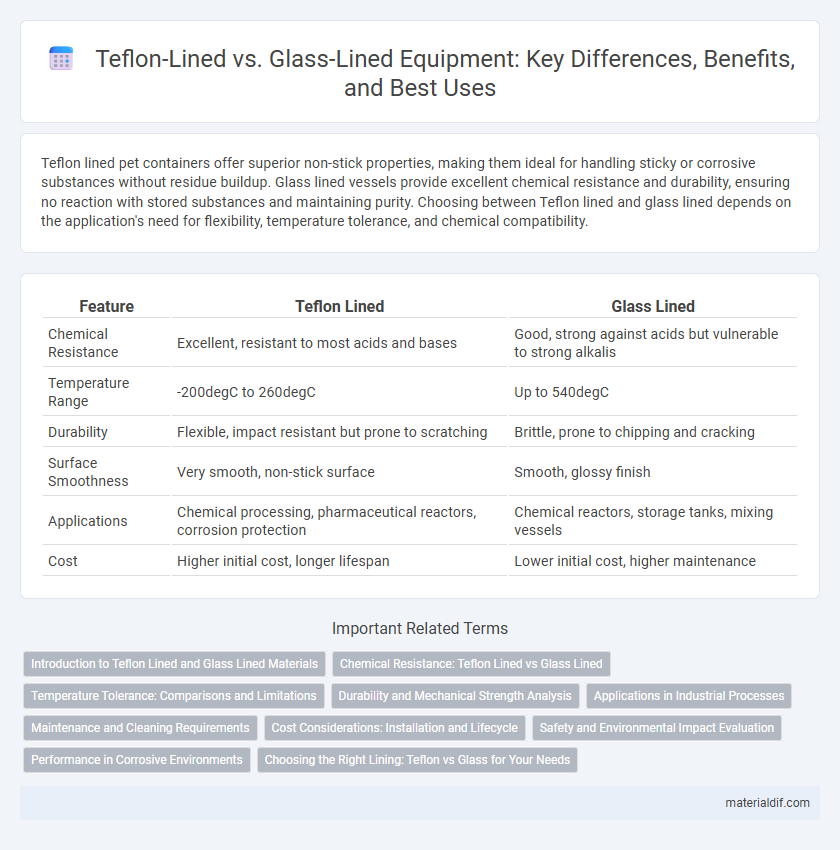
Teflon lined pet containers offer superior non-stick properties, making them ideal for handling sticky or corrosive substances without residue buildup. Glass lined vessels provide excellent chemical resistance and durability, ensuring no reaction with stored substances and maintaining purity. Choosing between Teflon lined and glass lined depends on the application's need for flexibility, temperature tolerance, and chemical compatibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Teflon Lined | Glass Lined |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to most acids and bases | Good, strong against acids but vulnerable to strong alkalis |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 260degC | Up to 540degC |
| Durability | Flexible, impact resistant but prone to scratching | Brittle, prone to chipping and cracking |
| Surface Smoothness | Very smooth, non-stick surface | Smooth, glossy finish |
| Applications | Chemical processing, pharmaceutical reactors, corrosion protection | Chemical reactors, storage tanks, mixing vessels |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, longer lifespan | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance |
Introduction to Teflon Lined and Glass Lined Materials
Teflon lined materials feature a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coating known for exceptional chemical resistance and non-stick properties, commonly used in corrosive environments to prevent contamination and extend equipment life. Glass lined materials consist of a fused glass coating bonded to metal substrates, offering high durability and resistance to acidic and alkaline substances, often preferred in pharmaceutical and chemical processing industries. Both materials provide protective barriers but differ in thermal tolerance and mechanical strength, influencing their application based on process requirements and chemical compatibility.
Chemical Resistance: Teflon Lined vs Glass Lined
Teflon lined surfaces provide superior chemical resistance against a wide range of aggressive acids, alkalis, and solvents compared to glass lined materials, making them ideal for handling highly reactive substances. Glass lined equipment offers good resistance to corrosion but is more susceptible to chipping and damage from thermal shock or mechanical impact, which can compromise chemical resistance. The non-porous, inert nature of Teflon ensures minimal interaction with corrosive agents, prolonging equipment lifespan in harsh chemical environments.
