High-purity nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced conductivity compared to commercial-grade nickel, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as electronics and aerospace components. Commercial-grade nickel, while more cost-effective, contains higher impurity levels that can affect its mechanical properties and long-term durability. Selecting high-purity nickel ensures optimal performance and longevity in precision-engineered products.
Table of Comparison
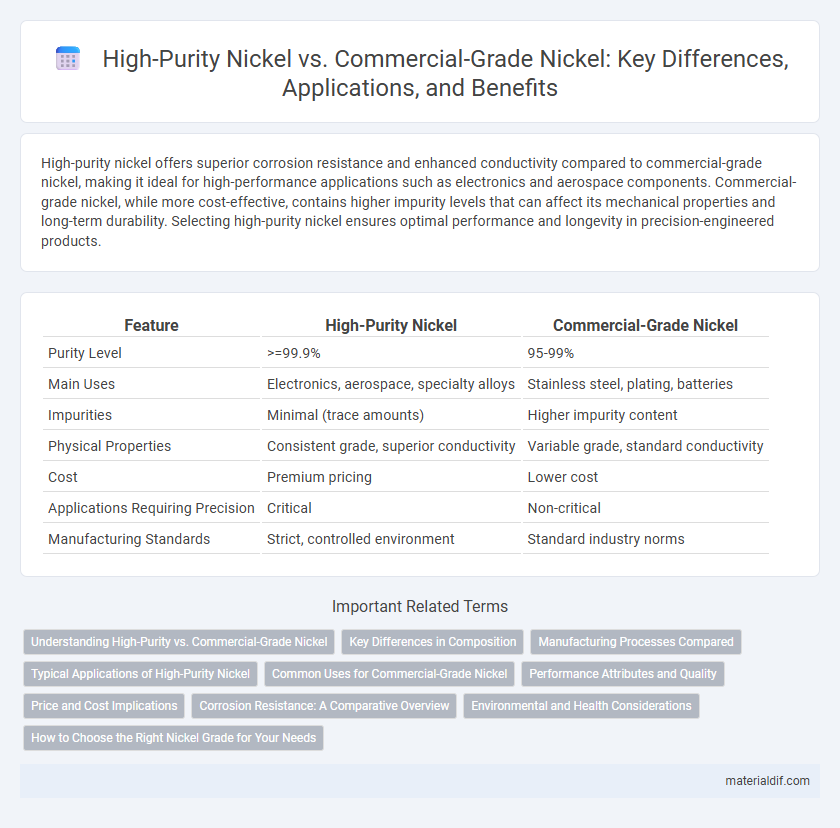
| Feature | High-Purity Nickel | Commercial-Grade Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Purity Level | >=99.9% | 95-99% |
| Main Uses | Electronics, aerospace, specialty alloys | Stainless steel, plating, batteries |
| Impurities | Minimal (trace amounts) | Higher impurity content |
| Physical Properties | Consistent grade, superior conductivity | Variable grade, standard conductivity |
| Cost | Premium pricing | Lower cost |
| Applications Requiring Precision | Critical | Non-critical |
| Manufacturing Standards | Strict, controlled environment | Standard industry norms |
Understanding High-Purity vs. Commercial-Grade Nickel
High-purity nickel contains 99.9% or higher nickel content, offering superior corrosion resistance, excellent electrical conductivity, and enhanced mechanical properties essential for aerospace, electronics, and battery applications. Commercial-grade nickel typically has lower purity levels, around 75-99%, making it more cost-effective but less suitable for demanding industrial uses due to impurities that can affect performance and durability. Choosing between high-purity and commercial-grade nickel depends on application-specific requirements such as conductivity, strength, and resistance to oxidation.
