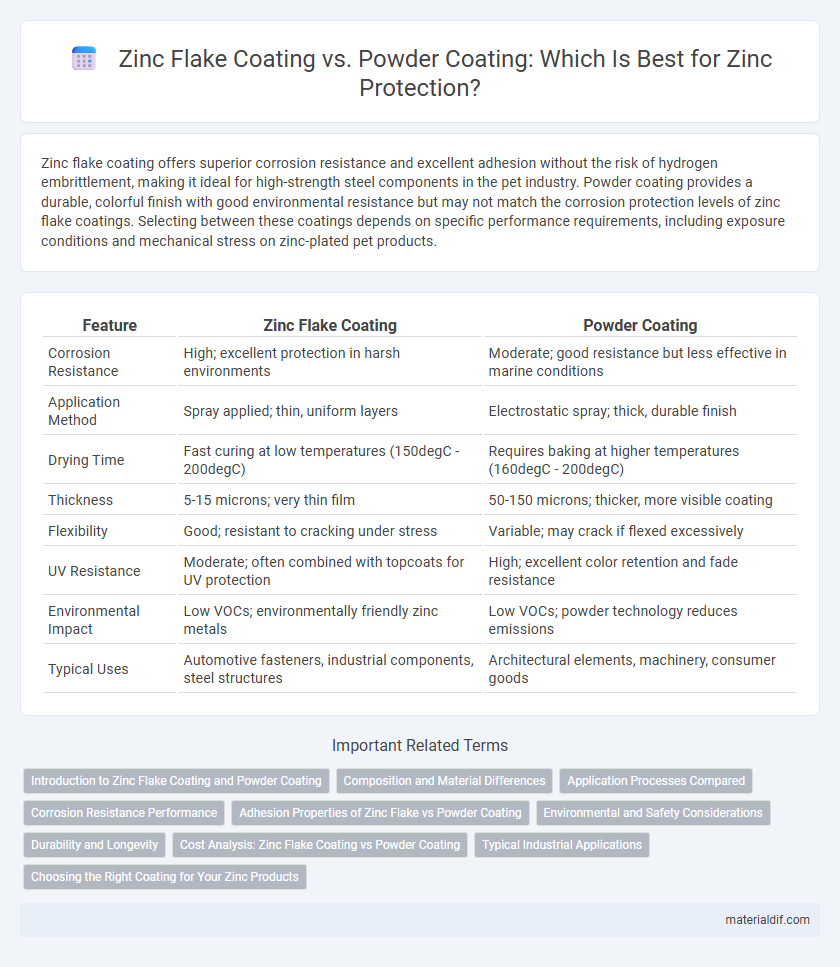
Zinc flake coating offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent adhesion without the risk of hydrogen embrittlement, making it ideal for high-strength steel components in the pet industry. Powder coating provides a durable, colorful finish with good environmental resistance but may not match the corrosion protection levels of zinc flake coatings. Selecting between these coatings depends on specific performance requirements, including exposure conditions and mechanical stress on zinc-plated pet products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zinc Flake Coating | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High; excellent protection in harsh environments | Moderate; good resistance but less effective in marine conditions |
| Application Method | Spray applied; thin, uniform layers | Electrostatic spray; thick, durable finish |
| Drying Time | Fast curing at low temperatures (150degC - 200degC) | Requires baking at higher temperatures (160degC - 200degC) |
| Thickness | 5-15 microns; very thin film | 50-150 microns; thicker, more visible coating |
| Flexibility | Good; resistant to cracking under stress | Variable; may crack if flexed excessively |
| UV Resistance | Moderate; often combined with topcoats for UV protection | High; excellent color retention and fade resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOCs; environmentally friendly zinc metals | Low VOCs; powder technology reduces emissions |
| Typical Uses | Automotive fasteners, industrial components, steel structures | Architectural elements, machinery, consumer goods |
Introduction to Zinc Flake Coating and Powder Coating
Zinc flake coating provides a thin, uniform layer of corrosion resistance by combining zinc and aluminum flakes without affecting the base metal's mechanical properties. Powder coating involves applying a dry powder, typically polyester or epoxy, which is then cured under heat to form a hard, durable finish. Both coatings enhance metal protection, with zinc flake focusing on galvanic corrosion prevention and powder coating offering broad aesthetic and environmental resistance.