Temperature Tolerance: Comparisons and Limitations
Teflon-lined equipment offers excellent temperature tolerance up to approximately 260degC (500degF), making it ideal for many chemical processing applications requiring non-stick and corrosion resistance properties. In contrast, glass-lined vessels typically withstand higher temperatures, often up to 540degC (1000degF), providing superior thermal durability for processes involving extreme heat. However, glass lining is more brittle and prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes, whereas Teflon lining provides better flexibility but has a lower maximum temperature limit.
Durability and Mechanical Strength Analysis
Teflon-lined materials exhibit superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties but have lower mechanical strength and durability compared to glass-lined coatings, which offer enhanced abrasion resistance and robustness under high pressure and temperature conditions. Glass lining provides excellent longevity in industrial applications due to its hardness and ability to withstand mechanical shocks, making it suitable for reactors and vessels subjected to rigorous use. Teflon's flexibility and corrosion resistance make it ideal for environments with aggressive chemicals, though it requires careful handling to prevent surface damage and degradation over time.
Applications in Industrial Processes
Teflon-lined equipment excels in chemical processing industries due to its exceptional resistance to corrosive acids and solvents, making it ideal for handling highly aggressive substances in reactors and storage tanks. Glass-lined vessels, known for their smooth, inert surface, are preferred in pharmaceutical and food industries where contamination prevention and easy cleaning are critical. Both linings enhance durability and chemical resistance, but Teflon offers superior flexibility and temperature tolerance, whereas glass lining provides excellent abrasion resistance and thermal stability.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Teflon-lined equipment requires minimal maintenance due to its non-stick surface, which resists corrosion and chemical buildup, enabling easy cleaning with mild detergents. Glass-lined vessels demand more careful handling to avoid chipping and cracking, with cleaning often involving specialized, non-abrasive agents to preserve the glass integrity. The superior chemical resistance and smoothness of Teflon surfaces reduce downtime and cleaning frequency compared to glass-lined alternatives.
Cost Considerations: Installation and Lifecycle
Teflon-lined equipment typically incurs higher initial installation costs due to the specialized application process and material expenses but offers superior chemical resistance and ease of maintenance, potentially lowering lifecycle costs. Glass-lined vessels often have lower upfront costs but can face higher repair and replacement expenses over time because of glass coating brittleness and susceptibility to damage. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires balancing upfront investment against durability, maintenance frequency, and specific operational conditions.
Safety and Environmental Impact Evaluation
Teflon-lined equipment offers superior chemical resistance and non-reactivity, minimizing contamination risks and ensuring safer handling of aggressive substances compared to glass-lined alternatives. Teflon's inert properties reduce the release of hazardous compounds, enhancing workplace safety and reducing environmental pollution during production and disposal. Glass-lined surfaces, while durable, can chip and expose reactive metal substrates, potentially leading to contamination and environmental hazards, making Teflon lining a more environmentally sustainable choice.
Performance in Corrosive Environments
Teflon-lined equipment offers superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties, making it highly effective in handling aggressive corrosive substances without degradation. Glass-lined surfaces provide excellent resistance to acids and alkalis but are more prone to chipping and cracking under mechanical stress. In corrosive environments, Teflon linings ensure longer durability and lower maintenance due to their flexibility and resistance to a broader range of chemicals compared to glass linings.
Choosing the Right Lining: Teflon vs Glass for Your Needs
Teflon lined surfaces offer exceptional chemical resistance and non-stick properties, making them ideal for processing highly corrosive or sticky substances in industrial applications. Glass lined equipment provides superior resistance to thermal shock and abrasion, suitable for high-temperature reactions and frequent cleaning cycles. Selecting between Teflon and glass linings depends on factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature range, mechanical durability, and process requirements.
Teflon lined vs Glass lined Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com