Latex rubber, derived from natural rubber trees, offers excellent elasticity, resilience, and biodegradability, making it ideal for medical gloves and balloons. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic alternative, provides superior chemical resistance, puncture durability, and hypoallergenic properties, suitable for industrial gloves and automotive parts. Choosing between latex and nitrile rubber depends on specific application needs, including sensitivity to allergens and exposure to harsh chemicals.
Table of Comparison
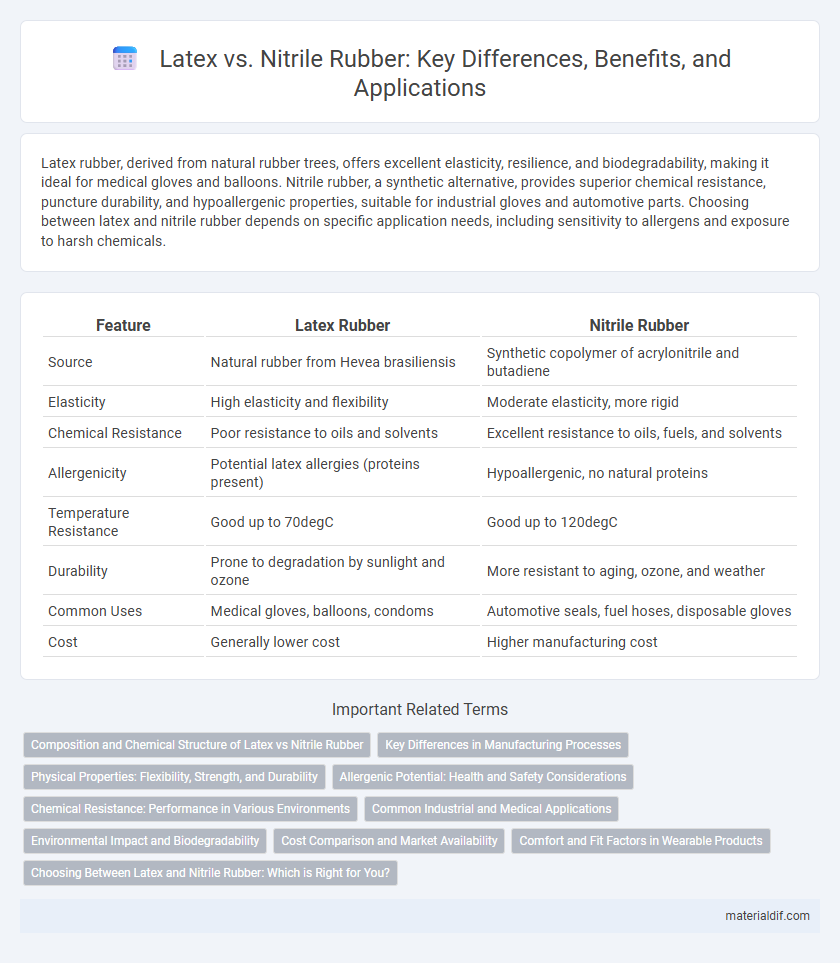
| Feature | Latex Rubber | Nitrile Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural rubber from Hevea brasiliensis | Synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility | Moderate elasticity, more rigid |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor resistance to oils and solvents | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents |
| Allergenicity | Potential latex allergies (proteins present) | Hypoallergenic, no natural proteins |
| Temperature Resistance | Good up to 70degC | Good up to 120degC |
| Durability | Prone to degradation by sunlight and ozone | More resistant to aging, ozone, and weather |
| Common Uses | Medical gloves, balloons, condoms | Automotive seals, fuel hoses, disposable gloves |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
Composition and Chemical Structure of Latex vs Nitrile Rubber
Latex, primarily composed of natural cis-1,4-polyisoprene, is a biodegradable polymer derived from Hevea brasiliensis trees, characterized by its amorphous structure and high elasticity. Nitrile rubber (NBR) consists of copolymers of acrylonitrile and butadiene, featuring polar acrylonitrile units that impart resistance to oils and chemicals, with a more crystalline microstructure compared to natural latex. The divergence in chemical composition and molecular architecture between latex and nitrile rubber directly influences their mechanical properties and application suitability in environments requiring flexibility versus chemical resistance.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Processes
Latex rubber is derived from natural rubber trees through a tapping process that collects the milky sap, which is then centrifuged and vulcanized to enhance elasticity and durability. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic variant, is produced via copolymerization of acrylonitrile and butadiene monomers, involving emulsion polymerization that allows customization of chemical resistance and mechanical properties. The manufacturing of latex emphasizes natural extraction and minimal chemical modification, whereas nitrile rubber relies on complex synthetic polymer chemistry for specialized applications.
