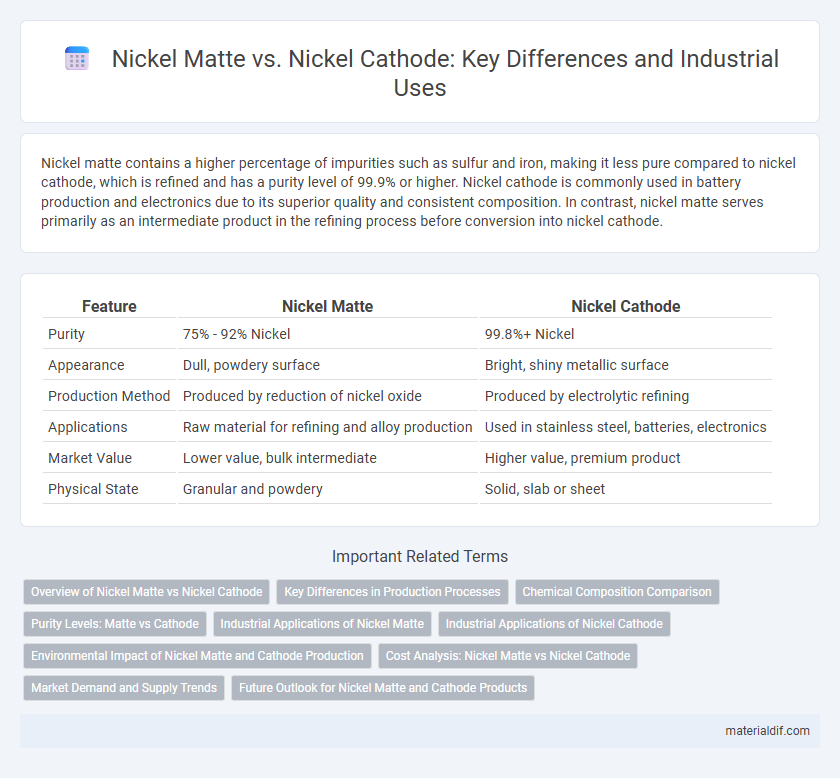
Nickel matte contains a higher percentage of impurities such as sulfur and iron, making it less pure compared to nickel cathode, which is refined and has a purity level of 99.9% or higher. Nickel cathode is commonly used in battery production and electronics due to its superior quality and consistent composition. In contrast, nickel matte serves primarily as an intermediate product in the refining process before conversion into nickel cathode.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nickel Matte | Nickel Cathode |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 75% - 92% Nickel | 99.8%+ Nickel |
| Appearance | Dull, powdery surface | Bright, shiny metallic surface |
| Production Method | Produced by reduction of nickel oxide | Produced by electrolytic refining |
| Applications | Raw material for refining and alloy production | Used in stainless steel, batteries, electronics |
| Market Value | Lower value, bulk intermediate | Higher value, premium product |
| Physical State | Granular and powdery | Solid, slab or sheet |
Overview of Nickel Matte vs Nickel Cathode
Nickel matte is an intermediate product in the nickel refining process containing about 70% nickel along with other metals like copper and iron, used mainly as feedstock for further refining. Nickel cathode is a high-purity product with over 99.5% nickel content, produced through electrolytic refining and widely used in stainless steel production and battery manufacturing. The main difference lies in the purity level and application, with nickel cathode serving as a finished product for industrial use, while nickel matte requires additional processing.
Key Differences in Production Processes
Nickel matte is produced through the smelting of nickel sulfide ores, resulting in an intermediate product rich in nickel, sulfur, and iron, requiring further refining. Nickel cathode is obtained through the electrolytic refining of nickel matte, using solvent extraction and electro-winning processes, yielding high-purity nickel with minimal impurities. The key difference lies in nickel matte representing a bulk, raw alloy form, while nickel cathode is a refined, commercially pure metal ready for industrial applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Nickel matte typically contains 70-75% nickel, along with sulfur, iron, and other impurities, resulting from the initial smelting process of nickel sulfide ores. Nickel cathode, produced through the refining of nickel matte via electrolysis, boasts a purity of 99.8% or higher, with minimal sulfur and iron content. The chemical composition difference significantly impacts their industrial applications, where nickel cathode's high purity is preferred for electronics and alloy production.
Purity Levels: Matte vs Cathode
Nickel matte typically contains purity levels ranging from 70% to 75%, with significant amounts of impurities such as iron, sulfur, and cobalt, requiring further refining. Nickel cathode demonstrates higher purity, generally exceeding 99.8%, making it suitable for direct use in stainless steel production and battery manufacturing. The refinement process from matte to cathode significantly enhances nickel quality by reducing contaminant content and improving metal consistency.
Industrial Applications of Nickel Matte
Nickel matte, containing approximately 70-75% nickel, serves as a crucial intermediate product in the metallurgical industry for further refining into high-purity nickel cathodes. Its primary industrial applications include use in the production of stainless steel, superalloys, and electroplating due to its high metal content and sulfur impurity levels suitable for these processes. Nickel matte's role in producing corrosion-resistant alloys and battery components underscores its importance in sectors such as aerospace, electronics, and electric vehicle manufacturing.
Industrial Applications of Nickel Cathode
Nickel cathode is widely used in industrial applications such as stainless steel production, battery manufacturing, and plating processes due to its high purity and excellent conductivity. Unlike nickel matte, which contains a mix of impurities and requires further refining, nickel cathode offers superior performance and consistency critical for high-quality alloy fabrication and electroplating. Its role in electric vehicle batteries and stainless steel alloys underscores its importance in modern industrial sectors.
Environmental Impact of Nickel Matte and Cathode Production
Nickel matte production generates higher levels of sulfur dioxide and heavy metal emissions compared to nickel cathode processing, which typically uses cleaner hydrometallurgical methods that reduce airborne pollutants. Wastewater from nickel matte smelting contains toxic contaminants requiring extensive treatment, whereas nickel cathode production results in lower volumes of hazardous effluents due to improved refining technologies. Energy consumption in nickel matte smelting is generally higher, contributing to a larger carbon footprint than the more energy-efficient nickel cathode electrolysis process.
Cost Analysis: Nickel Matte vs Nickel Cathode
Nickel matte typically offers lower upfront costs due to its less refined state, which requires further processing to achieve high purity, making it more suitable for downstream industries with refining capabilities. Nickel cathode commands higher prices because of its superior purity (>=99.8%), ready for immediate use in battery manufacturing and electronics, reducing processing expenses for end-users. Cost analysis must consider refining charges, transportation, and application-specific requirements, with nickel cathode often yielding higher returns despite higher initial investment.
Market Demand and Supply Trends
Nickel matte, primarily used for extracting refined nickel, shows fluctuating demand driven by stainless steel production cycles, while nickel cathode experiences stronger market growth due to its direct application in battery manufacturing for electric vehicles. Supply trends indicate increasing investments toward nickel cathode production capacity, reflecting the shift toward clean energy technologies and electric mobility. Market analysts project nickel cathode demand to outpace nickel matte, driven by global decarbonization initiatives and expanding lithium-ion battery markets.
Future Outlook for Nickel Matte and Cathode Products
Nickel matte and nickel cathode represent critical stages in nickel processing with distinct market trajectories. Growing demand for high-purity nickel cathode in electric vehicle batteries is driving investments in refining technologies, while nickel matte remains essential for stainless steel production and alloy manufacturing. Future outlook suggests increased integration of nickel matte refining into cathode production to meet stringent environmental standards and supply chain sustainability goals.
Nickel matte vs Nickel cathode Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com