Polystyrene foam offers excellent rigidity, moisture resistance, and insulation properties, making it ideal for packaging and structural applications. Polyurethane foam boasts superior flexibility, cushioning, and thermal insulation, commonly used in furniture, automotive seating, and bedding. Both materials provide effective insulation but differ significantly in durability, compressive strength, and application scope.
Table of Comparison
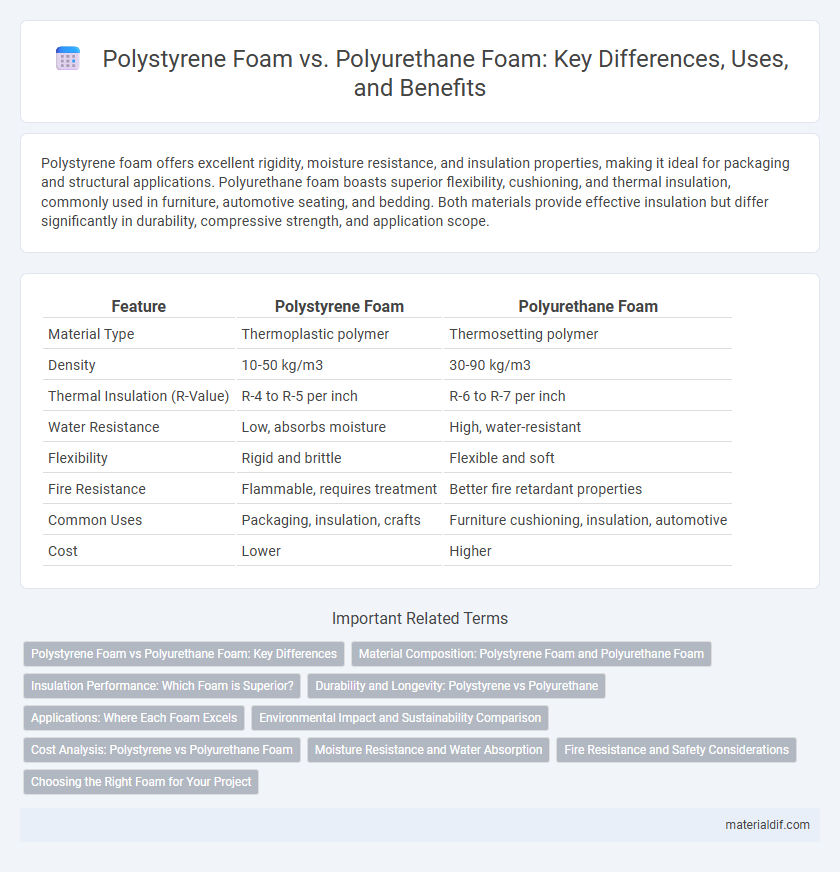
| Feature | Polystyrene Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermosetting polymer |
| Density | 10-50 kg/m3 | 30-90 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation (R-Value) | R-4 to R-5 per inch | R-6 to R-7 per inch |
| Water Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture | High, water-resistant |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Flexible and soft |
| Fire Resistance | Flammable, requires treatment | Better fire retardant properties |
| Common Uses | Packaging, insulation, crafts | Furniture cushioning, insulation, automotive |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Polystyrene Foam vs Polyurethane Foam: Key Differences
Polystyrene foam is a rigid, lightweight material known for its excellent insulation properties, making it ideal for packaging and thermal insulation applications, while polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and cushioning, commonly used in furniture and automotive seating. Polystyrene foam is more resistant to moisture and chemicals, whereas polyurethane foam provides better sound absorption and durability under compression. Price-wise, polystyrene foam tends to be more cost-effective for large-scale insulation, while polyurethane foam is preferred for comfort and impact resistance in specialized uses.
