Single-use polyethylene (PE) products are designed for limited lifespan applications, often leading to increased environmental waste and resource consumption. Reusable PE items, by contrast, offer enhanced durability and cost-efficiency, minimizing waste through repeated utilization. Choosing reusable PE significantly supports sustainability by reducing plastic pollution and conserving raw materials over time.
Table of Comparison
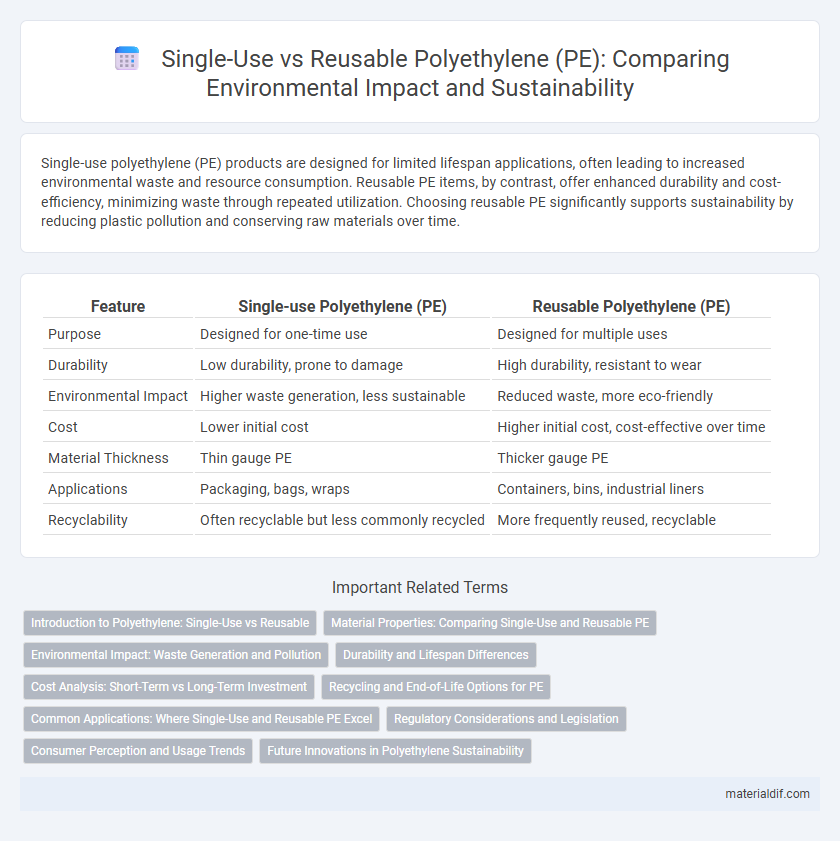
| Feature | Single-use Polyethylene (PE) | Reusable Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed for one-time use | Designed for multiple uses |
| Durability | Low durability, prone to damage | High durability, resistant to wear |
| Environmental Impact | Higher waste generation, less sustainable | Reduced waste, more eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective over time |
| Material Thickness | Thin gauge PE | Thicker gauge PE |
| Applications | Packaging, bags, wraps | Containers, bins, industrial liners |
| Recyclability | Often recyclable but less commonly recycled | More frequently reused, recyclable |
Introduction to Polyethylene: Single-Use vs Reusable
Polyethylene (PE) is a versatile polymer commonly used in single-use products like packaging films and disposable bags due to its low cost and durability. Reusable PE items, such as containers and heavy-duty bags, are designed for extended use and withstand multiple cleaning cycles without significant degradation. The key difference lies in molecular weight and density variations, influencing the material's mechanical strength and environmental impact.
Material Properties: Comparing Single-Use and Reusable PE
Single-use polyethylene (PE) is typically manufactured with lower molecular weight and reduced density, resulting in less durability and a thinner structure optimized for disposability and cost-efficiency. Reusable PE, often produced with high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and increased molecular weight, exhibits superior tensile strength, chemical resistance, and thickness, enabling multiple uses without degradation. These material property differences significantly influence their environmental impact, performance longevity, and suitability for packaging or containment applications.
Environmental Impact: Waste Generation and Pollution
Single-use polyethylene (PE) products significantly contribute to environmental pollution due to their short lifespan and low recycling rates, often ending up as persistent plastic waste in landfills and oceans. Reusable PE alternatives reduce overall waste generation by extending product life cycles and promoting circular plastic use, decreasing leakage into ecosystems. Life cycle assessments reveal that shifting from single-use to reusable PE decreases carbon footprints and plastic pollution while enhancing resource efficiency.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Single-use polyethylene (PE) products are designed for short-term applications, typically lasting from a few minutes to several hours, leading to rapid degradation and disposal. Reusable PE items are manufactured with enhanced durability through higher molecular weight and cross-linking techniques, extending their lifespan to months or even years under regular use. This durability difference significantly impacts environmental footprint, with reusable PE reducing waste generation compared to single-use counterparts.
Cost Analysis: Short-Term vs Long-Term Investment
Single-use polyethylene (PE) offers lower initial costs but leads to higher long-term expenses due to frequent replacement and increased waste management fees. Reusable PE products require a higher upfront investment but provide significant cost savings over time through durability, reduced disposal, and lower resource consumption. Factoring lifecycle costs highlights reusable PE as a more sustainable and economically efficient solution for businesses and consumers.
Recycling and End-of-Life Options for PE
Single-use polyethylene (PE) products often face limited recycling rates due to contamination and collection challenges, leading to higher landfill or incineration disposal. Reusable PE items, designed for durability, typically have improved recyclability and extended lifecycle options, facilitating multiple reuse cycles before recycling. Advanced recycling technologies, such as chemical recycling, are increasingly applied to both single-use and reusable PE to enhance material recovery and reduce environmental impact.
Common Applications: Where Single-Use and Reusable PE Excel
Single-use polyethylene (PE) is typically utilized in packaging applications such as plastic bags, food wrap, and disposable containers, where lightweight and cost-effectiveness are essential. Reusable PE excels in products like heavy-duty storage bins, agricultural films, and durable containers, offering enhanced strength and longevity for repeated use. Both single-use and reusable PE contribute significantly to various industries by balancing functional requirements with environmental considerations.
Regulatory Considerations and Legislation
Regulatory considerations for single-use polyethylene (PE) products often involve strict bans or limitations to reduce environmental pollution and promote sustainable waste management, with many regions enforcing directives such as the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive. Reusable polyethylene items face regulations emphasizing material durability and safety compliance, including food contact standards and lifecycle assessments under frameworks like the US FDA and REACH regulations. Legislation increasingly mandates labeling, recyclability standards, and producer responsibility schemes to incentivize the shift from disposable to reusable PE applications.
Consumer Perception and Usage Trends
Consumer perception of single-use polyethylene (PE) is increasingly negative due to environmental concerns, driving a shift towards reusable PE products perceived as more sustainable and cost-effective over time. Usage trends indicate a growing preference for reusable PE items like bags and containers, reflecting heightened awareness and regulatory measures promoting plastic reduction. Market data reveals a steady decline in single-use PE demand, while demand for durable, reusable PE alternatives continues to rise globally.
Future Innovations in Polyethylene Sustainability
Future innovations in polyethylene sustainability emphasize developing biodegradable additives and advanced recycling techniques to enhance single-use PE's environmental footprint. Reusable PE products are being engineered with higher durability and compatibility with circular economy models, promoting multiple life cycles without performance loss. Emerging technologies also prioritize carbon-neutral production methods and chemical recycling to reduce reliance on virgin fossil resources.
Single-use PE vs Reusable PE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com