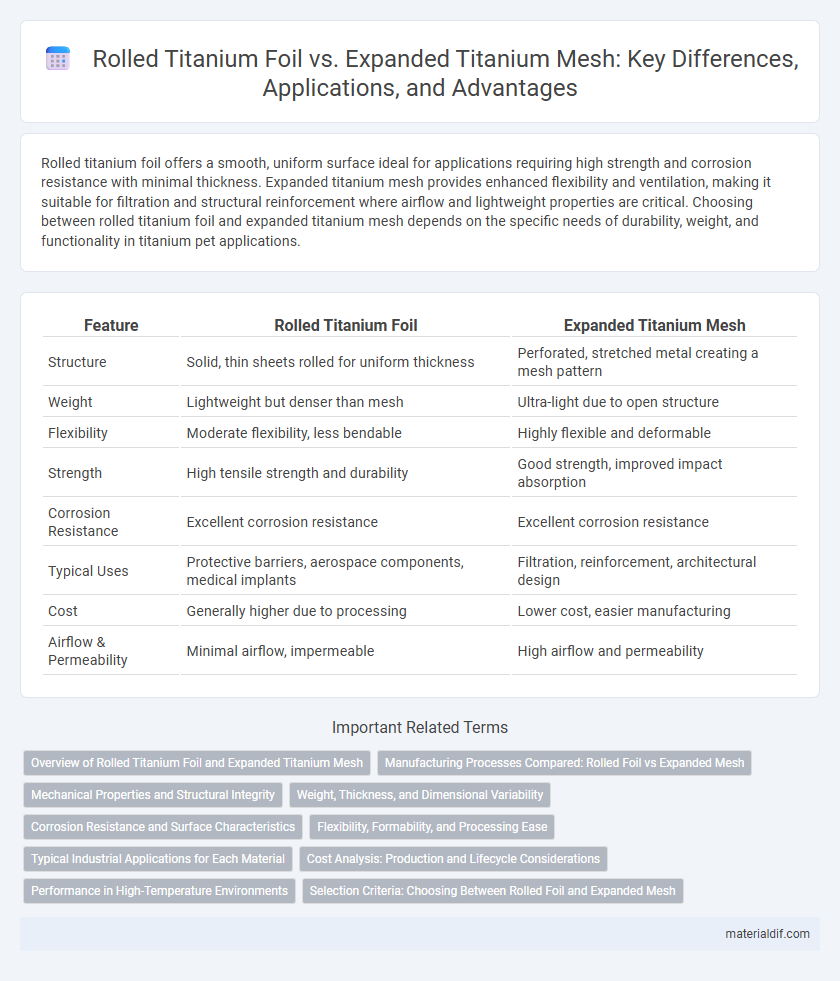
Rolled titanium foil offers a smooth, uniform surface ideal for applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance with minimal thickness. Expanded titanium mesh provides enhanced flexibility and ventilation, making it suitable for filtration and structural reinforcement where airflow and lightweight properties are critical. Choosing between rolled titanium foil and expanded titanium mesh depends on the specific needs of durability, weight, and functionality in titanium pet applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rolled Titanium Foil | Expanded Titanium Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Solid, thin sheets rolled for uniform thickness | Perforated, stretched metal creating a mesh pattern |
| Weight | Lightweight but denser than mesh | Ultra-light due to open structure |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, less bendable | Highly flexible and deformable |
| Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Good strength, improved impact absorption |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| Typical Uses | Protective barriers, aerospace components, medical implants | Filtration, reinforcement, architectural design |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower cost, easier manufacturing |
| Airflow & Permeability | Minimal airflow, impermeable | High airflow and permeability |
Overview of Rolled Titanium Foil and Expanded Titanium Mesh
Rolled titanium foil is a thin, flexible material produced by rolling titanium metal into sheets with precise thickness, offering excellent corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. Expanded titanium mesh is created by slitting and stretching titanium sheets to form a porous, lightweight structure that enhances airflow, filtration, and structural support in architectural and engineering uses. Both materials maximize titanium's durability and performance but serve distinct purposes based on form factor and mechanical properties.