Material Composition: Polystyrene Foam and Polyurethane Foam
Polystyrene foam is composed primarily of expanded or extruded polystyrene beads, a polymer derived from styrene monomers, known for its rigid structure and excellent thermal insulation properties. Polyurethane foam consists of urethane polymers formed by the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a versatile material that offers flexibility, durability, and superior cushioning. The fundamental difference in chemical composition impacts their applications, with polystyrene foam favored for insulation and packaging, while polyurethane foam is preferred in furniture, automotive, and bedding industries.
Insulation Performance: Which Foam is Superior?
Polystyrene foam offers excellent thermal insulation with a typical R-value of 4 to 5 per inch, making it highly effective in reducing heat transfer. Polyurethane foam generally provides superior insulation performance, achieving R-values of 6 to 7 per inch due to its closed-cell structure that minimizes air infiltration. Its higher density and moisture resistance make polyurethane foam the preferred choice for energy-efficient building insulation where maximum thermal resistance is critical.
Durability and Longevity: Polystyrene vs Polyurethane
Polystyrene foam offers excellent resistance to moisture and chemical exposure, providing consistent durability in various applications, while polyurethane foam typically delivers superior flexibility and resilience under mechanical stress. The longevity of polystyrene foam is enhanced by its stable closed-cell structure, which resists degradation and maintains insulating properties over time, contrasting with polyurethane's tendency to compress and age faster in high-stress environments. Both materials have distinct performance profiles, with polystyrene favored for long-term insulation and polyurethane preferred for cushioning and impact absorption.
Applications: Where Each Foam Excels
Polystyrene foam excels in insulation for packaging, thermal insulation in construction, and lightweight structural components due to its rigidity and moisture resistance. Polyurethane foam is preferred for furniture, bedding, automotive seats, and soundproofing because of its superior flexibility, cushioning, and durability. Both foams serve distinct purposes; polystyrene for hard, protective applications, and polyurethane for comfort and impact absorption.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Comparison
Polystyrene foam produces higher levels of greenhouse gases during manufacturing and is less biodegradable compared to polyurethane foam, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Polyurethane foam, while also derived from petrochemicals, offers better energy efficiency due to its superior insulation properties, which can reduce overall carbon emissions in building applications. Both materials pose recycling challenges, but advancements in chemical recycling techniques for polyurethane foam demonstrate greater potential for sustainable reuse.
Cost Analysis: Polystyrene vs Polyurethane Foam
Polystyrene foam typically costs less per cubic foot compared to polyurethane foam, making it a budget-friendly option for insulation and packaging. Polyurethane foam provides superior thermal insulation and durability but comes at a higher price point, reflecting its enhanced performance characteristics. Cost-effectiveness depends on project requirements, with polystyrene favored for low-cost applications and polyurethane chosen for long-term energy savings and structural benefits.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Polystyrene foam exhibits superior moisture resistance and lower water absorption compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for applications where exposure to water is a concern. Closed-cell structures in polystyrene restrict water penetration, whereas polyurethane foam's open-cell composition tends to absorb more moisture. This difference significantly impacts insulation performance and durability in humid or wet environments.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Polystyrene foam exhibits lower fire resistance compared to polyurethane foam, as it ignites more easily and emits toxic fumes when burned, necessitating careful use in fire-sensitive applications. Polyurethane foam often contains flame retardants that enhance its fire resistance and reduce smoke production, making it a safer choice for insulation and cushioning in environments subject to fire regulations. Safety considerations require evaluating both materials' flame spread ratings and compliance with local fire codes to ensure optimal protection.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Project
Polystyrene foam offers excellent insulation with high rigidity, making it ideal for lightweight structural applications and packaging where moisture resistance is essential. Polyurethane foam provides superior flexibility and cushioning, suited for furniture, automotive interiors, and soundproofing projects requiring enhanced comfort and shock absorption. Selecting the right foam depends on project requirements such as thermal insulation, mechanical strength, moisture exposure, and budget constraints.
Polystyrene Foam vs Polyurethane Foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com