Composition and Material Differences
Zinc flake coating consists of microscopic zinc and aluminum flakes suspended in a binder, creating a thin, non-electrolytic layer that provides superior corrosion resistance and excellent adhesion to steel surfaces. Powder coating, composed of polymer resin powders that melt and cure under heat, offers a thicker, decorative finish but lacks the sacrificial protection properties inherent to zinc flakes. The key material difference lies in zinc flake's metal-based protective mechanism versus powder coating's organic polymer film, making zinc flake ideal for heavy-duty corrosion environments.
Application Processes Compared
Zinc flake coating involves applying a thin layer of inorganic zinc and aluminum flakes through a wet spray or dip process, offering uniform coverage on complex geometries and requiring curing at lower temperatures around 200degC. Powder coating, by contrast, utilizes electrostatically charged powdered paint applied via spraying, which is then baked at higher temperatures between 160degC and 210degC to form a durable, thick protective layer. The zinc flake method excels in corrosion resistance with minimal thickness, suitable for fasteners and automotive parts, while powder coating provides robust mechanical and aesthetic finishes but may face challenges in coating intricate surfaces evenly.
Corrosion Resistance Performance
Zinc flake coating offers superior corrosion resistance compared to powder coating due to its multi-layered, sacrificial protection mechanism that effectively prevents rust in harsh environments. Unlike powder coating, which primarily provides a physical barrier, zinc flake coatings chemically react with the substrate to inhibit oxidation, extending the lifespan of metal components. This makes zinc flake coatings the preferred choice in automotive, construction, and industrial applications where long-term corrosion protection is critical.
Adhesion Properties of Zinc Flake vs Powder Coating
Zinc flake coating exhibits superior adhesion properties compared to powder coating, providing enhanced corrosion resistance on complex geometries and threaded components. Its thin, uniform layer bonds chemically and mechanically to substrates, ensuring durable protection under stress and exposure. Powder coating, while robust in appearance, often lacks the same consistent adhesion on intricate surfaces, potentially leading to premature coating failure.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Zinc flake coating offers superior corrosion resistance without the use of hazardous heavy metals, making it an environmentally safer alternative compared to traditional powder coatings that may contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The application process of zinc flake coatings involves lower energy consumption and emits fewer pollutants, enhancing workplace safety by reducing exposure to harmful chemicals. In contrast, powder coating requires high-temperature curing, which can pose fire hazards and increase carbon emissions during manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity
Zinc flake coating offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to powder coating, making it ideal for harsh environments and automotive applications. It provides a thin, uniform layer that ensures long-lasting protection without cracking or peeling under mechanical stress. Powder coating, while visually appealing and resistant to chipping, generally lacks the same level of corrosion resistance and longevity found in zinc flake coatings.
Cost Analysis: Zinc Flake Coating vs Powder Coating
Zinc flake coating generally offers a lower overall cost compared to powder coating due to its thinner application, reduced material usage, and faster curing times that enhance production efficiency. Although powder coating may have a lower initial material cost, its longer curing process and higher energy consumption increase operational expenses. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including maintenance and durability, zinc flake coating often proves more cost-effective in corrosion protection applications.
Typical Industrial Applications
Zinc flake coating is widely used in automotive and aerospace industries due to its superior corrosion resistance and thin, uniform layer ideal for fasteners and metal components exposed to harsh environments. Powder coating is favored in heavy machinery and structural steel applications for its thicker, durable finish that withstands mechanical wear and UV exposure. Both coatings enhance metal longevity, but zinc flake excels in anti-corrosion on precision parts, while powder coating provides robust protection for larger surfaces.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Zinc Products
Zinc flake coating offers exceptional corrosion resistance and thin film thickness, making it ideal for fasteners and complex geometries requiring precise tolerances, while powder coating provides a thicker, more durable finish suited for aesthetic applications on larger surfaces. Consider environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and desired appearance when selecting between zinc flake and powder coating for zinc products to ensure optimal protection and longevity. Evaluating factors such as salt spray resistance, coating thickness, and application method helps determine the most effective coating solution for your specific zinc components.
Zinc Flake Coating vs Powder Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com