Manufacturing Processes Compared: Rolled Foil vs Expanded Mesh
Rolled titanium foil is produced by compressing titanium slabs through heavy rollers to achieve a thin, uniform sheet with enhanced surface smoothness and density, ideal for applications requiring precise thickness control and high corrosion resistance. Expanded titanium mesh is manufactured by slitting and stretching titanium sheets to create a patterned network, offering superior strength-to-weight ratio and improved airflow or fluid passage for filtration and structural reinforcement. The rolling process emphasizes dimensional uniformity and surface integrity, whereas mesh expansion prioritizes mechanical flexibility and permeability for specialized engineering uses.
Mechanical Properties and Structural Integrity
Rolled titanium foil offers superior tensile strength and enhanced surface finish, making it ideal for applications requiring precise mechanical properties and high corrosion resistance. Expanded titanium mesh, featuring a lattice structure, provides excellent structural integrity with optimized weight-to-strength ratios, promoting flexibility and impact absorption in aerospace and biomedical fields. Both materials demonstrate high fatigue resistance, but rolled foil excels in uniformity and density while expanded mesh benefits from increased surface area and improved load distribution.
Weight, Thickness, and Dimensional Variability
Rolled titanium foil offers superior uniformity in thickness and lower weight compared to expanded titanium mesh, making it ideal for applications requiring precise dimensional control. Expanded titanium mesh exhibits greater dimensional variability due to its interconnected open structure and typically has increased thickness, resulting in added weight. The choice between rolled titanium foil and expanded mesh depends on balancing weight sensitivity with the need for structural airflow and flexibility.
Corrosion Resistance and Surface Characteristics
Rolled titanium foil offers superior corrosion resistance due to its uniform, dense surface structure that minimizes exposure to corrosive elements. Expanded titanium mesh, characterized by its porous, grid-like surface, provides increased surface area but may be more susceptible to localized corrosion in aggressive environments. The smooth, continuous surface of rolled titanium foil enhances passivation layer formation, resulting in long-lasting protection against corrosion compared to the textured nature of expanded titanium mesh.
Flexibility, Formability, and Processing Ease
Rolled titanium foil offers superior flexibility and formability due to its thin, uniform structure, enabling precise shaping with minimal effort. Expanded titanium mesh provides enhanced processing ease for applications requiring ventilation or weight reduction but sacrifices some degree of flexibility compared to foil. The choice between rolled titanium foil and expanded titanium mesh depends on specific application demands, balancing flexibility and processing requirements.
Typical Industrial Applications for Each Material
Rolled titanium foil is commonly used in aerospace fuel cells, chemical processing gaskets, and medical implant fabrication due to its excellent corrosion resistance and precise thickness control. Expanded titanium mesh finds applications in filtration systems, thermal insulation, and lightweight structural components for automotive and architectural industries because of its high strength-to-weight ratio and permeability. Both materials serve critical roles in environments requiring durability, lightweight properties, and resistance to harsh chemicals.
Cost Analysis: Production and Lifecycle Considerations
Rolled titanium foil offers lower initial production costs due to simpler manufacturing processes compared to the more complex expansion required for titanium mesh, which involves precise cutting and stretching. Lifecycle cost analysis reveals rolled foil excels in applications demanding smooth, continuous surfaces resistant to corrosion, reducing maintenance expenses, whereas expanded titanium mesh provides superior strength-to-weight ratios at a higher upfront cost but potentially lowers overall replacement needs. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights rolled foil as cost-effective for sealing and insulation uses, while expanded mesh proves economically advantageous in structural applications with stress distribution demands.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Rolled titanium foil offers superior performance in high-temperature environments due to its dense structure, which provides excellent resistance to oxidation and thermal fatigue. Expanded titanium mesh, while beneficial for applications requiring ventilation and reduced weight, exhibits lower thermal stability and faster degradation when exposed to extreme heat. Engineers often select rolled foil for critical aerospace and industrial uses where maintaining integrity under sustained elevated temperatures is essential.
Selection Criteria: Choosing Between Rolled Foil and Expanded Mesh
Selection criteria between rolled titanium foil and expanded titanium mesh depend on application requirements such as flexibility, strength, and surface area. Rolled titanium foil offers a smooth, uniform surface ideal for sealing and shielding, while expanded titanium mesh provides enhanced structural integrity and ventilation due to its open framework. Material thickness, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties also influence the choice based on specific industrial or biomedical uses.
Rolled Titanium Foil vs Expanded Titanium Mesh Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com