Physical Properties: Flexibility, Strength, and Durability
Latex rubber offers superior flexibility and elasticity, making it ideal for products requiring high stretchability and comfort. Nitrile rubber exhibits greater strength and resistance to abrasion, oils, and chemicals, enhancing its durability in harsh environments. While latex excels in softness and flexibility, nitrile provides enhanced toughness and resilience for industrial applications.
Allergenic Potential: Health and Safety Considerations
Latex rubber, derived from natural rubber latex, contains proteins that can trigger allergic reactions ranging from mild skin irritation to severe anaphylaxis, posing health risks for sensitive individuals. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic alternative, is free from natural latex proteins, significantly reducing allergenic potential and making it safer for use in medical gloves and products requiring direct skin contact. Choosing nitrile over latex is a critical health and safety consideration in environments where allergen exposure must be minimized.
Chemical Resistance: Performance in Various Environments
Latex rubber offers excellent elasticity and comfort but has limited chemical resistance, particularly vulnerable to oils, solvents, and certain acids. Nitrile rubber demonstrates superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for environments exposed to petroleum-based products, oils, and greases. Its robustness against chemicals extends the lifespan of gloves and seals in harsh industrial and automotive applications.
Common Industrial and Medical Applications
Latex rubber, derived from natural rubber trees, is widely used in medical gloves, surgical equipment, and catheters due to its excellent elasticity, comfort, and biodegradability. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic alternative, offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and punctures, making it ideal for industrial gloves, seals, and hoses in automotive and chemical manufacturing. Both materials are critical in healthcare and industrial sectors, with latex favored for sensitivity and nitrile preferred for durability and chemical protection.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Latex rubber, derived from natural rubber trees, is biodegradable and has a significantly lower environmental impact due to its renewable origin and ability to decompose naturally in soil. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic polymer made from petroleum-based chemicals, is non-biodegradable and contributes to long-term environmental pollution through persistent waste. Choosing latex over nitrile rubber supports sustainable practices by reducing synthetic waste and promoting eco-friendly material cycles.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Latex rubber generally offers lower production costs due to its natural sourcing from rubber trees, making it more economical for large-scale applications. Nitrile rubber, derived from synthetic copolymerization of butadiene and acrylonitrile, commands higher prices attributed to its enhanced chemical resistance and durability. Market availability of latex is widespread in regions with established rubber plantations, while nitrile rubber dominates industrial sectors requiring oil and chemical resistance, often resulting in fluctuating supply based on petrochemical market trends.
Comfort and Fit Factors in Wearable Products
Latex rubber offers superior elasticity and conformability, providing a snug fit ideal for wearable products requiring high tactile sensitivity and comfort. Nitrile rubber, while less elastic, excels in durability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for gloves where protection outweighs the need for extreme flexibility. The choice between latex and nitrile significantly impacts user comfort and fit, with latex preferred for extended wear due to its soft, flexible nature.
Choosing Between Latex and Nitrile Rubber: Which is Right for You?
Latex rubber offers excellent elasticity and biodegradability, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and eco-friendliness, such as medical gloves and balloons. Nitrile rubber provides superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and punctures, often preferred in industrial and automotive settings where durability and protection are essential. Selecting between latex and nitrile rubber depends on specific use cases, with latex suited for sensitive skin and environmental concerns, while nitrile excels in harsh chemical exposure and mechanical resilience.
Latex vs Nitrile Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com