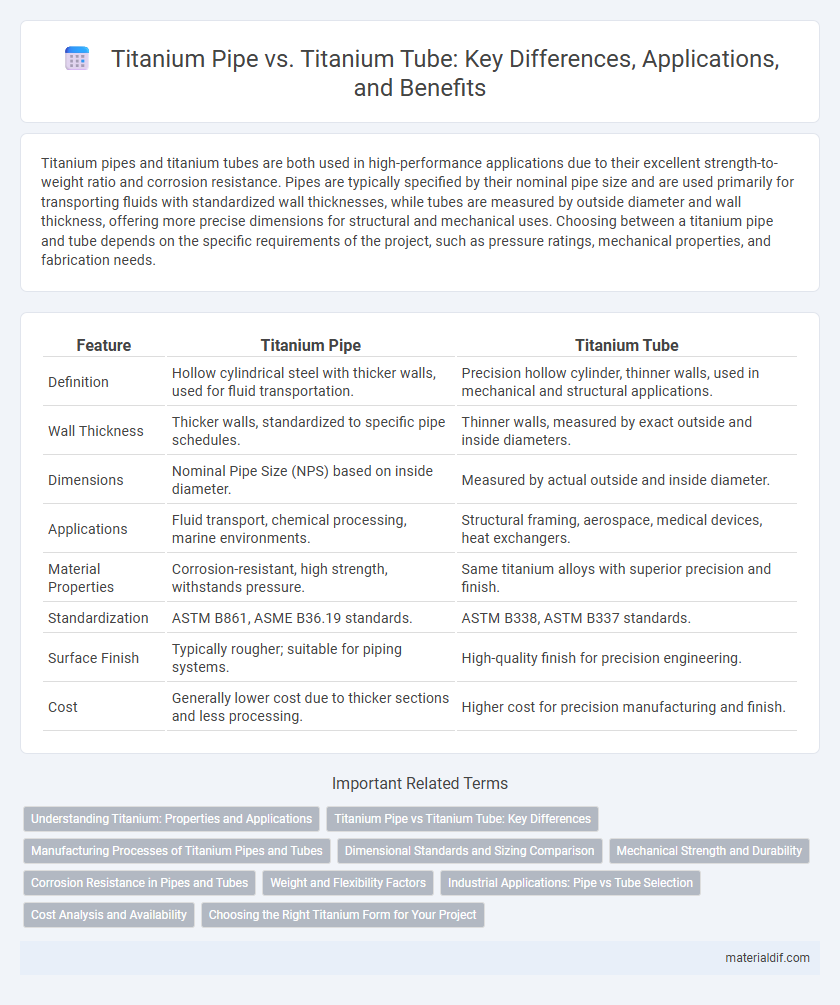
Titanium pipes and titanium tubes are both used in high-performance applications due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Pipes are typically specified by their nominal pipe size and are used primarily for transporting fluids with standardized wall thicknesses, while tubes are measured by outside diameter and wall thickness, offering more precise dimensions for structural and mechanical uses. Choosing between a titanium pipe and tube depends on the specific requirements of the project, such as pressure ratings, mechanical properties, and fabrication needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Titanium Pipe | Titanium Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hollow cylindrical steel with thicker walls, used for fluid transportation. | Precision hollow cylinder, thinner walls, used in mechanical and structural applications. |
| Wall Thickness | Thicker walls, standardized to specific pipe schedules. | Thinner walls, measured by exact outside and inside diameters. |
| Dimensions | Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) based on inside diameter. | Measured by actual outside and inside diameter. |
| Applications | Fluid transport, chemical processing, marine environments. | Structural framing, aerospace, medical devices, heat exchangers. |
| Material Properties | Corrosion-resistant, high strength, withstands pressure. | Same titanium alloys with superior precision and finish. |
| Standardization | ASTM B861, ASME B36.19 standards. | ASTM B338, ASTM B337 standards. |
| Surface Finish | Typically rougher; suitable for piping systems. | High-quality finish for precision engineering. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to thicker sections and less processing. | Higher cost for precision manufacturing and finish. |
Understanding Titanium: Properties and Applications
Titanium pipes and titanium tubes are both corrosion-resistant and lightweight, making them ideal for aerospace, medical, and chemical processing applications. Titanium tubes typically have tighter dimensional tolerances and thinner walls, enhancing strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility for heat exchangers and structural components. Titanium pipes are generally thicker and used for high-pressure fluid transport, ensuring durability in oil and gas pipelines and marine environments.
