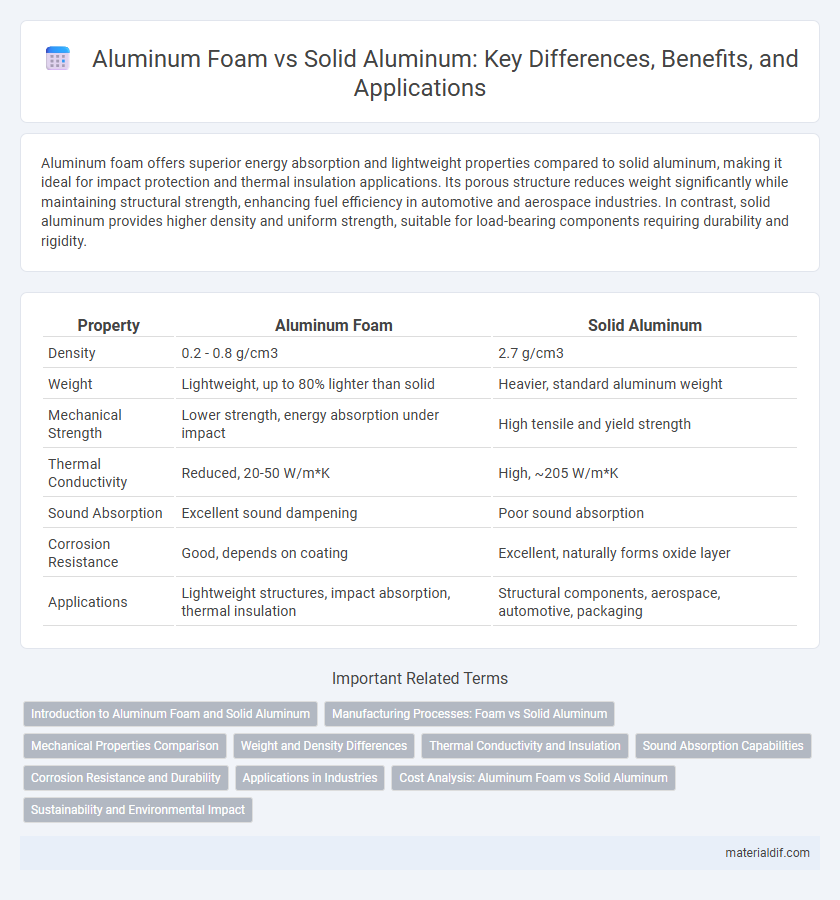
Aluminum foam offers superior energy absorption and lightweight properties compared to solid aluminum, making it ideal for impact protection and thermal insulation applications. Its porous structure reduces weight significantly while maintaining structural strength, enhancing fuel efficiency in automotive and aerospace industries. In contrast, solid aluminum provides higher density and uniform strength, suitable for load-bearing components requiring durability and rigidity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminum Foam | Solid Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.2 - 0.8 g/cm3 | 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Weight | Lightweight, up to 80% lighter than solid | Heavier, standard aluminum weight |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower strength, energy absorption under impact | High tensile and yield strength |
| Thermal Conductivity | Reduced, 20-50 W/m*K | High, ~205 W/m*K |
| Sound Absorption | Excellent sound dampening | Poor sound absorption |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, depends on coating | Excellent, naturally forms oxide layer |
| Applications | Lightweight structures, impact absorption, thermal insulation | Structural components, aerospace, automotive, packaging |
Introduction to Aluminum Foam and Solid Aluminum
Aluminum foam is a lightweight, porous material characterized by a cellular structure that offers excellent energy absorption, thermal insulation, and sound dampening properties. Solid aluminum, in contrast, is a dense and homogenous metal known for its strength, corrosion resistance, and high thermal conductivity. The choice between aluminum foam and solid aluminum depends on specific application requirements such as weight reduction, impact resistance, and structural integrity.
