Anti-static rubber prevents the buildup of static electricity by dissipating electrical charges at a slow rate, making it ideal for environments sensitive to static discharge. Conductive rubber, on the other hand, offers a much higher level of electrical conductivity, allowing current to pass through easily for applications requiring efficient grounding or electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Choosing between anti-static and conductive rubber depends on the specific electrical needs, with anti-static providing surface charge control and conductive rubber enabling complete electrical conduction.
Table of Comparison
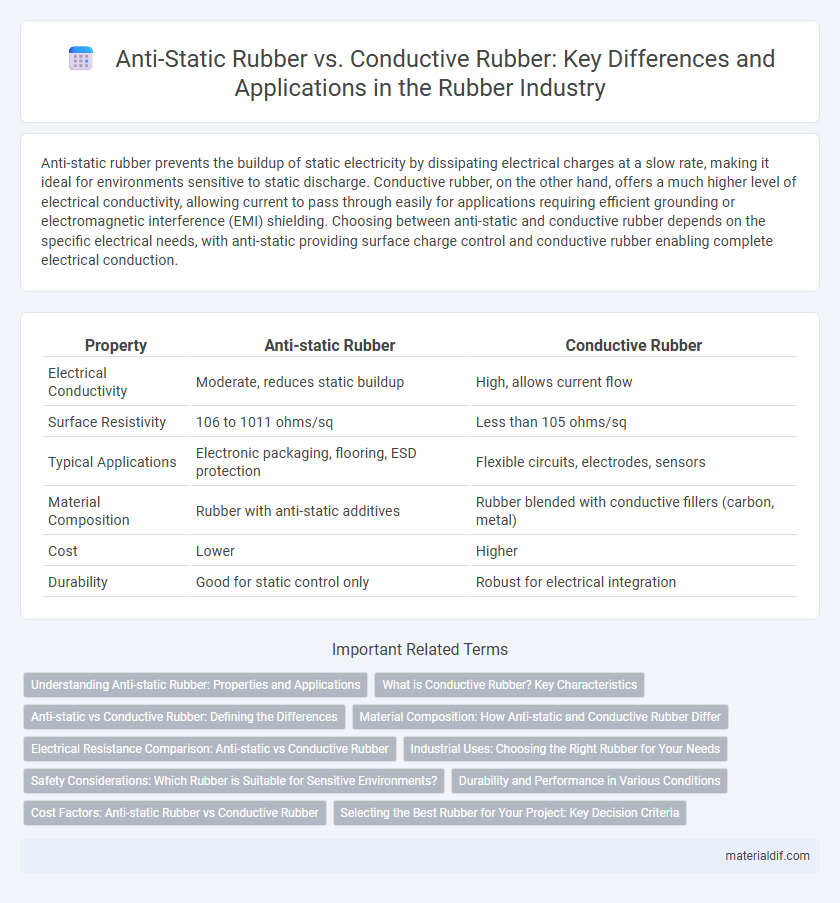
| Property | Anti-static Rubber | Conductive Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate, reduces static buildup | High, allows current flow |
| Surface Resistivity | 106 to 1011 ohms/sq | Less than 105 ohms/sq |
| Typical Applications | Electronic packaging, flooring, ESD protection | Flexible circuits, electrodes, sensors |
| Material Composition | Rubber with anti-static additives | Rubber blended with conductive fillers (carbon, metal) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Durability | Good for static control only | Robust for electrical integration |
Understanding Anti-static Rubber: Properties and Applications
Anti-static rubber is designed to prevent the buildup of static electricity by allowing a controlled dissipation of electrical charges, featuring surface resistivity typically between 10^6 to 10^11 ohms. It is commonly used in applications such as electronic device housing, flooring, and protective mats where static charge reduction is critical to prevent damage or interference. Unlike conductive rubber, which has much lower resistivity and is used to create electrical pathways, anti-static rubber provides intermediate resistance to minimize static without conducting electricity freely.