Titanium Pipe vs Titanium Tube: Key Differences
Titanium pipe and titanium tube differ primarily in their manufacturing process, dimensions, and applications, with pipes typically being larger, having thicker walls, and designed for fluid transport systems requiring pressure resistance. Titanium tubes offer more precise dimensions with thinner walls, making them suitable for structural, medical, and aerospace uses where strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance are critical. Understanding these distinctions helps select the right titanium product for specific industrial needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Manufacturing Processes of Titanium Pipes and Tubes
Titanium pipes and tubes are manufactured using precise processes like extrusion and seamless drawing, ensuring high strength and corrosion resistance. Pipes typically involve a welding process or seamless extrusion followed by cold drawing to meet diameter and thickness specifications, while tubes are often produced through cold drawing or hot rolling for tighter tolerances and smoother finishes. Both manufacturing methods require controlled heat treatment and surface finishing to maintain titanium's mechanical properties and durability in demanding industrial applications.
Dimensional Standards and Sizing Comparison
Titanium pipes are manufactured according to ASTM B861 and ASTM B337 standards, featuring a consistent outer diameter with a specified wall thickness suitable for high-pressure applications. In contrast, titanium tubes, governed by ASTM B862 and ASTM B337, provide precise dimensional tolerances with varying outer diameters and wall thicknesses tailored for structural or mechanical uses. The sizing comparison highlights that titanium pipes are measured by nominal pipe size (NPS) and schedule, while titanium tubes are specified by exact outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness, essential for fitting and design accuracy.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Titanium pipes feature thicker walls and a rounder cross-section, enhancing their mechanical strength and pressure resistance compared to titanium tubes, which often have thinner walls designed for lighter applications. The superior durability of titanium pipes allows them to withstand harsher environments and higher internal pressures, making them ideal for industrial and structural uses. Titanium tubes provide excellent corrosion resistance and flexibility but generally offer less robustness under mechanical stress than titanium pipes.
Corrosion Resistance in Pipes and Tubes
Titanium pipes and tubes both exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, making them ideal for harsh environments such as seawater and chemical processing. Titanium pipes typically have thicker walls, providing enhanced durability against corrosion and mechanical stress compared to tubes, which are often designed with thinner walls for fluid transport applications. The superior oxide layer on titanium surfaces ensures long-lasting protection in both pipes and tubes, reducing maintenance costs and extending service life.
Weight and Flexibility Factors
Titanium pipes generally possess greater wall thickness, making them heavier but more durable under high pressure compared to titanium tubes, which are lighter due to thinner walls and suited for applications requiring flexibility. The weight difference impacts transportation and installation, with titanium tubes offering easier handling and adaptability in curved or confined spaces. Flexibility in titanium tubes enhances performance in dynamic environments, while the rigidity of titanium pipes ensures structural integrity in static, high-stress conditions.
Industrial Applications: Pipe vs Tube Selection
Titanium pipes offer superior resistance to corrosion and high pressure, making them ideal for demanding chemical processing and oil refinery applications. Titanium tubes, with precise dimensional tolerances and smooth finishes, are favored in heat exchangers and aerospace components where accuracy and heat transfer efficiency are critical. Selecting between titanium pipe and tube depends on specific industrial requirements such as pressure ratings, dimensional precision, and fluid dynamics.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Titanium pipes generally incur higher costs than titanium tubes due to their thicker walls and more complex manufacturing processes, which increase material usage and fabrication expenses. Availability of titanium tubes is typically greater, as they are produced in a wider range of standard sizes and are more commonly stocked by suppliers, facilitating quicker procurement. Cost analysis reveals that while titanium pipes offer enhanced durability for high-pressure applications, titanium tubes provide a more economical solution for lightweight structural and heat exchanger uses.
Choosing the Right Titanium Form for Your Project
Selecting between titanium pipe and titanium tube depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as pressure ratings, fabrication techniques, and dimensional precision. Titanium pipes are typically used in applications requiring high corrosion resistance and pressure handling, with thicker walls and standardized diameters, while titanium tubes offer tighter dimensional tolerances and are suitable for structural or instrumentation purposes. Understanding the differences in mechanical properties and manufacturing standards ensures optimal performance and longevity in aerospace, chemical processing, or marine environments.
Titanium Pipe vs Titanium Tube Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com