Plastic extrusion produces continuous shapes by forcing melted plastic through a shaped die, ideal for creating pipes, sheets, and profiles with consistent cross-sections. Plastic compression molding shapes plastic by placing material in a heated mold cavity and applying pressure, making it suitable for complex, thicker parts such as automotive components. Extrusion offers high production speed and uniformity, while compression molding excels in precision and strength for durable, customized items.
Table of Comparison
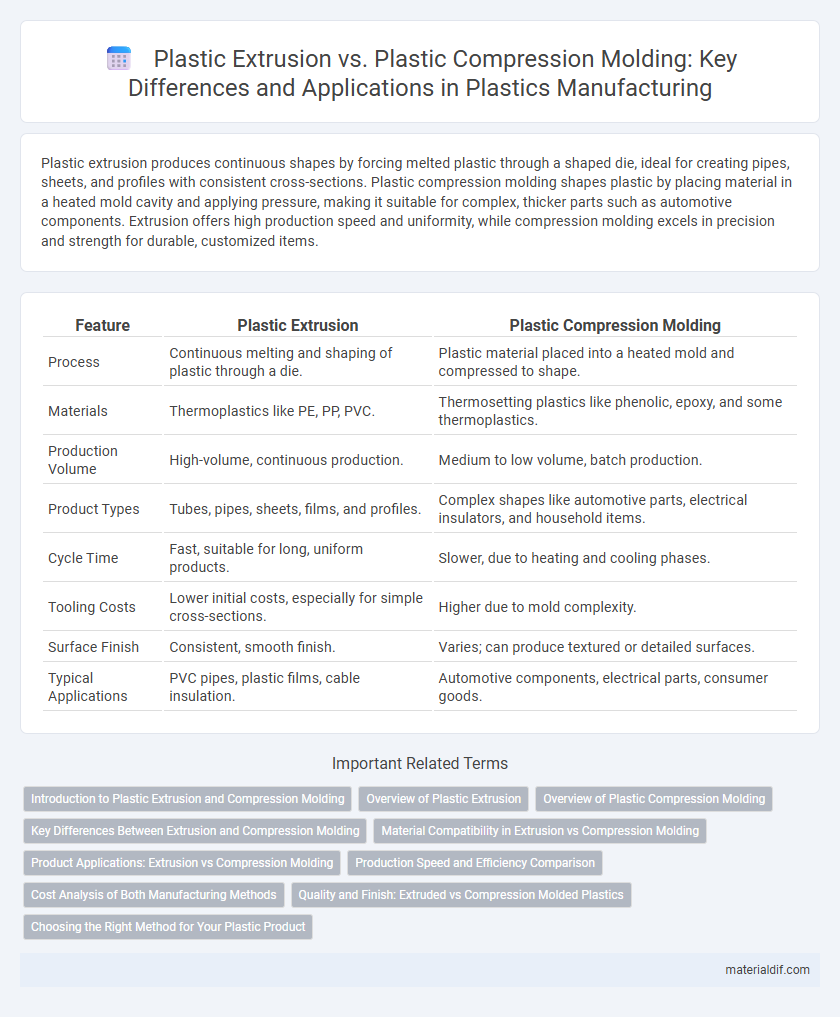
| Feature | Plastic Extrusion | Plastic Compression Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Continuous melting and shaping of plastic through a die. | Plastic material placed into a heated mold and compressed to shape. |
| Materials | Thermoplastics like PE, PP, PVC. | Thermosetting plastics like phenolic, epoxy, and some thermoplastics. |
| Production Volume | High-volume, continuous production. | Medium to low volume, batch production. |
| Product Types | Tubes, pipes, sheets, films, and profiles. | Complex shapes like automotive parts, electrical insulators, and household items. |
| Cycle Time | Fast, suitable for long, uniform products. | Slower, due to heating and cooling phases. |
| Tooling Costs | Lower initial costs, especially for simple cross-sections. | Higher due to mold complexity. |
| Surface Finish | Consistent, smooth finish. | Varies; can produce textured or detailed surfaces. |
| Typical Applications | PVC pipes, plastic films, cable insulation. | Automotive components, electrical parts, consumer goods. |
Introduction to Plastic Extrusion and Compression Molding
Plastic extrusion involves melting raw plastic material and forcing it through a shaped die to create continuous profiles like pipes, sheets, or films, offering high production speeds and uniform cross-sections. Compression molding presses heated plastic material into a mold cavity to form complex, high-strength parts, typically used for thermosetting polymers and large components. Both methods optimize material usage and enable diverse applications across automotive, packaging, and consumer goods industries.
