Low viscosity resin offers superior flowability, making it ideal for intricate molds and detailed casting where precision is crucial. High viscosity resin provides greater thickness and strength, suitable for applications requiring durable, impact-resistant finishes. Selecting between these resins depends on the balance between ease of use and the structural requirements of the final product.
Table of Comparison
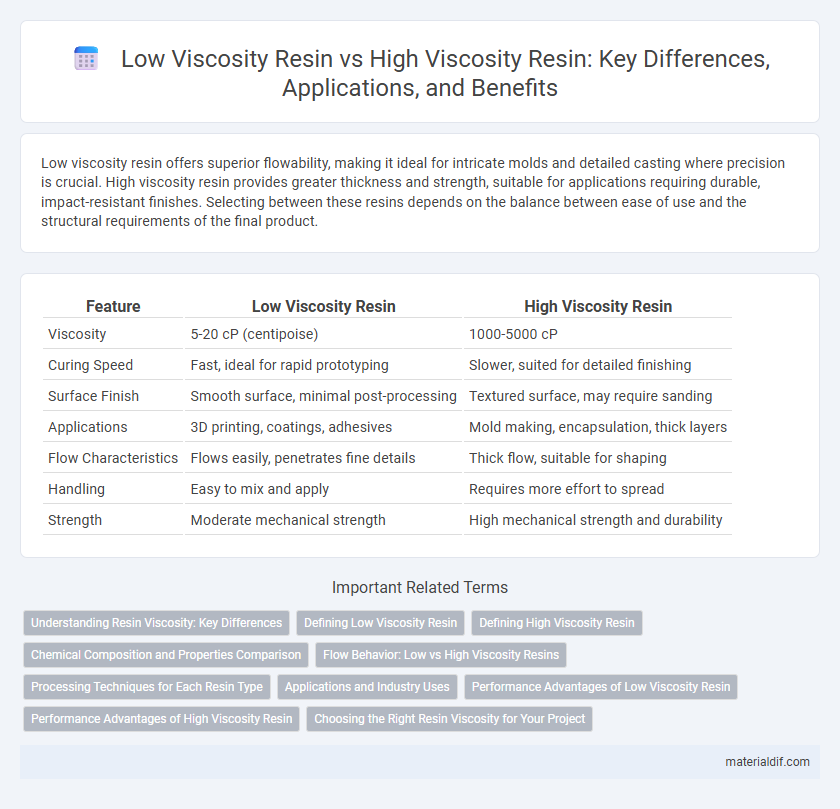
| Feature | Low Viscosity Resin | High Viscosity Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | 5-20 cP (centipoise) | 1000-5000 cP |
| Curing Speed | Fast, ideal for rapid prototyping | Slower, suited for detailed finishing |
| Surface Finish | Smooth surface, minimal post-processing | Textured surface, may require sanding |
| Applications | 3D printing, coatings, adhesives | Mold making, encapsulation, thick layers |
| Flow Characteristics | Flows easily, penetrates fine details | Thick flow, suitable for shaping |
| Handling | Easy to mix and apply | Requires more effort to spread |
| Strength | Moderate mechanical strength | High mechanical strength and durability |
Understanding Resin Viscosity: Key Differences
Low viscosity resin flows smoothly and penetrates intricate molds, making it ideal for detailed casting and easy application in 3D printing or encapsulation processes. High viscosity resin has a thicker consistency, providing greater structural support and durability for applications requiring enhanced mechanical strength and resistance. Understanding these key differences allows for selecting the appropriate resin type based on project requirements such as curing time, surface finish, and environmental exposure.
Defining Low Viscosity Resin
Low viscosity resin is characterized by its thin, fluid consistency, allowing for easy flow and penetration into detailed molds or intricate surfaces. This type of resin typically exhibits a viscosity below 1000 centipoises, making it ideal for applications requiring fast curing and high-resolution finishes. Compared to high viscosity resin, low viscosity formulas enable smoother casting processes, reduced air bubble entrapment, and enhanced adhesion to substrates.
Defining High Viscosity Resin
High viscosity resin is characterized by its thick, syrup-like consistency, which slows its flow and curing process compared to low viscosity resin. This type of resin is ideal for applications requiring structural strength, gap filling, or minimal penetration into porous surfaces due to its dense molecular composition. High viscosity resins typically exhibit superior mechanical properties such as enhanced toughness, abrasion resistance, and improved bonding in composite materials.
Chemical Composition and Properties Comparison
Low viscosity resin typically contains lower molecular weight oligomers and fewer crosslinking agents, resulting in reduced polymer chain entanglement and improved flow characteristics, which enhance ease of application and faster curing times. High viscosity resin is characterized by higher molecular weight components and increased crosslink density, providing superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability but requiring elevated temperatures or pressure for proper molding. The chemical composition directly influences resin properties, where low viscosity resins are favored for thin coatings or detailed molding, while high viscosity resins are optimal for structural composites demanding higher load-bearing capacity.
Flow Behavior: Low vs High Viscosity Resins
Low viscosity resin exhibits superior flow behavior, allowing it to penetrate intricate molds and detailed patterns with ease, making it ideal for applications requiring fine resolution. High viscosity resin flows more slowly, offering better control in applications demanding thicker layers or structural stability but risking incomplete mold filling in complex geometries. Selecting the appropriate resin viscosity depends on balancing flow characteristics with the desired application's precision and mechanical requirements.
Processing Techniques for Each Resin Type
Low viscosity resin enables faster mixing and easier mold filling, making it ideal for infusion, injection molding, and resin transfer molding (RTM) processes where thorough fiber wet-out is critical. High viscosity resin demands higher pressure or temperature during processing, suitable for hand lay-up, spray-up, and compression molding techniques where controlled flow and reduced resin runoff are necessary. Selecting the appropriate processing technique based on resin viscosity optimizes cure time, surface finish, and mechanical performance in composite manufacturing.
Applications and Industry Uses
Low viscosity resin is ideal for applications requiring deep penetration and fast curing, such as in electronics potting, composite molding, and coatings for intricate surfaces in aerospace and automotive industries. High viscosity resin is preferred in structural applications where thickness and gap-filling are necessary, including marine composites, construction adhesives, and heavy-duty laminates. Both types serve critical roles in industrial manufacturing, with viscosity selection significantly influencing processing techniques and final product performance.
Performance Advantages of Low Viscosity Resin
Low viscosity resin offers superior penetration and wetting capabilities, enhancing adhesion and reducing void formation in composite materials. Its fluidity enables faster application and better surface coverage, improving curing efficiency and mechanical strength. These performance advantages make low viscosity resin ideal for high-precision coatings and advanced composite manufacturing.
Performance Advantages of High Viscosity Resin
High viscosity resin offers superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to low viscosity alternatives, making it ideal for applications requiring robust structural integrity. Its higher molecular weight contributes to improved thermal stability and resistance to deformation under stress. This type of resin also facilitates better bonding and adhesion in composite materials, resulting in longer-lasting and more reliable end products.
Choosing the Right Resin Viscosity for Your Project
Low viscosity resin flows easily, making it ideal for detailed molds, thin coatings, and projects requiring quick curing with minimal air bubbles. High viscosity resin is thicker, offering better control for casting larger objects, embedding items, or creating textured surfaces without excessive dripping. Selecting the right resin viscosity depends on project complexity, desired finish, and curing time, ensuring optimal results and durability.
Low Viscosity Resin vs High Viscosity Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com