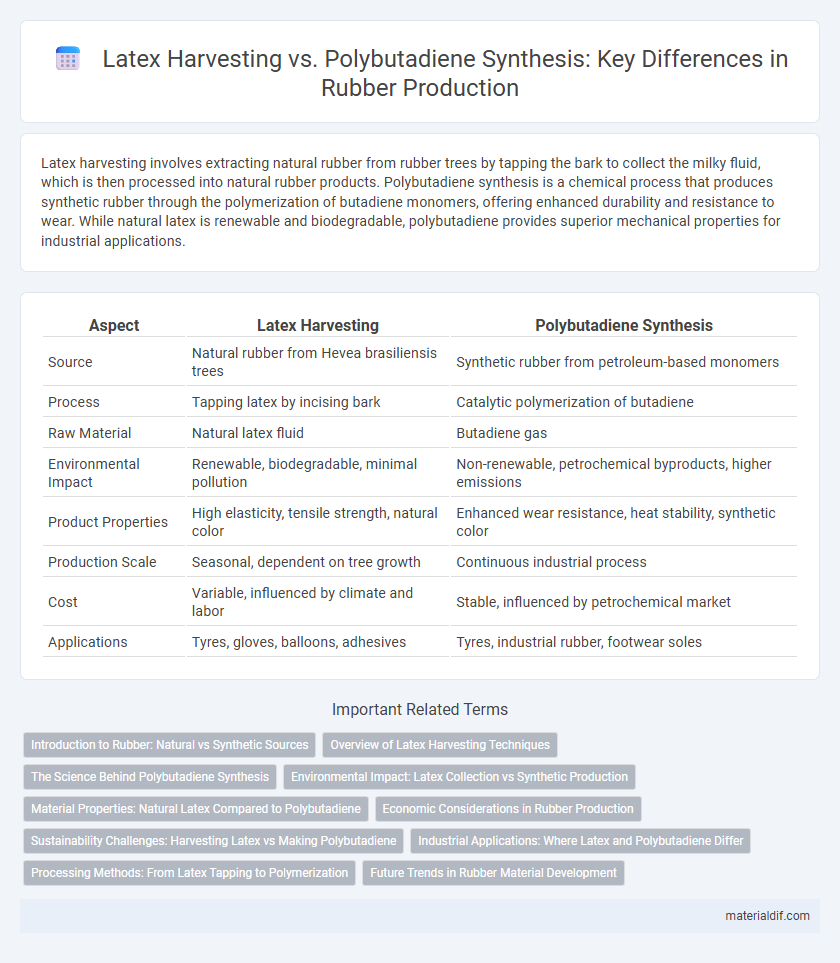
Latex harvesting involves extracting natural rubber from rubber trees by tapping the bark to collect the milky fluid, which is then processed into natural rubber products. Polybutadiene synthesis is a chemical process that produces synthetic rubber through the polymerization of butadiene monomers, offering enhanced durability and resistance to wear. While natural latex is renewable and biodegradable, polybutadiene provides superior mechanical properties for industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Latex Harvesting | Polybutadiene Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural rubber from Hevea brasiliensis trees | Synthetic rubber from petroleum-based monomers |
| Process | Tapping latex by incising bark | Catalytic polymerization of butadiene |
| Raw Material | Natural latex fluid | Butadiene gas |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, minimal pollution | Non-renewable, petrochemical byproducts, higher emissions |
| Product Properties | High elasticity, tensile strength, natural color | Enhanced wear resistance, heat stability, synthetic color |
| Production Scale | Seasonal, dependent on tree growth | Continuous industrial process |
| Cost | Variable, influenced by climate and labor | Stable, influenced by petrochemical market |
| Applications | Tyres, gloves, balloons, adhesives | Tyres, industrial rubber, footwear soles |
Introduction to Rubber: Natural vs Synthetic Sources
Natural rubber is derived from latex, a milky fluid harvested primarily from Hevea brasiliensis trees through a process called tapping, which involves carefully incising the bark to collect the latex without harming the tree. Synthetic rubber, such as polybutadiene, is produced through chemical polymerization of monomers derived from petroleum byproducts, offering controlled properties and consistency. The distinct sourcing methods--biological extraction for natural rubber and industrial synthesis for polybutadiene--highlight the fundamental differences in raw materials, sustainability, and applications of each rubber type.