Manufacturing Processes: Foam vs Solid Aluminum
Aluminum foam is produced through methods such as powder metallurgy, melt infiltration, and gas injection, creating a porous structure that significantly reduces weight while maintaining strength. Solid aluminum manufacturing involves processes like casting, rolling, and extrusion, resulting in a dense, uniform material with high tensile strength and conductivity. The choice between aluminum foam and solid aluminum depends on application requirements for lightweight properties versus structural integrity and thermal performance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Aluminum foam exhibits significantly lower density and compressive strength compared to solid aluminum, but it offers superior energy absorption and impact resistance due to its porous structure. Its mechanical properties include high stiffness-to-weight ratio and excellent damping capacity, making it ideal for lightweight structural applications and shock mitigation. Solid aluminum, on the other hand, provides higher tensile strength and rigidity, suitable for load-bearing components where strength is critical.
Weight and Density Differences
Aluminum foam exhibits a significantly lower density ranging from 0.2 to 0.6 g/cm3 compared to solid aluminum's density of approximately 2.7 g/cm3, resulting in substantial weight reduction. This lightweight characteristic makes aluminum foam ideal for applications requiring enhanced strength-to-weight ratios, such as aerospace and automotive industries. Despite its reduced mass, aluminum foam maintains structural integrity through its porous microstructure, offering a balance between weight savings and mechanical performance.
Thermal Conductivity and Insulation
Aluminum foam exhibits significantly lower thermal conductivity compared to solid aluminum, typically ranging from 0.1 to 0.8 W/m*K versus solid aluminum's 205 W/m*K, making it an excellent thermal insulator. The porous structure of aluminum foam traps air within its cells, drastically reducing heat transfer and enhancing insulation properties. This unique combination allows aluminum foam to offer lightweight strength with superior thermal insulation performance in applications where controlling heat flow is critical.
Sound Absorption Capabilities
Aluminum foam exhibits superior sound absorption capabilities compared to solid aluminum due to its porous structure that dissipates sound energy effectively. The interconnected cells within aluminum foam reduce noise by trapping and diffusing sound waves, making it ideal for acoustic insulation applications. Solid aluminum, being dense and non-porous, reflects sound rather than absorbing it, resulting in minimal noise reduction.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Aluminum foam offers enhanced corrosion resistance due to its porous structure allowing for effective oxide layer formation, which protects against environmental degradation better than solid aluminum. While solid aluminum exhibits high durability under mechanical stress, aluminum foam provides improved impact absorption and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring a balance of lightweight strength and longevity. The foam's surface area and microstructure play a critical role in increasing its resistance to corrosion-related damage compared to dense aluminum.
Applications in Industries
Aluminum foam offers superior energy absorption and lightweight properties, making it ideal for automotive crash protection, aerospace structural components, and sound insulation in construction. Solid aluminum provides higher strength and durability, preferred for aircraft frames, heavy machinery, and electrical conductors. Industries often select aluminum foam for impact resistance and vibration damping, while solid aluminum is favored for load-bearing applications and thermal conductivity.
Cost Analysis: Aluminum Foam vs Solid Aluminum
Aluminum foam typically incurs higher initial manufacturing costs compared to solid aluminum due to its complex production process involving foaming agents and precise temperature control. However, aluminum foam offers cost advantages in applications requiring lightweight materials with excellent energy absorption, potentially reducing transportation and assembly expenses. Solid aluminum remains more cost-effective for applications prioritizing machinability and structural strength without the need for specialized properties of foam.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Aluminum foam offers superior sustainability compared to solid aluminum due to its lightweight structure, which reduces material usage and lowers transportation emissions. Its enhanced energy absorption characteristics contribute to longer product lifespans and improved recyclability, minimizing environmental impact. Solid aluminum, while recyclable, typically requires more raw material extraction and energy-intensive processing, resulting in a higher carbon footprint.
Aluminum foam vs solid aluminum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com