Polystyrene blocks are lightweight and inexpensive, making them ideal for cost-effective prototyping and model making, but they offer lower impact resistance and durability compared to polycarbonate blocks. Polycarbonate blocks provide superior strength, high impact resistance, and excellent thermal stability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications where durability is crucial. Choosing between polystyrene and polycarbonate blocks depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for mechanical performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
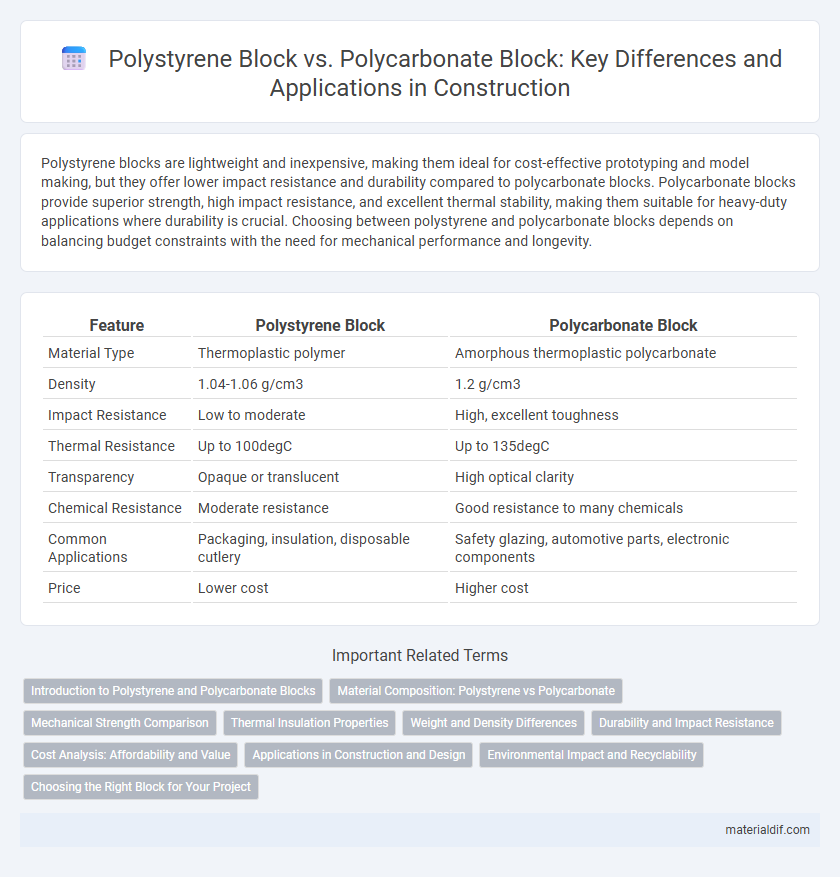
| Feature | Polystyrene Block | Polycarbonate Block |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Amorphous thermoplastic polycarbonate |
| Density | 1.04-1.06 g/cm3 | 1.2 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate | High, excellent toughness |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 135degC |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | High optical clarity |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | Good resistance to many chemicals |
| Common Applications | Packaging, insulation, disposable cutlery | Safety glazing, automotive parts, electronic components |
| Price | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polystyrene and Polycarbonate Blocks
Polystyrene blocks are lightweight, rigid foam materials widely used for insulation, packaging, and prototyping due to their excellent thermal properties and ease of shaping. In contrast, polycarbonate blocks offer superior impact resistance, clarity, and heat resistance, making them ideal for engineering applications requiring durability and transparency. Both materials serve distinct purposes: polystyrene excels in lightweight and cost-effective insulation, while polycarbonate provides strength and resilience for structural components.
Material Composition: Polystyrene vs Polycarbonate
Polystyrene blocks consist of a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer made from the monomer styrene, characterized by a rigid, transparent, and lightweight structure with excellent insulating properties. In contrast, polycarbonate blocks are composed of a durable thermoplastic polymer derived from bisphenol A and phosgene, known for its high impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat resistance. The distinct chemical compositions result in polystyrene offering superior insulation and cost-effectiveness, while polycarbonate provides enhanced strength and thermal stability for demanding applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polystyrene blocks exhibit lower mechanical strength compared to polycarbonate blocks, with tensile strength typically around 30-50 MPa versus polycarbonate's 60-70 MPa. Polycarbonate's superior impact resistance and higher flexural modulus make it more suitable for applications requiring durability and structural integrity. This strength difference is critical in engineering and manufacturing where load-bearing capacity and impact resistance are prioritized.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Polystyrene blocks exhibit superior thermal insulation properties due to their closed-cell foam structure, which reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency in building applications. In contrast, polycarbonate blocks have lower thermal resistance but offer greater impact resistance and durability, making them more suitable for environments demanding mechanical strength. Polystyrene's thermal conductivity typically ranges from 0.03 to 0.04 W/m*K, significantly outperforming polycarbonate's thermal conductivity of approximately 0.19 W/m*K.
Weight and Density Differences
Polystyrene blocks exhibit a density typically around 1.05 g/cm3, making them lighter compared to polycarbonate blocks, which have a density range of approximately 1.2 to 1.22 g/cm3. This difference in density directly impacts the weight, as polystyrene offers a lower weight solution in applications where reduced mass is critical. The lower weight of polystyrene blocks enhances ease of handling and transport, while polycarbonate blocks provide increased durability and strength due to their higher density.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Polystyrene blocks offer moderate impact resistance but are more prone to cracking and wear over time compared to polycarbonate blocks. Polycarbonate blocks demonstrate superior durability, with high impact resistance and excellent ability to withstand stress without deformation. This makes polycarbonate a preferred choice for applications requiring toughness and longevity under demanding conditions.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Value
Polystyrene blocks generally offer a more affordable option compared to polycarbonate blocks, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects without compromising basic structural needs. Polycarbonate blocks, though higher in cost, provide superior durability, impact resistance, and UV stability, delivering better long-term value in demanding environments. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement, often positions polycarbonate as the more economical choice for applications requiring enhanced performance.
Applications in Construction and Design
Polystyrene blocks are widely used in construction for thermal insulation, lightweight concrete forms, and soundproofing due to their excellent insulating properties and ease of shaping. Polycarbonate blocks offer superior impact resistance, transparency, and UV protection, making them ideal for architectural glazing, skylights, and structural panels in modern design projects. Their distinct mechanical and optical characteristics influence material choice based on project requirements for durability, aesthetics, and energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene blocks exhibit lower recyclability and often contribute to environmental pollution due to their slow degradation and difficulty in processing. Polycarbonate blocks, while more energy-intensive to produce, offer better recyclability and durability, reducing the frequency of replacement and long-term waste. The environmental impact of polystyrene is further compounded by its tendency to generate microplastics, whereas polycarbonate's robust chemical structure enables more efficient recycling streams.
Choosing the Right Block for Your Project
Polystyrene blocks offer lightweight, cost-effective solutions with excellent insulation properties, ideal for applications requiring thermal resistance and easy shaping. Polycarbonate blocks provide superior impact resistance, transparency, and durability, making them suitable for projects demanding high strength and clarity under stress. Selecting the right block depends on project requirements such as mechanical strength, thermal insulation, and budget constraints.
Polystyrene Block vs Polycarbonate Block Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com