Polystyrene offers lightweight and cost-effective properties ideal for disposable plastic pet containers but lacks the durability and impact resistance of polycarbonate. Polycarbonate provides superior strength and clarity, making it suitable for reusable pet products that demand longevity and safety. Choosing between polystyrene and polycarbonate depends on balancing affordability with the need for durability in plastic pet applications.
Table of Comparison
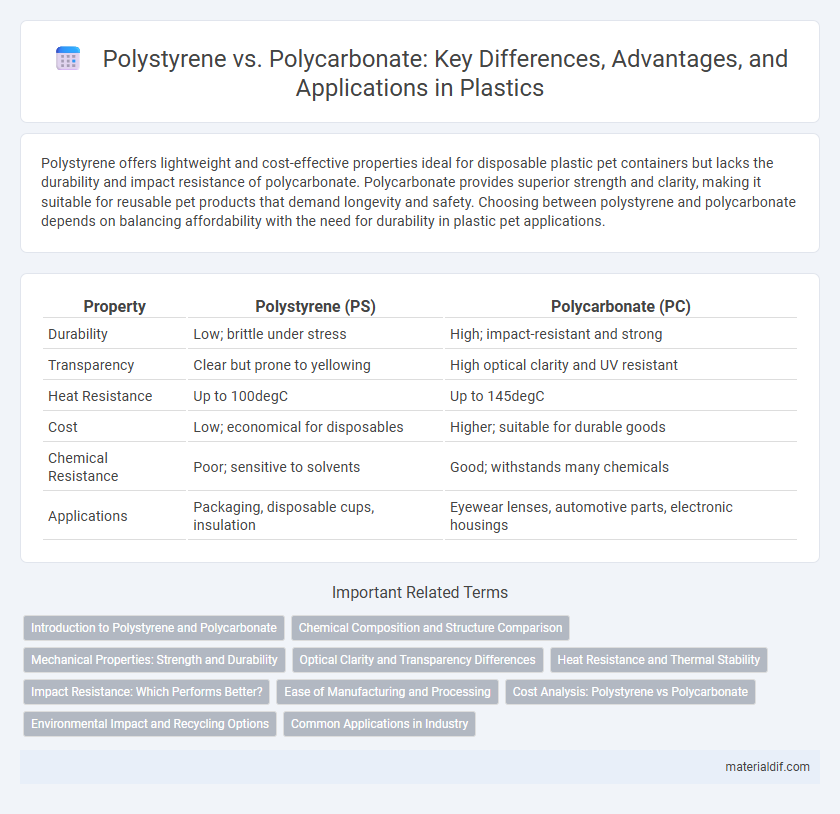
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Low; brittle under stress | High; impact-resistant and strong |
| Transparency | Clear but prone to yellowing | High optical clarity and UV resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 145degC |
| Cost | Low; economical for disposables | Higher; suitable for durable goods |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor; sensitive to solvents | Good; withstands many chemicals |
| Applications | Packaging, disposable cups, insulation | Eyewear lenses, automotive parts, electronic housings |
Introduction to Polystyrene and Polycarbonate
Polystyrene (PS) is a lightweight, rigid plastic known for its clarity and ease of molding, commonly used in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation materials. Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic with high optical clarity, widely utilized in eyewear lenses, automotive components, and electronic housings. Both polymers offer distinct advantages in strength, transparency, and thermal resistance, making them suitable for different industrial and consumer applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polystyrene is a aromatic hydrocarbon polymer composed of repeating styrene monomers featuring a phenyl group attached to a carbon backbone, resulting in a rigid, glassy structure. Polycarbonate consists of bisphenol A units linked by carbonate groups, forming a strong, transparent polymer with high impact resistance and thermal stability. The presence of carbonate linkages in polycarbonate provides enhanced durability compared to the simpler vinyl backbone in polystyrene.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Polystyrene offers moderate strength and rigidity but is brittle, making it less durable under impact or stress compared to polycarbonate. Polycarbonate exhibits superior mechanical strength, high impact resistance, and excellent durability, often used in applications requiring toughness and long-term performance. Its ability to withstand significant deformation without cracking makes polycarbonate ideal for protective gear, automotive components, and optical lenses.
Optical Clarity and Transparency Differences
Polystyrene offers good optical clarity with a high level of transparency, making it suitable for applications like food containers and display cases where clear visibility is essential. Polycarbonate surpasses polystyrene in optical clarity, providing superior transparency and better impact resistance, which is why it is widely used in eyewear lenses, safety shields, and high-performance optical components. The differences in molecular structure contribute to polycarbonate's enhanced light transmission and durability compared to the more brittle and less impact-resistant polystyrene.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polystyrene exhibits lower heat resistance, typically with a maximum service temperature around 70-90degC, making it prone to deformation under moderate heat. Polycarbonate demonstrates superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 130degC or higher, suitable for applications requiring higher heat endurance. The higher glass transition temperature and impact resistance of polycarbonate contribute to its enhanced performance in heat-sensitive environments compared to polystyrene.
Impact Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and toughness. Polystyrene is more brittle and prone to cracking under stress, limiting its use in high-impact environments. The molecular structure of polycarbonate provides enhanced flexibility and energy absorption, resulting in significantly better performance against impacts.
Ease of Manufacturing and Processing
Polystyrene offers ease of manufacturing through injection molding and thermoforming due to its low melting point and good flow characteristics, making it cost-effective for mass production of rigid and transparent items. Polycarbonate, while more challenging to process because of its higher melting temperature and sensitivity to moisture, provides superior impact resistance and dimensional stability, requiring precise temperature control and drying before molding or extrusion. The choice between polystyrene and polycarbonate hinges on balancing manufacturing simplicity and the performance requirements of the final product.
Cost Analysis: Polystyrene vs Polycarbonate
Polystyrene is significantly more affordable than polycarbonate, making it a cost-effective choice for applications requiring lower durability and impact resistance. Polycarbonate commands a higher price due to its superior strength, thermal stability, and optical clarity, justifying the investment in industries like automotive and electronics. Cost analysis should balance the upfront material expense with the long-term performance benefits offered by polycarbonate compared to the economical but brittle nature of polystyrene.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Options
Polystyrene produces significant environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature and limited recycling infrastructure, often ending up in landfills or oceans where it breaks into harmful microplastics. Polycarbonate, although more durable and recyclable through specialized processes, involves complex chemical recycling methods that are less widespread but reduce landfill dependency. Both materials present challenges in waste management, with polycarbonate offering better long-term recycling potential compared to the environmentally taxing disposal of polystyrene.
Common Applications in Industry
Polystyrene is widely used in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation materials due to its lightweight and cost-effective properties. Polycarbonate finds common applications in optical lenses, automotive components, and electronic device housings because of its high impact resistance and clarity. Both plastics serve crucial but distinct roles in industry, with polystyrene favored for single-use products and polycarbonate preferred for durable, high-performance parts.
Polystyrene vs Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com