Mylar offers superior moisture and oxygen barrier properties compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for long-term pet food storage and freshness preservation. While polypropylene is more flexible and cost-effective, Mylar's durability and resistance to punctures provide enhanced protection against environmental factors. Choosing Mylar over polypropylene ensures extended shelf life and maintains the nutritional quality of pet supplies.
Table of Comparison
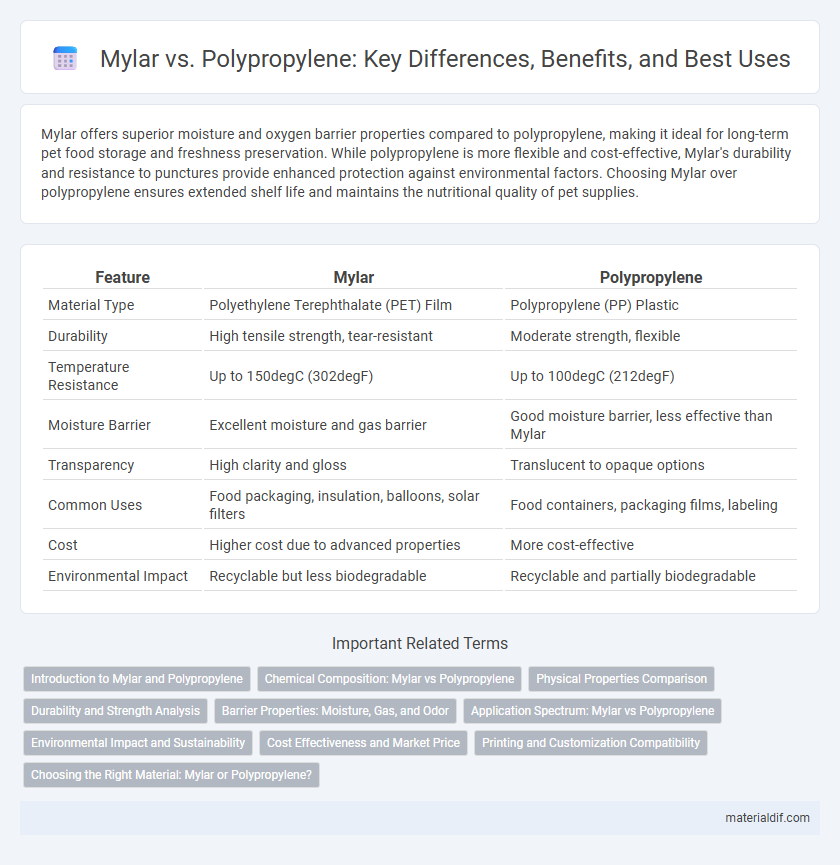
| Feature | Mylar | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Film | Polypropylene (PP) Plastic |
| Durability | High tensile strength, tear-resistant | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 100degC (212degF) |
| Moisture Barrier | Excellent moisture and gas barrier | Good moisture barrier, less effective than Mylar |
| Transparency | High clarity and gloss | Translucent to opaque options |
| Common Uses | Food packaging, insulation, balloons, solar filters | Food containers, packaging films, labeling |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | More cost-effective |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but less biodegradable | Recyclable and partially biodegradable |
Introduction to Mylar and Polypropylene
Mylar, a brand name for biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET), offers superior tensile strength, chemical stability, and dimensional accuracy compared to polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer commonly used in packaging and labeling. Mylar's exceptional barrier properties against moisture, gases, and chemicals make it ideal for applications requiring long-term preservation and durability, whereas polypropylene is favored for its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of manufacturing. Understanding the material composition and performance characteristics of Mylar and polypropylene is essential for selecting the appropriate film for specific industrial or consumer uses.
Chemical Composition: Mylar vs Polypropylene
Mylar is a polyester film made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), characterized by its strong molecular chains and excellent barrier properties. Polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer composed of propylene monomers, offers chemical resistance but lower tensile strength compared to Mylar. The chemical composition of Mylar provides superior durability and dimensional stability, making it preferable in applications requiring high thermal and chemical resilience.
Physical Properties Comparison
Mylar exhibits superior tensile strength and dimensional stability compared to polypropylene, making it more resistant to stretching and deformation under stress. Its higher melting point around 250degC enhances thermal resistance, whereas polypropylene melts between 160-170degC, limiting its use in high-temperature applications. Mylar's excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases outperform polypropylene, which provides moderate protection but is less effective in preventing permeability.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Mylar, a brand of biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET), offers superior durability and tensile strength compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring resistance to tear and environmental stress. The enhanced molecular orientation in Mylar provides exceptional dimensional stability and higher elongation at break, which surpasses the mechanical properties of polypropylene. This strength advantage enables Mylar to maintain structural integrity under prolonged exposure to heat, moisture, and chemicals, outperforming polypropylene in demanding industrial and packaging uses.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Odor
Mylar, a biaxially oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET) film, offers superior moisture, gas, and odor barrier properties compared to polypropylene films, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced preservation and protection. Mylar's dense molecular structure significantly reduces water vapor transmission rates (WVTR) and oxygen permeability, which are critical for maintaining product freshness and preventing contamination. In contrast, polypropylene exhibits higher permeability to moisture and gases, limiting its effectiveness in barrier-sensitive packaging and industrial uses.
Application Spectrum: Mylar vs Polypropylene
Mylar, a polyester film known for its high tensile strength, chemical stability, and excellent barrier properties, is widely used in applications requiring superior durability and moisture resistance such as electrical insulation, solar filters, and food packaging. Polypropylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer, is favored in packaging, textiles, and automotive components due to its flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness but offers lower barrier and thermal stability compared to Mylar. The application spectrum of Mylar extends into high-performance sectors demanding long-lasting and reliable materials, while polypropylene is preferred for cost-sensitive, flexible packaging and disposable goods.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mylar, a polyester film, offers superior durability and recyclability compared to polypropylene, which is less efficient in recycling processes and often contributes more to environmental waste. The production of Mylar generally involves lower carbon emissions than polypropylene, making it a more sustainable choice for packaging and insulation. Both materials are widely used, but Mylar's ability to be recycled multiple times enhances its environmental benefits over polypropylene.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Price
Mylar generally commands a higher market price than polypropylene due to its superior durability and barrier properties, making it a preferred choice in premium packaging applications. Polypropylene offers cost-effective advantages with lower raw material and production costs, appealing to budget-conscious manufacturers seeking flexibility and efficiency. Market trends show Mylar's price stability driven by demand in high-performance sectors, whereas polypropylene prices fluctuate more with resin market changes.
Printing and Customization Compatibility
Mylar offers superior printing and customization compatibility compared to polypropylene due to its smoother surface and higher heat resistance, enabling sharper and more vibrant print quality. Polypropylene tends to have a more porous texture, which can result in less precise printing and limited customization options. Mylar's durability also allows for a wider range of inks and printing techniques, making it ideal for high-resolution graphics and detailed customization projects.
Choosing the Right Material: Mylar or Polypropylene?
Mylar offers superior tensile strength, thermal resistance, and moisture barrier properties compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronics or food products requiring extended shelf life. Polypropylene excels in flexibility, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness, often preferred for applications needing lightweight, recyclable materials such as disposable containers and packaging films. Selecting between Mylar and polypropylene depends on specific requirements like durability, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and protection.
Mylar vs Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com