by advancements in formulation technology and growing regulatory pressures on volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Cutback Asphalt vs Emulsion Asphalt Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com