Overview of Latex Harvesting Techniques
Latex harvesting techniques primarily involve tapping Hevea brasiliensis trees, where incisions allow the natural latex sap to flow into collection cups, representing the most traditional and sustainable method. Efficient tapping methods, such as spiral and half-spiral cuts, optimize latex yield while minimizing tree damage and ensuring continuous production over multiple years. Modern advancements include stimulant applications like ethephon to enhance latex flow and precision tapping tools that improve harvesting accuracy and reduce tree stress.
The Science Behind Polybutadiene Synthesis
Polybutadiene synthesis involves the polymerization of 1,3-butadiene monomers through anionic or coordination polymerization techniques to produce a high-molecular-weight synthetic rubber. The process enables precise control over microstructure, including cis-1,4, trans-1,4, and 1,2-vinyl configurations, which directly influence the polymer's mechanical properties such as elasticity, abrasion resistance, and resilience. Unlike natural latex harvesting from Hevea brasiliensis trees, polybutadiene production relies on petrochemical feedstocks and advanced catalysts to tailor rubber characteristics for specific industrial applications like tire manufacturing and impact-resistant materials.
Environmental Impact: Latex Collection vs Synthetic Production
Latex harvesting involves tapping rubber trees to collect natural latex, a renewable process with a lower carbon footprint due to minimal energy use and biodegradability of by-products. In contrast, polybutadiene synthesis relies on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, fossil fuel depletion, and chemical waste concerns. Sustainable latex collection supports biodiversity and carbon sequestration, whereas synthetic rubber production poses risks of environmental pollution and resource scarcity.
Material Properties: Natural Latex Compared to Polybutadiene
Natural latex, harvested from rubber trees, exhibits high elasticity, excellent tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance due to its molecular structure of cis-1,4-polyisoprene. In contrast, polybutadiene, a synthetic rubber produced via chemical polymerization, offers enhanced low-temperature flexibility and exceptional impact resistance, making it ideal for tire manufacturing. While natural latex provides biodegradability and hypoallergenic properties, polybutadiene excels in durability and chemical resistance under harsh industrial conditions.
Economic Considerations in Rubber Production
Latex harvesting from Hevea brasiliensis provides a renewable and labor-intensive source of natural rubber with fluctuating market prices influenced by climate and labor costs. In contrast, polybutadiene synthesis, derived from petrochemical feedstocks, offers consistent quality and scalable production but is subject to volatile oil prices and higher capital investments. Economic considerations in rubber production weigh the lower raw material costs and environmental benefits of latex against the reliability and controlled properties of synthetic polybutadiene rubber.
Sustainability Challenges: Harvesting Latex vs Making Polybutadiene
Latex harvesting relies on natural rubber trees, promoting renewable resource use but faces challenges such as deforestation, biodiversity loss, and labor-intensive practices. Polybutadiene synthesis depends on petrochemical feedstocks, resulting in significant carbon emissions and resource depletion. Sustainable solutions require balancing ecological impacts of rubber plantations with innovations in green chemistry and bio-based synthetic rubber alternatives.
Industrial Applications: Where Latex and Polybutadiene Differ
Latex harvesting from rubber trees provides a natural, renewable source of high-quality latex used extensively in medical gloves, balloons, and adhesives due to its elasticity and biodegradability. Polybutadiene synthesis, a chemical process derived from petroleum, produces synthetic rubber essential for manufacturing durable tires, golf balls, and automotive parts, offering superior wear resistance and low-temperature performance. Industrial applications of natural latex prioritize flexibility and eco-friendliness, while polybutadiene is favored for its strength, abrasion resistance, and versatility in heavy-duty manufacturing.
Processing Methods: From Latex Tapping to Polymerization
Latex harvesting involves the careful tapping of Hevea brasiliensis trees to collect natural latex, which undergoes coagulation and centrifugation to produce raw rubber. In contrast, polybutadiene synthesis relies on polymerization techniques such as emulsion or solution polymerization to create synthetic rubber from butadiene monomers. These distinct processing methods impact the elasticity, durability, and application of the final rubber products, influencing industries from tire manufacturing to medical devices.
Future Trends in Rubber Material Development
Latex harvesting remains essential for producing natural rubber with unmatched elasticity and sustainability. Polybutadiene synthesis advances the development of high-performance synthetic rubber by enabling tailored molecular structures for enhanced durability and heat resistance. Future trends emphasize hybrid materials integrating natural latex and polybutadiene polymers to achieve superior mechanical properties and environmental resilience.
Latex Harvesting vs Polybutadiene Synthesis Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com