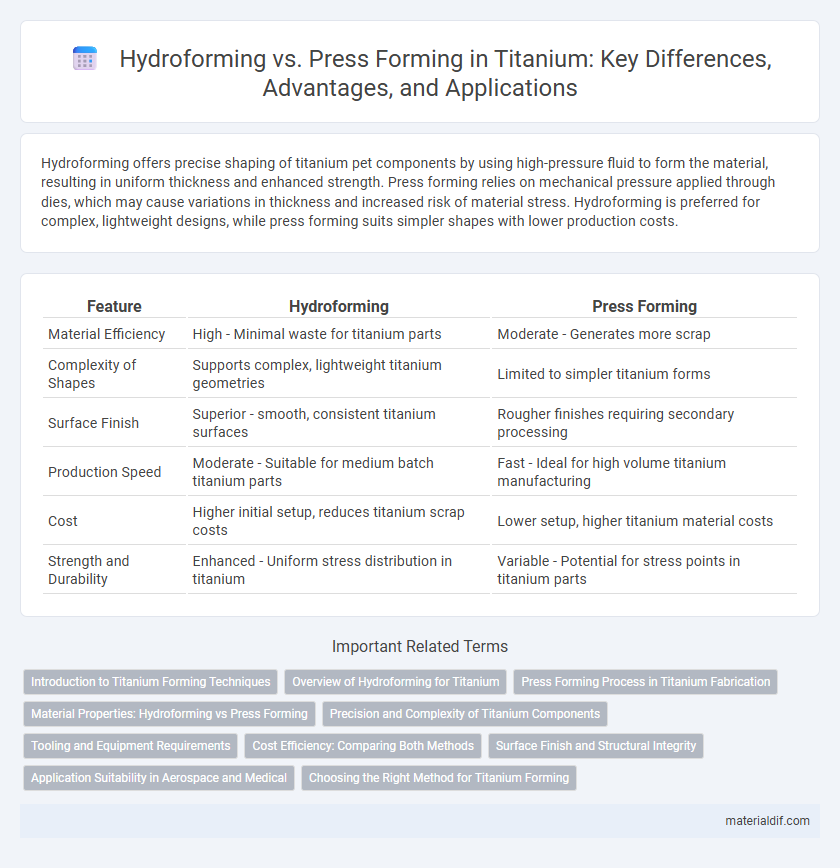
Hydroforming offers precise shaping of titanium pet components by using high-pressure fluid to form the material, resulting in uniform thickness and enhanced strength. Press forming relies on mechanical pressure applied through dies, which may cause variations in thickness and increased risk of material stress. Hydroforming is preferred for complex, lightweight designs, while press forming suits simpler shapes with lower production costs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydroforming | Press Forming |
|---|---|---|
| Material Efficiency | High - Minimal waste for titanium parts | Moderate - Generates more scrap |
| Complexity of Shapes | Supports complex, lightweight titanium geometries | Limited to simpler titanium forms |
| Surface Finish | Superior - smooth, consistent titanium surfaces | Rougher finishes requiring secondary processing |
| Production Speed | Moderate - Suitable for medium batch titanium parts | Fast - Ideal for high volume titanium manufacturing |
| Cost | Higher initial setup, reduces titanium scrap costs | Lower setup, higher titanium material costs |
| Strength and Durability | Enhanced - Uniform stress distribution in titanium | Variable - Potential for stress points in titanium parts |
Introduction to Titanium Forming Techniques
Hydroforming and press forming are key titanium forming techniques used in aerospace and automotive industries to create lightweight, complex shapes with high strength-to-weight ratios. Hydroforming utilizes fluid pressure to shape titanium sheets uniformly, minimizing material stress and enhancing structural integrity. Press forming applies mechanical force with dies to shape titanium components, offering high precision but potentially increased risk of localized material deformation.
Overview of Hydroforming for Titanium
Hydroforming for titanium involves using high-pressure hydraulic fluid to shape titanium sheets or tubes into complex geometries with uniform thickness and minimal stress. This method enhances material strength and reduces weight, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications requiring precision and durability. Compared to press forming, hydroforming offers superior flexibility and the ability to produce intricate designs without the need for multiple tooling changes.
Press Forming Process in Titanium Fabrication
Press forming in titanium fabrication involves shaping titanium sheets using high-pressure mechanical presses, enabling precise and consistent component production. This process excels in producing complex geometries with tight tolerances while maintaining the metal's strength and corrosion resistance. Titanium press forming is widely used in aerospace and automotive industries due to its efficiency and ability to produce lightweight, high-performance parts.
Material Properties: Hydroforming vs Press Forming
Hydroforming of titanium offers superior control over complex geometries while preserving the metal's high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, minimizing work hardening and maintaining ductility. Press forming applies localized mechanical forces that can induce residual stresses and potential microstructural changes, affecting titanium's fatigue resistance and toughness. The choice between hydroforming and press forming directly impacts the material properties, with hydroforming generally providing enhanced formability and better structural integrity for high-performance titanium components.
Precision and Complexity of Titanium Components
Hydroforming offers superior precision for titanium components, allowing intricate shapes with uniform wall thickness and minimal material stress, essential for aerospace and medical applications. Press forming, while effective for simpler geometries, often struggles with the complexity and precision required for advanced titanium parts due to potential springback and uneven deformation. The hydroforming process enhances repeatability and dimensional accuracy, making it the preferred method for complex titanium component manufacturing.
Tooling and Equipment Requirements
Hydroforming titanium requires high-pressure fluid systems and flexible dies capable of withstanding extreme stresses, optimizing material flow and reducing springback for complex geometries. Press forming of titanium relies on robust mechanical presses and rigid steel dies designed to handle high forming loads, often necessitating additional lubrication and precise temperature control to prevent cracking. Tooling for hydroforming typically demands advanced sealing technologies and corrosion-resistant materials, whereas press forming tools focus on durability and repetitive impact resistance.
Cost Efficiency: Comparing Both Methods
Hydroforming offers superior cost efficiency for complex titanium parts by reducing material waste and tool maintenance compared to press forming. Press forming incurs higher expenses due to frequent die replacements and increased energy consumption during high-force operations. Overall, hydroforming minimizes production costs in low to medium volume titanium manufacturing, making it a more economical choice.
Surface Finish and Structural Integrity
Hydroforming titanium offers superior surface finish due to uniform fluid pressure, minimizing tool marks and reducing surface defects compared to press forming. The process enhances structural integrity by evenly distributing stress, which decreases the risk of micro-cracks and distortions common in traditional press-formed titanium components. This makes hydroforming ideal for producing complex, high-precision titanium parts requiring consistent mechanical properties and aesthetic quality.
Application Suitability in Aerospace and Medical
Hydroforming is ideal for aerospace components requiring complex geometries and lightweight strength, such as titanium airframe structures, due to its ability to produce seamless, high-precision parts with reduced material waste. Press forming suits medical applications like titanium implants and surgical devices where consistent thickness and surface finish are critical for biocompatibility and durability. The choice between hydroforming and press forming depends on titanium part complexity, production volume, and mechanical performance requirements specific to aerospace or medical sectors.
Choosing the Right Method for Titanium Forming
Hydroforming titanium offers superior precision and uniform thickness distribution, making it ideal for complex, lightweight aerospace components where strength-to-weight ratio is critical. Press forming excels in high-volume production with simpler geometries, providing cost-effective and rapid shaping for automotive and industrial parts. Selecting the right method depends on application complexity, dimensional accuracy requirements, and production volume constraints.
Hydroforming vs Press Forming Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com