Overview of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is a continuous manufacturing process where raw plastic pellets are melted and forced through a shaped die to create long, uniform profiles such as pipes, sheets, and films. This method offers high production speeds and excellent control over cross-sectional dimensions, making it ideal for producing consistent, intricate shapes. The process works well with thermoplastics like polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC, enabling efficient, large-scale fabrication with minimal waste.
Overview of Plastic Compression Molding
Plastic compression molding involves placing preheated plastic material into a heated mold cavity, where pressure is applied to shape and cure the material. This process is ideal for creating large, durable parts with complex geometries using thermosetting resins. Compression molding offers advantages such as reduced material waste, improved mechanical properties, and cost-effectiveness for high-volume production.
Key Differences Between Extrusion and Compression Molding
Plastic extrusion involves forcing melted plastic through a shaped die to create continuous profiles, ideal for producing pipes, sheets, and tubes. Compression molding uses a heated mold to shape plastic by pressing material into a cavity, suitable for complex, high-strength parts like automotive components. Key differences include extrusion's continuous process versus compression molding's batch processing, distinct product shapes, and varying levels of detail and mechanical properties achievable.
Material Compatibility in Extrusion vs Compression Molding
Plastic extrusion excels in processing thermoplastics like polyethylene and polypropylene, which melt and flow easily through the die, enabling continuous production of uniform profiles. Compression molding is more versatile with thermosetting plastics such as epoxy and phenolic resins, where heat and pressure cure the material into complex, high-strength shapes. Material compatibility in extrusion favors polymers with good melt flow characteristics, whereas compression molding accommodates materials requiring chemical curing and higher pressure resistance.
Product Applications: Extrusion vs Compression Molding
Plastic extrusion is ideal for producing continuous profiles such as pipes, tubing, and sheets used in construction, automotive, and packaging industries due to its ability to create uniform cross-sections efficiently. Compression molding is better suited for complex, high-strength components like automotive parts, electrical housings, and aerospace panels, where precise thickness and intricate shapes are required. Each process's product applications depend on factors like production volume, material type, and design complexity.
Production Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Plastic extrusion offers higher production speeds by continuously shaping molten plastic through a die, enabling efficient mass production with minimal downtime. Plastic compression molding, while providing superior detail and strength for complex parts, operates at slower cycle times due to molding and curing phases, reducing overall throughput. Efficiency in extrusion is driven by consistent, automated processes, whereas compression molding requires more manual intervention and longer production cycles.
Cost Analysis of Both Manufacturing Methods
Plastic extrusion typically features lower initial tooling costs and faster production rates, making it cost-effective for high-volume runs. Plastic compression molding incurs higher setup expenses due to mold complexity but offers lower material waste and reduced energy consumption, which can decrease overall costs for medium-to-low volume production. Evaluating the total cost requires balancing upfront investment against long-term efficiency, with extrusion favored for continuous profiles and compression molding preferred for intricate, durable parts.
Quality and Finish: Extruded vs Compression Molded Plastics
Extruded plastics typically exhibit uniform thickness and smooth surface finishes due to continuous shaping through the die, making them ideal for products requiring consistent profiles and minimal surface imperfections. Compression molded plastics often offer superior mechanical strength and intricate detailing, with surface finishes that can range from rough to glossy depending on mold quality and molding parameters. Quality and finish in plastic products thus depend on the application requirements, where extrusion favors dimensional consistency and compression molding excels in structural integrity and complex designs.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Plastic Product
Selecting the right method between plastic extrusion and plastic compression molding depends on the product's design complexity, production volume, and material type. Plastic extrusion excels in creating continuous profiles like pipes and sheets with high efficiency, while compression molding suits producing detailed, thermoset parts with superior strength and surface finish. Evaluating factors such as dimensional tolerances, cycle time, and cost-effectiveness ensures optimal manufacturing performance and product quality.
Plastic Extrusion vs Plastic Compression Molding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com