Key Differences in Composition
High-purity nickel typically contains 99.9% or higher nickel content, with minimal impurities such as iron, cobalt, and sulfur, ensuring superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Commercial-grade nickel often has a lower purity level, around 99%, with higher concentrations of contaminants that can affect its mechanical properties and performance in specialized applications. The key difference in composition directly impacts the suitability of each type for industries like electronics, aerospace, and chemical processing.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
High-purity nickel undergoes rigorous refining processes such as vacuum distillation and electrorefining to achieve purity levels exceeding 99.9%, essential for specialized applications like electronics and aerospace. Commercial-grade nickel typically involves smelting and hydrometallurgical techniques, producing lower purity levels around 99.2% to 99.5%, suitable for stainless steel and general industrial uses. The manufacturing processes for high-purity nickel emphasize contaminant removal and precision, while commercial-grade nickel prioritizes cost-efficiency and large-scale production.
Typical Applications of High-Purity Nickel
High-purity nickel is essential in manufacturing advanced electronic components, aerospace parts, and chemical processing equipment due to its superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. It is widely used in batteries for electric vehicles, stainless steel production with stringent quality requirements, and precision alloy formulations in medical instruments. Commercial-grade nickel, with lower purity levels, suits general industrial applications such as construction and plating, where extreme material performance is less critical.
Common Uses for Commercial-Grade Nickel
Commercial-grade nickel is widely used in stainless steel production, alloys for aerospace components, and plating applications due to its cost-effectiveness and adequate corrosion resistance. It is employed in manufacturing batteries, particularly in nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride cells, for consumer electronics and electric vehicles. Industrial equipment, chemical processing plants, and piping systems also rely on commercial-grade nickel for durability and resistance in harsh environments.
Performance Attributes and Quality
High-purity nickel offers superior corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength compared to commercial-grade nickel, making it essential for advanced applications in aerospace, electronics, and chemical processing. Its reduced impurity levels enhance thermal stability and magnetic properties, ensuring consistent performance under extreme conditions. Commercial-grade nickel, while more cost-effective, contains higher levels of impurities that can compromise durability and efficiency in precision-dependent uses.
Price and Cost Implications
High-purity nickel commands a significantly higher price than commercial-grade nickel due to its refined extraction and processing methods, which remove impurities for enhanced performance in demanding applications like electronics and aerospace. The cost implications of using high-purity nickel include increased raw material expenses and production costs, impacting the overall budget of manufacturing projects requiring superior corrosion resistance and conductivity. Conversely, commercial-grade nickel offers a more affordable option for industries with less stringent quality requirements, balancing cost-efficiency with acceptable performance.
Corrosion Resistance: A Comparative Overview
High-purity nickel exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to commercial-grade nickel due to its reduced levels of impurities such as sulfur, iron, and carbon, which can cause localized corrosion and pitting. The enhanced purity enables the formation of a more stable and protective oxide layer, significantly improving performance in harsh environments like chemical processing and marine applications. Commercial-grade nickel, containing higher impurity concentrations, typically shows lower resistance to corrosion, making it less suitable for critical applications requiring long-term durability.
Environmental and Health Considerations
High-purity nickel produces fewer impurities, reducing emissions of harmful substances during refining and usage, which minimizes environmental pollution compared to commercial-grade nickel. Commercial-grade nickel often contains higher levels of contaminants such as sulfur and heavy metals, contributing to greater risks of soil and water contamination and occupational health hazards. Using high-purity nickel in industrial applications enhances safety by lowering exposure to toxic elements and supports sustainable practices through cleaner production processes.
How to Choose the Right Nickel Grade for Your Needs
High-purity nickel, containing above 99.9% nickel content, is essential for applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, such as electronics and aerospace industries. Commercial-grade nickel, typically around 98-99% purity, is suitable for general industrial uses, including plating and alloy production, where cost-efficiency outweighs the need for extreme purity. Selecting the right nickel grade depends on specific performance requirements, budget constraints, and the intended environment of use to ensure optimal functionality and durability.
High-purity nickel vs Commercial-grade nickel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com