What is Conductive Rubber? Key Characteristics
Conductive rubber is a type of rubber composite embedded with conductive fillers such as carbon black, metal particles, or conductive polymers, enabling it to conduct electricity. Key characteristics include low electrical resistance, flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and temperature fluctuations. These properties make conductive rubber ideal for applications in electronics, sensors, and electromagnetic interference shielding.
Anti-static vs Conductive Rubber: Defining the Differences
Anti-static rubber prevents the buildup of static electricity by dissipating electrical charges slowly, making it ideal for environments sensitive to static discharge such as electronics manufacturing. Conductive rubber, on the other hand, offers a lower electrical resistance, enabling it to conduct current efficiently and is commonly used in applications requiring reliable electrical grounding or shielding. The primary difference lies in conductivity levels: anti-static rubber targets moderate resistance to control static, while conductive rubber ensures continuous electrical flow for effective conductivity.
Material Composition: How Anti-static and Conductive Rubber Differ
Anti-static rubber incorporates additives like carbon black or metal oxides in low concentrations to dissipate static electricity without allowing significant current flow. Conductive rubber contains higher amounts of conductive fillers such as carbon nanotubes or silver particles, creating a continuous conductive network for efficient electrical conductivity. The variation in filler type and concentration directly influences their electrical properties and specific industrial applications.
Electrical Resistance Comparison: Anti-static vs Conductive Rubber
Anti-static rubber typically exhibits electrical resistance ranging from 10^5 to 10^11 ohms, effectively dissipating static charges without allowing continuous current flow. Conductive rubber, in contrast, has much lower resistance, usually between 10^-2 to 10^5 ohms, enabling efficient electrical conductivity for grounding and shielding applications. The significant difference in electrical resistance directly influences their suitability: anti-static rubber prevents static buildup, while conductive rubber facilitates consistent electrical current passage.
Industrial Uses: Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Anti-static rubber is ideal for industrial applications where preventing static discharge is crucial, such as electronics manufacturing and packaging, due to its ability to dissipate static electricity without conducting current. Conductive rubber is suited for environments requiring efficient electrical conductivity, including grounding components and EMI shielding in industrial machinery. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific industrial needs: choose anti-static rubber for static control and conductive rubber for electrical conduction and grounding purposes.
Safety Considerations: Which Rubber is Suitable for Sensitive Environments?
Anti-static rubber reduces static electricity build-up by dissipating charges slowly, making it ideal for environments with sensitive electronic equipment where preventing static discharge is critical. Conductive rubber, with its higher electrical conductivity, offers rapid charge dissipation but may pose risks of unintended current flow, potentially compromising sensitive device safety. For safety considerations in sensitive environments, anti-static rubber is generally preferred due to its controlled charge dissipation and reduced risk of electrical hazards.
Durability and Performance in Various Conditions
Anti-static rubber provides moderate durability with resistance to static charge buildup in dry and clean environments, making it suitable for electronic applications. Conductive rubber excels in performance under harsher conditions such as moisture and mechanical stress due to its enhanced electrical conductivity and structural integrity. Both materials offer specific advantages, but conductive rubber generally outperforms anti-static rubber in longevity and reliability across diverse industrial settings.
Cost Factors: Anti-static Rubber vs Conductive Rubber
Anti-static rubber typically incurs lower manufacturing costs due to less complex additives and simpler production processes compared to conductive rubber. Conductive rubber requires expensive conductive fillers like carbon black or metal particles to achieve higher electrical conductivity, increasing raw material expenses. The choice between anti-static and conductive rubber significantly impacts overall project budget considerations based on performance requirements and electrical resistance levels.
Selecting the Best Rubber for Your Project: Key Decision Criteria
Anti-static rubber prevents buildup of static electricity by dissipating charges and is ideal for environments sensitive to static discharge, while conductive rubber offers higher electrical conductivity for applications requiring efficient current flow. Key decision criteria include the specific electrical resistance requirements, environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature, and the mechanical properties needed for durability and flexibility. Understanding these factors ensures selecting the best rubber type that balances conductivity, safety, and performance for your project's unique demands.
Anti-static Rubber vs Conductive Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com